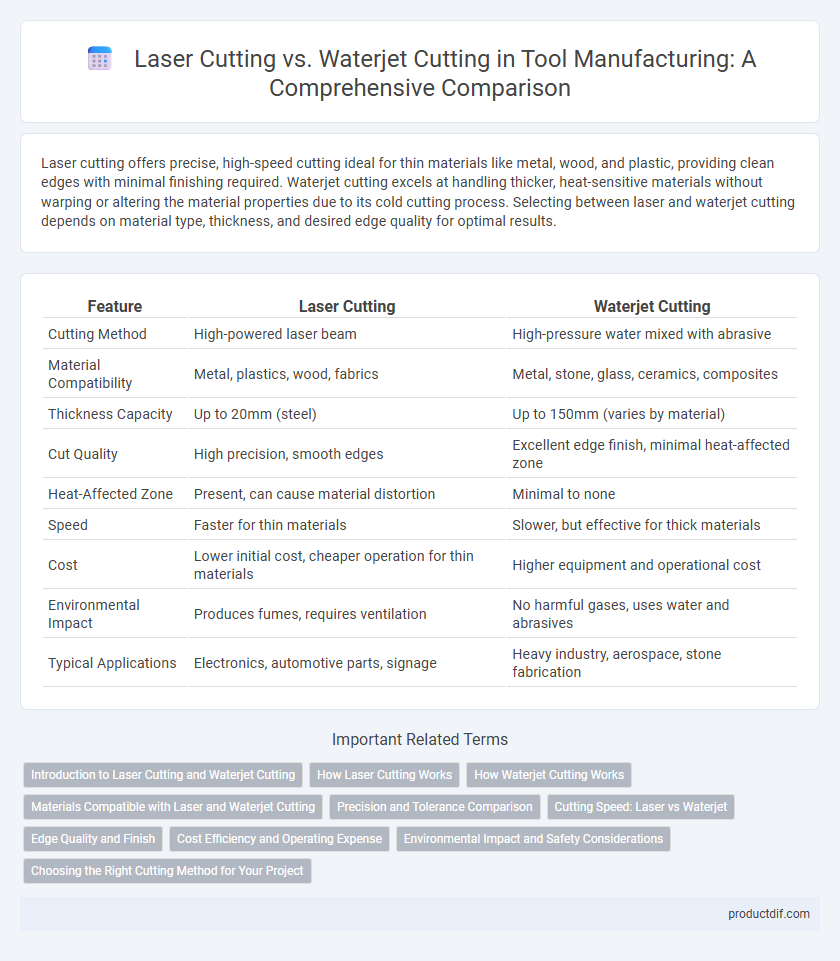
Laser cutting offers precise, high-speed cutting ideal for thin materials like metal, wood, and plastic, providing clean edges with minimal finishing required. Waterjet cutting excels at handling thicker, heat-sensitive materials without warping or altering the material properties due to its cold cutting process. Selecting between laser and waterjet cutting depends on material type, thickness, and desired edge quality for optimal results.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laser Cutting | Waterjet Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Method | High-powered laser beam | High-pressure water mixed with abrasive |
| Material Compatibility | Metal, plastics, wood, fabrics | Metal, stone, glass, ceramics, composites |
| Thickness Capacity | Up to 20mm (steel) | Up to 150mm (varies by material) |
| Cut Quality | High precision, smooth edges | Excellent edge finish, minimal heat-affected zone |
| Heat-Affected Zone | Present, can cause material distortion | Minimal to none |
| Speed | Faster for thin materials | Slower, but effective for thick materials |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, cheaper operation for thin materials | Higher equipment and operational cost |
| Environmental Impact | Produces fumes, requires ventilation | No harmful gases, uses water and abrasives |
| Typical Applications | Electronics, automotive parts, signage | Heavy industry, aerospace, stone fabrication |
Introduction to Laser Cutting and Waterjet Cutting
Laser cutting employs a focused laser beam to precisely cut materials by melting, burning, or vaporizing them, offering high accuracy and clean edges for metals, plastics, and wood. Waterjet cutting uses a high-pressure stream of water, often mixed with abrasive substances, to slice through a variety of materials without generating heat, preserving material integrity and reducing thermal distortion. Both technologies provide versatile solutions for industrial manufacturing, prototyping, and custom fabrication across multiple industries.
