A jig guides the cutting tool's motion to ensure precision during machining, while a fixture holds the workpiece securely in place without guiding the tool. Jigs are essential for repetitive tasks requiring exact tool paths, whereas fixtures provide stability and support to prevent movement under cutting forces. Choosing between jig and fixture depends on whether tool guidance or workpiece positioning is the priority in the manufacturing process.
Table of Comparison
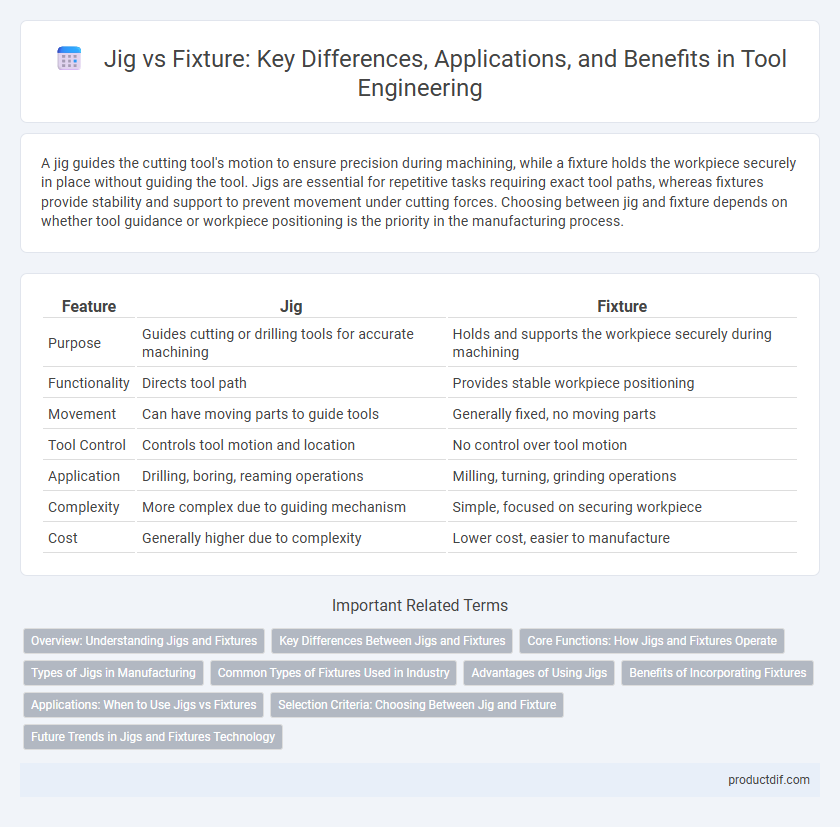
| Feature | Jig | Fixture |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Guides cutting or drilling tools for accurate machining | Holds and supports the workpiece securely during machining |
| Functionality | Directs tool path | Provides stable workpiece positioning |
| Movement | Can have moving parts to guide tools | Generally fixed, no moving parts |
| Tool Control | Controls tool motion and location | No control over tool motion |
| Application | Drilling, boring, reaming operations | Milling, turning, grinding operations |
| Complexity | More complex due to guiding mechanism | Simple, focused on securing workpiece |
| Cost | Generally higher due to complexity | Lower cost, easier to manufacture |
Overview: Understanding Jigs and Fixtures
Jigs and fixtures are essential tooling devices used to enhance manufacturing accuracy and efficiency by securely holding workpieces during machining processes. A jig guides the cutting tool, ensuring precise tool movement, while a fixture firmly supports and positions the workpiece without guiding the tool itself. Understanding the distinct functions and applications of jigs versus fixtures is crucial for optimizing production quality and reducing manufacturing errors.
Key Differences Between Jigs and Fixtures
Jigs guide the cutting tool and control its motion during machining, ensuring precise hole location, while fixtures securely hold the workpiece in a fixed position without guiding the tool. Jigs are typically used for operations requiring tool guidance such as drilling, whereas fixtures are preferred for tasks like milling or grinding that demand stable workpiece support. The key difference lies in jigs providing both location and tool direction, whereas fixtures only provide location and clamping.
Core Functions: How Jigs and Fixtures Operate
Jigs guide cutting tools precisely, ensuring accurate hole placement and drilling angles, which enhances machining efficiency and repeatability. Fixtures securely hold and position workpieces during various manufacturing processes, providing stability and reducing vibration for consistent quality. Both tools are essential for maintaining dimensional accuracy and production speed in industrial settings.
Types of Jigs in Manufacturing
Types of jigs in manufacturing include template jigs, plate jigs, and leaf jigs, each designed for specific applications to enhance precision and repeatability. Template jigs guide the cutting tool along a predetermined path, commonly used in woodworking and sheet metal work. Plate jigs feature a flat base with bushings for drill bits, ideal for drilling operations, while leaf jigs consist of multiple plates that clamp workpieces securely during machining processes.
Common Types of Fixtures Used in Industry
Common types of fixtures used in the industry include milling fixtures, turning fixtures, and welding fixtures, each designed to securely hold workpieces during machining or assembly processes. Milling fixtures are engineered to stabilize components for precise cutting operations, while turning fixtures support rotary machining tasks. Welding fixtures ensure accurate alignment and clamping of parts to achieve strong, consistent welds, enhancing production efficiency and product quality.
Advantages of Using Jigs
Jigs enhance machining accuracy by guiding cutting tools precisely, reducing human error and increasing repeatability in production. They significantly lower setup time, enabling faster workpiece alignment and consistent part quality across large manufacturing runs. By integrating tool positioning and support, jigs improve efficiency and cost-effectiveness in complex fabrication processes.
Benefits of Incorporating Fixtures
Fixtures provide enhanced stability and repeatability during machining, reducing setup times and minimizing the risk of errors. They support consistent part alignment and can handle heavier workpieces, improving overall production efficiency. Incorporating fixtures leads to higher precision and better quality control compared to jigs in manufacturing processes.
Applications: When to Use Jigs vs Fixtures
Jigs are primarily used in manufacturing processes that require precise drill hole placements or guiding tools during assembly, ideal for repetitive drilling or tapping tasks. Fixtures are designed to securely hold and support workpieces during machining operations, ensuring consistent positioning for milling, grinding, or welding. Choosing jigs suits applications demanding tool guidance, while fixtures are preferred for stabilizing parts to maintain accuracy in various production stages.
Selection Criteria: Choosing Between Jig and Fixture
Selection criteria for choosing between a jig and a fixture depend heavily on the type of machining operation and desired precision; jigs guide the cutting tool, making them ideal for drilling and reaming, while fixtures hold the workpiece stationary, ensuring stability during milling or grinding. Consider factors such as repeatability, setup time, and cost-effectiveness; jigs reduce operator skill requirements and increase efficiency in high-volume production, whereas fixtures provide robust support for complex machining tasks requiring tight tolerances. The choice ultimately aligns with the specific application needs, production volume, and the nature of workpiece manipulation.
Future Trends in Jigs and Fixtures Technology
Emerging trends in jigs and fixtures technology emphasize automation integration and smart manufacturing, incorporating IoT sensors for real-time monitoring and adaptive control. Advanced materials such as carbon fiber composites and additive manufacturing techniques enhance durability and customization while reducing production costs. The shift towards Industry 4.0 enables predictive maintenance and digital twin simulations, optimizing efficiency and precision in machining and assembly processes.
Jig vs Fixture Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com