Corded tools offer consistent power and are ideal for heavy-duty tasks requiring extended use without interruption, providing reliable performance without the need for battery recharging. Cordless tools deliver greater portability and convenience, allowing users to work in remote or tight spaces without being tethered to a power outlet. Choosing between corded and cordless tools depends on the balance between mobility needs and the demand for sustained, high power output.
Table of Comparison
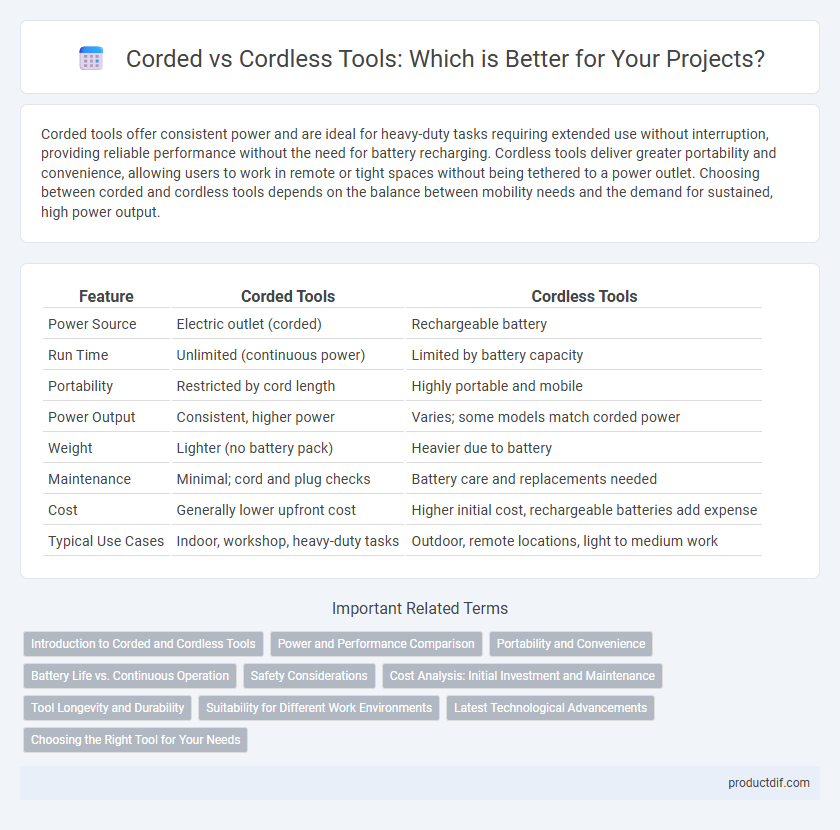
| Feature | Corded Tools | Cordless Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Electric outlet (corded) | Rechargeable battery |
| Run Time | Unlimited (continuous power) | Limited by battery capacity |
| Portability | Restricted by cord length | Highly portable and mobile |
| Power Output | Consistent, higher power | Varies; some models match corded power |
| Weight | Lighter (no battery pack) | Heavier due to battery |
| Maintenance | Minimal; cord and plug checks | Battery care and replacements needed |
| Cost | Generally lower upfront cost | Higher initial cost, rechargeable batteries add expense |
| Typical Use Cases | Indoor, workshop, heavy-duty tasks | Outdoor, remote locations, light to medium work |
Introduction to Corded and Cordless Tools
Corded tools are powered directly through an electrical outlet, providing consistent power and unlimited runtime, making them ideal for heavy-duty tasks and continuous use. Cordless tools operate on rechargeable batteries, offering enhanced portability and convenience, which is beneficial for work in locations without easy access to power sources. Both types cater to different job requirements, with corded tools excelling in power-intensive applications and cordless tools favored for flexibility and mobility.
Power and Performance Comparison
Corded tools deliver consistent and higher power output, making them ideal for heavy-duty tasks requiring sustained performance. Cordless tools offer the advantage of portability but typically have lower power capacity and shorter runtime due to battery limitations. Advances in lithium-ion battery technology have improved cordless tool performance, yet corded tools remain superior for continuous high-power applications.
Portability and Convenience
Cordless tools offer superior portability and convenience due to their battery-powered design, allowing users to operate them freely without the restriction of a power cord. Corded tools provide continuous power without the need for battery recharging, but their mobility is limited by cord length and availability of power outlets. For projects requiring work in remote or tight spaces, cordless tools enhance efficiency and ease of use, while corded tools are better suited for extended tasks needing consistent power supply.
Battery Life vs. Continuous Operation
Corded tools provide uninterrupted continuous operation by drawing consistent power from an outlet, making them ideal for extended projects without downtime. Cordless tools rely on battery life, which limits runtime and requires periodic recharging or battery swaps, affecting productivity during prolonged use. Advances in battery technology are improving cordless tool runtimes, but corded tools still outperform in scenarios demanding constant power delivery.
Safety Considerations
Corded tools consistently offer a stable power source, reducing the risk of sudden shutdowns that can cause accidents. Cordless tools eliminate the hazard of tripping over cords but require careful battery maintenance to prevent overheating or leaks. Proper handling and regular inspection of both types ensure optimal safety during operation.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Maintenance
Corded tools typically require a lower initial investment compared to cordless tools due to simpler battery-free designs and fewer electronic components. Maintenance costs for corded tools are generally lower since they lack rechargeable batteries that need periodic replacement or specialized chargers. However, cordless tools may incur higher long-term expenses from battery replacements and potential electronic repairs, offsetting their upfront convenience benefits.
Tool Longevity and Durability
Corded tools generally offer greater longevity and durability due to their consistent power supply, eliminating battery degradation concerns common in cordless models. High-quality corded tools feature robust internal components designed for extended use under heavy workloads, ensuring reliable performance over years. In contrast, cordless tools rely on rechargeable batteries that diminish capacity over time, potentially reducing the overall lifespan despite advancements in lithium-ion battery technology.
Suitability for Different Work Environments
Corded tools provide consistent power and are ideal for stationary or indoor tasks with accessible electrical outlets, ensuring uninterrupted operation for extended projects. Cordless tools offer superior portability and flexibility, making them suitable for outdoor or remote work sites where mobility and ease of use are crucial. The choice between corded and cordless tools depends on the specific work environment, project duration, and power requirements.
Latest Technological Advancements
Corded tools now feature advanced brushless motors and improved power management systems that deliver consistent performance and longer lifespans. Cordless tools benefit from lithium-ion battery innovations, offering faster charging times, increased energy density, and enhanced runtime for extended use. Integration of smart technology in both tool types allows real-time performance monitoring and predictive maintenance, optimizing overall efficiency.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs
Corded tools deliver consistent power ideal for prolonged tasks, ensuring uninterrupted performance on demanding jobsites. Cordless tools offer unmatched portability and ease of use, powered by rechargeable batteries suited for light to medium-duty projects without access to power outlets. Selecting the right tool depends on balancing power requirements, mobility, and task duration to optimize efficiency and convenience.
Corded tools vs Cordless tools Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com