How Laser Cutting Works
Laser cutting operates by directing a focused beam of high-powered laser light onto a material, causing it to melt, burn, or vaporize with precision. The laser beam, guided by computer numerical control (CNC), delivers intense heat that enables fast and accurate cuts through metals, plastics, and other materials. Technology like CO2 or fiber lasers enhances cutting speed and quality, making laser cutting ideal for intricate designs and detailed fabrication.
How Waterjet Cutting Works
Waterjet cutting uses a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive particles to precisely cut through materials without generating heat, preserving material integrity. The process involves a pump that pressurizes water up to 60,000 psi, which is then forced through a tiny sapphire or diamond nozzle, creating an ultra-fine jet capable of slicing metals, stone, or composites. This cold cutting method is ideal for heat-sensitive materials and complex shapes, offering minimal thermal distortion and clean, accurate edges.
Materials Compatible with Laser and Waterjet Cutting
Laser cutting excels at processing materials like stainless steel, aluminum, acrylic, wood, and leather with high precision and smooth edges. Waterjet cutting is compatible with a broader range, including metals, stone, glass, ceramics, and composites, making it ideal for heat-sensitive or thicker materials. Both technologies accommodate different thicknesses and material types, but waterjet is preferred for materials prone to thermal distortion.
Precision and Tolerance Comparison
Laser cutting offers superior precision with tolerances typically around +-0.1 mm, making it ideal for intricate designs and detailed work. Waterjet cutting provides slightly wider tolerances, generally +-0.2 mm, but excels in cutting thicker materials without heat distortion. Both methods deliver high accuracy, yet laser cutting outperforms waterjet in fine detail and edge quality.
Cutting Speed: Laser vs Waterjet
Laser cutting offers significantly faster cutting speeds compared to waterjet cutting, especially when working with thin to medium-thickness materials such as sheet metal, plastics, and wood. Waterjet cutting, while slower, excels in cutting thicker, harder materials like stone and metals without heat-affected zones, preserving material integrity. Choosing between laser and waterjet cutting depends on the specific application, with laser preferred for speed and precision on lighter materials and waterjet for versatility and material compatibility.
Edge Quality and Finish
Laser cutting produces smooth, precise edges with minimal burring, ideal for intricate designs and thin materials. Waterjet cutting offers superior edge quality on thicker or heat-sensitive materials by avoiding thermal distortion and producing a clean, burr-free finish. Both methods deliver high-quality finishes, but waterjet excels in maintaining material integrity without heat-affected zones.
Cost Efficiency and Operating Expense
Laser cutting typically offers higher cost efficiency for thinner materials due to faster processing speeds and lower energy consumption compared to waterjet cutting. Waterjet cutting incurs higher operating expenses because of abrasive material costs and slower cutting rates but excels in versatility with thicker or heat-sensitive materials. Factoring equipment maintenance and part quality, laser cutting reduces long-term expenses in high-volume production, whereas waterjet cutting may increase costs in these scenarios.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Laser cutting produces fewer emissions but consumes significant electricity, raising concerns about energy sources, while waterjet cutting uses high-pressure water mixed with abrasives, producing slurry waste that requires proper disposal to prevent environmental harm. Laser cutting poses risks such as laser radiation and fumes that necessitate adequate ventilation and protective measures, whereas waterjet cutting involves high-pressure water jets that can cause physical injuries, demanding strict safety protocols and protective gear. Choosing between these methods depends on balancing energy consumption, waste management, and workplace safety requirements for sustainable manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Cutting Method for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate cutting method depends on material type, thickness, and required precision. Laser cutting excels in high-speed processing of thin metals and plastics with fine detail, while waterjet cutting handles thicker materials, including stone and metals, without heat-affected zones. Evaluate factors such as material sensitivity, edge quality, and budget constraints to determine the optimal technology for your project's needs.
Laser Cutting vs Waterjet Cutting Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com