Cordless tools offer unmatched portability and ease of use without the constraint of power cords, making them ideal for jobs in remote or hard-to-reach locations. Corded tools provide consistent power output and are often preferred for heavy-duty tasks that require continuous operation without the need for battery recharging. Choosing between cordless and corded tools depends on the balance between mobility and power demands for specific applications.
Table of Comparison
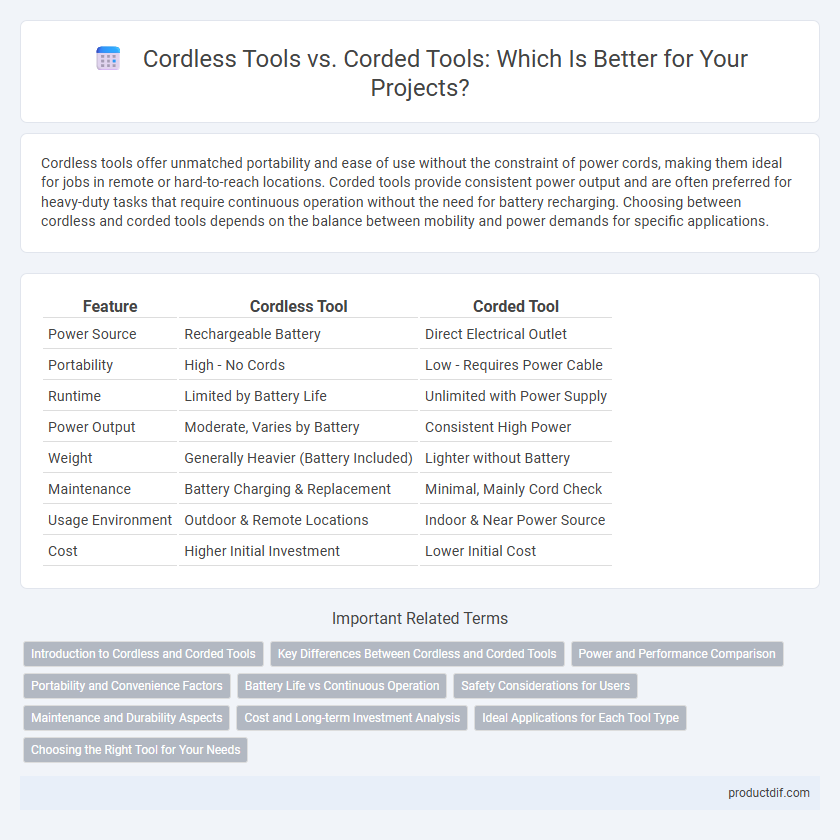
| Feature | Cordless Tool | Corded Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Rechargeable Battery | Direct Electrical Outlet |
| Portability | High - No Cords | Low - Requires Power Cable |
| Runtime | Limited by Battery Life | Unlimited with Power Supply |
| Power Output | Moderate, Varies by Battery | Consistent High Power |
| Weight | Generally Heavier (Battery Included) | Lighter without Battery |
| Maintenance | Battery Charging & Replacement | Minimal, Mainly Cord Check |
| Usage Environment | Outdoor & Remote Locations | Indoor & Near Power Source |
| Cost | Higher Initial Investment | Lower Initial Cost |
Introduction to Cordless and Corded Tools
Cordless tools operate on rechargeable batteries, providing enhanced mobility and convenience for tasks without the need for a power outlet, making them ideal for outdoor or remote work. Corded tools draw power directly from an electrical outlet, ensuring consistent performance and unlimited runtime, which is essential for heavy-duty or prolonged use. Understanding the differences in power source, portability, and application helps users select the appropriate tool for specific projects.
Key Differences Between Cordless and Corded Tools
Cordless tools offer enhanced portability and convenience by operating on rechargeable batteries, making them ideal for remote or outdoor use without access to power outlets. Corded tools deliver consistent power and unlimited runtime, making them better suited for heavy-duty tasks requiring sustained energy output. Battery life, weight, and power stability are critical factors distinguishing cordless tools from the typically heavier but more power-consistent corded tools.
Power and Performance Comparison
Cordless tools offer enhanced portability and convenience with lithium-ion batteries delivering up to 60V, suitable for light to medium tasks but may face power limitations during extended use. Corded tools provide consistent, high power output with unlimited runtime, ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring continuous performance and torque stability. Performance differences hinge on power source reliability, with corded tools excelling in sustained power-intensive jobs, while cordless tools prioritize flexibility and ease of movement.
Portability and Convenience Factors
Cordless tools offer superior portability and convenience due to their battery-powered design, eliminating the need for power outlets and tangled cords. These tools enable users to work freely in remote or tight spaces without restriction, enhancing mobility on job sites. In contrast, corded tools provide consistent power but limit movement, making them less ideal for tasks requiring flexibility and on-the-go operation.
Battery Life vs Continuous Operation
Cordless tools offer the flexibility of portability powered by rechargeable lithium-ion batteries, typically providing a runtime of 30 to 60 minutes depending on the model and usage. Corded tools deliver continuous operation with consistent power output, making them ideal for extended tasks without the need for battery recharge. Battery life in cordless tools limits runtime, whereas corded tools ensure uninterrupted performance for industrial or heavy-duty applications.
Safety Considerations for Users
Cordless tools offer enhanced mobility and reduce trip hazards associated with cords, improving user safety in various work environments. Corded tools require constant power connection, increasing the risk of electric shock and cord damage that can lead to accidents. Proper maintenance and use of insulated gloves are critical for safe operation of both types, with cordless tools generally considered safer due to their lower voltage and absence of exposed cords.
Maintenance and Durability Aspects
Cordless tools require regular battery maintenance, such as charging cycles and proper storage, to maximize lifespan and performance, while corded tools generally offer longer durability due to consistent power supply and fewer battery-related issues. The durability of corded tools often surpasses cordless variants because they lack rechargeable batteries prone to degradation over time. Proper care, including cleaning and timely inspection, enhances the lifespan of both tool types, but corded tools typically demand less ongoing maintenance.
Cost and Long-term Investment Analysis
Cordless tools typically have a higher upfront cost than corded tools due to the inclusion of batteries and chargers, but they offer greater mobility and convenience. Over time, corded tools tend to be more cost-effective as they require less maintenance and no battery replacements, which can add to the long-term expenses of cordless tools. Evaluating total ownership costs, including energy consumption, replacement parts, and durability, is essential for determining the best investment between cordless and corded tools.
Ideal Applications for Each Tool Type
Cordless tools offer the advantage of portability and are ideal for tasks requiring mobility, such as outdoor landscaping or site work with limited power access. Corded tools provide consistent power output, making them perfect for prolonged use in workshops or construction projects where electrical outlets are readily available. Choosing between cordless and corded tools depends on the need for convenience versus continuous power supply for optimal performance.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs
Choosing the right tool depends on the project's power requirements and mobility needs; cordless tools offer freedom from power outlets and ease of use in remote locations, while corded tools provide consistent power for heavy-duty tasks without worrying about battery life. Battery technology advancements in cordless tools have improved runtime and charging speed, making them suitable for many professional applications. Evaluate factors such as job duration, power intensity, and accessibility before deciding between cordless and corded tools to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
Cordless Tool vs Corded Tool Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com