Functional prototyping prioritizes testing the operational aspects and performance of equipment, ensuring all mechanical and electronic systems work as intended under real-world conditions. Aesthetic prototyping, in contrast, focuses on the visual design, form, and user interface, helping to refine the look and feel to meet customer expectations. Choosing the right prototyping approach depends on whether validating functionality or visual appeal is the primary goal during the product development cycle.
Table of Comparison
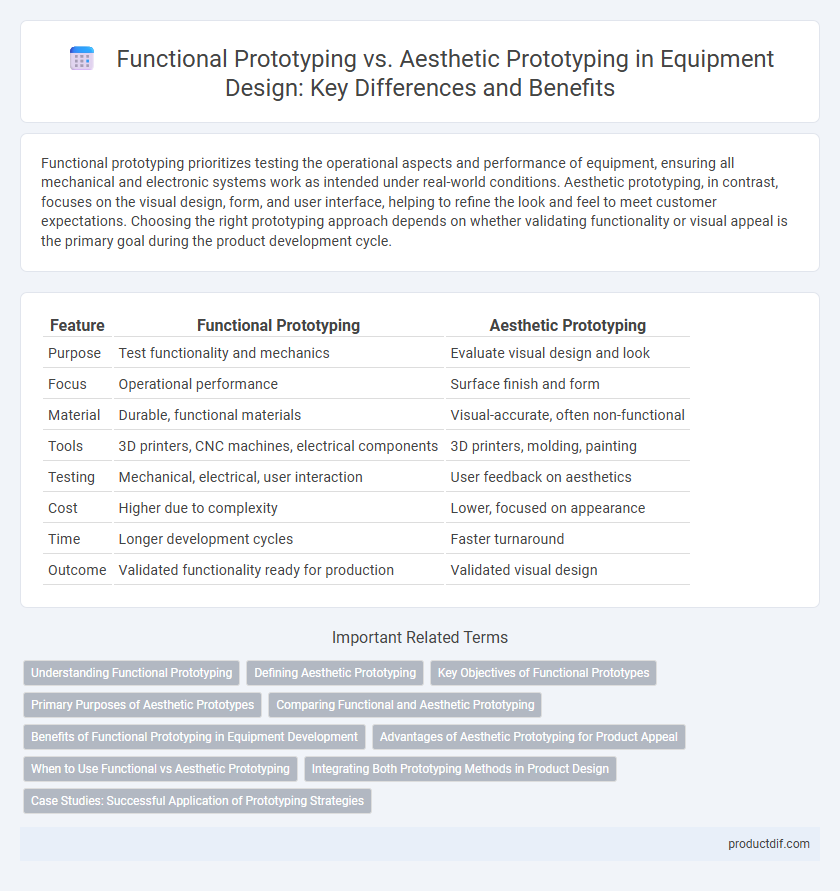
| Feature | Functional Prototyping | Aesthetic Prototyping |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Test functionality and mechanics | Evaluate visual design and look |
| Focus | Operational performance | Surface finish and form |
| Material | Durable, functional materials | Visual-accurate, often non-functional |
| Tools | 3D printers, CNC machines, electrical components | 3D printers, molding, painting |
| Testing | Mechanical, electrical, user interaction | User feedback on aesthetics |
| Cost | Higher due to complexity | Lower, focused on appearance |
| Time | Longer development cycles | Faster turnaround |
| Outcome | Validated functionality ready for production | Validated visual design |
Understanding Functional Prototyping
Functional prototyping emphasizes testing a product's performance, mechanics, and usability to ensure it operates as intended before mass production. This process uses materials and components that closely mimic the final equipment, allowing engineers to identify and resolve technical issues effectively. Functional prototypes enable iterative refinement, reducing costly errors and improving overall product reliability and user experience.
Defining Aesthetic Prototyping
Aesthetic prototyping emphasizes the visual and tactile aspects of equipment, aiming to replicate the look, feel, and surface finish of the final product without focusing on functionality. It helps designers assess user appeal, ergonomics, and branding elements before full production. This approach contrasts with functional prototyping, which prioritizes performance and operational testing over appearance.
Key Objectives of Functional Prototypes
Functional prototypes prioritize validating the performance, usability, and mechanical functionality of equipment under real-world conditions to ensure design feasibility and operational reliability. They enable iterative testing of critical components and systems, helping identify and resolve technical issues before mass production. Focusing on functional prototypes minimizes costly design flaws by confirming equipment meets required specifications and user needs effectively.
Primary Purposes of Aesthetic Prototypes
Aesthetic prototypes primarily serve to evaluate the visual appeal, form, and tactile experience of equipment designs, ensuring alignment with user expectations and brand identity. They help identify design flaws related to appearance and ergonomics before full-scale production. These prototypes are essential for stakeholder presentations and market testing, emphasizing look and feel over functionality.
Comparing Functional and Aesthetic Prototyping
Functional prototyping focuses on testing the operational aspects and mechanical performance of equipment, ensuring that systems work as intended under real-world conditions. Aesthetic prototyping emphasizes the visual design, form, and user interface, allowing designers to evaluate look, feel, and ergonomics before mass production. Comparing the two, functional prototypes prioritize usability and technical validation, while aesthetic prototypes are essential for market appeal and user experience refinement.
Benefits of Functional Prototyping in Equipment Development
Functional prototyping in equipment development enables designers to test and validate mechanical performance, durability, and operational efficiency under real-world conditions, accelerating the identification of design flaws. This approach reduces costly revisions in later production stages by ensuring the prototype meets functional requirements before manufacturing. Functional prototypes also facilitate user feedback on usability and safety, leading to improved product reliability and market acceptance.
Advantages of Aesthetic Prototyping for Product Appeal
Aesthetic prototyping enhances product appeal by accurately representing the final design's look and feel, which attracts customer interest and strengthens brand perception. This type of prototyping allows designers to assess color, texture, and form, ensuring alignment with market preferences and improving user experience. High-fidelity aesthetic models facilitate stakeholder buy-in and provide a competitive edge by showcasing realistic visuals during product presentations and marketing campaigns.
When to Use Functional vs Aesthetic Prototyping
Functional prototyping is used when testing the usability, mechanics, and performance of equipment is crucial, allowing engineers to identify design flaws and improve operational functionality. Aesthetic prototyping is ideal for evaluating the visual appeal, ergonomics, and user interface to ensure the equipment meets brand and customer expectations. Selecting between functional and aesthetic prototyping depends on project goals, with functional prototypes prioritized during engineering validation and aesthetic prototypes during market research or design approval phases.
Integrating Both Prototyping Methods in Product Design
Integrating functional prototyping with aesthetic prototyping enhances product design by combining performance verification with visual appeal assessment, ensuring comprehensive evaluation of equipment functionality and user experience. Utilizing rapid prototyping technologies such as 3D printing and CNC machining allows simultaneous development of mechanical components and surface finishes, accelerating design iterations while maintaining high fidelity in both operational and cosmetic features. This integrated approach reduces time-to-market and improves product reliability by addressing engineering requirements and market expectations in a unified workflow.
Case Studies: Successful Application of Prototyping Strategies
Case studies reveal that functional prototyping excels in refining equipment performance and usability by simulating real-world operating conditions, as demonstrated by automotive manufacturers reducing development cycles by 30%. Aesthetic prototyping proves crucial for consumer electronics brands, enhancing market appeal through realistic design models that increase pre-launch user engagement by 25%. Combining both strategies, aerospace firms optimize design validation and brand perception, resulting in a 40% improvement in overall product success rates.
Functional prototyping vs Aesthetic prototyping Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com