Die casting offers superior precision and surface finish compared to sand casting, making it ideal for high-volume production of complex metal parts. Sand casting provides greater flexibility in design changes and is more cost-effective for low-volume or large-sized components. Both methods have unique advantages, with die casting excelling in speed and consistency, while sand casting allows for broader alloy selection and easier prototyping.
Table of Comparison
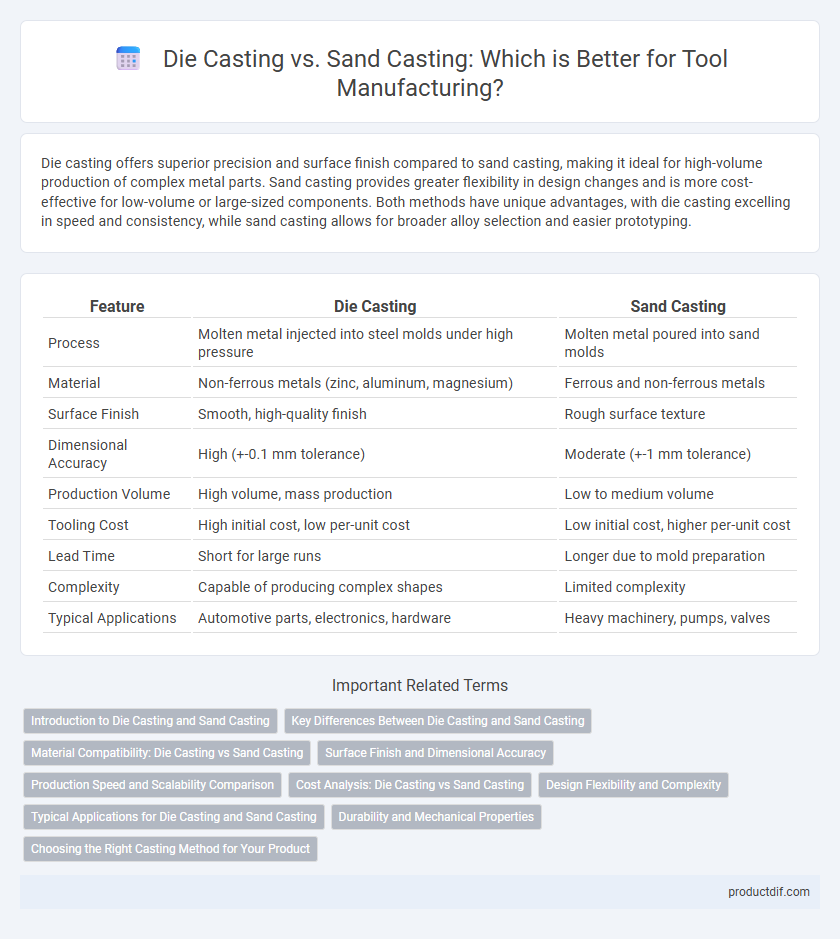
| Feature | Die Casting | Sand Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Molten metal injected into steel molds under high pressure | Molten metal poured into sand molds |
| Material | Non-ferrous metals (zinc, aluminum, magnesium) | Ferrous and non-ferrous metals |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, high-quality finish | Rough surface texture |
| Dimensional Accuracy | High (+-0.1 mm tolerance) | Moderate (+-1 mm tolerance) |
| Production Volume | High volume, mass production | Low to medium volume |
| Tooling Cost | High initial cost, low per-unit cost | Low initial cost, higher per-unit cost |
| Lead Time | Short for large runs | Longer due to mold preparation |
| Complexity | Capable of producing complex shapes | Limited complexity |
| Typical Applications | Automotive parts, electronics, hardware | Heavy machinery, pumps, valves |
Introduction to Die Casting and Sand Casting
Die casting involves forcing molten metal into a mold cavity under high pressure, producing precise and complex shapes with excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Sand casting uses a sand-based mold to shape molten metal, offering flexibility for large or intricate parts with lower production costs but less precision and surface detail. Both methods are widely used in metalworking industries, with die casting suited for high-volume manufacturing and sand casting ideal for prototypes and small runs.
Key Differences Between Die Casting and Sand Casting
Die casting produces high-precision metal parts using molten metal injected into reusable steel molds, offering excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Sand casting utilizes expendable sand molds, suitable for complex shapes and larger parts but with coarser surface quality and lower precision. Die casting is ideal for high-volume production, while sand casting provides flexibility for smaller runs and diverse alloys.
Material Compatibility: Die Casting vs Sand Casting
Die casting offers superior material compatibility for non-ferrous metals like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium, enabling high-precision, complex shapes with excellent surface finish. Sand casting accommodates a broader range of metals, including ferrous alloys such as cast iron and steel, making it ideal for large or heavy parts with less critical dimensional tolerance. Material selection between die casting and sand casting depends on factors like alloy properties, production volume, and required mechanical strength.
Surface Finish and Dimensional Accuracy
Die casting offers superior surface finish with smoother, more uniform surfaces due to high-pressure metal injection into precision molds, resulting in minimal post-processing. Sand casting typically produces rougher surfaces with visible grain and requires extensive machining to achieve comparable smoothness. Dimensional accuracy in die casting is higher, maintaining tight tolerances within +-0.1 mm, while sand casting tolerances often vary by +-0.5 mm or more because of mold material flexibility and shrinkage.
Production Speed and Scalability Comparison
Die casting offers significantly faster production speeds compared to sand casting due to its automated process and quick solidification of molten metal in reusable steel molds. Scalability in die casting is superior as it supports high-volume manufacturing with consistent precision, whereas sand casting suits low to medium production runs because of its labor-intensive mold making and longer cycle times. Choosing die casting enhances rapid mass production efficiency, while sand casting provides flexible scalability for custom or limited-quantity tooling needs.
Cost Analysis: Die Casting vs Sand Casting
Die casting offers lower per-unit costs in high-volume production due to reusable metal molds, while sand casting incurs higher expenses from mold recreation for each batch. Initial tooling costs for die casting are significantly higher, making sand casting more cost-effective for small production runs and prototypes. Overall, die casting reduces long-term production costs through speed and precision, whereas sand casting remains economical for custom or low-volume projects.
Design Flexibility and Complexity
Die casting offers superior design flexibility and complexity by enabling intricate, precise, and thin-walled components with fine surface finishes, ideal for high-volume production. Sand casting allows for larger, heavier parts with complex geometries and undercuts, but with lower dimensional accuracy and rougher surface textures. The choice depends on balancing the need for detailed, tight-tolerance designs against the size and material constraints of the casting process.
Typical Applications for Die Casting and Sand Casting
Die casting is ideal for producing high-volume, precision metal parts such as automotive components, consumer electronics housings, and industrial machinery parts due to its ability to create complex shapes with tight tolerances and smooth surfaces. Sand casting is preferred for low-volume production or large-scale parts like engine blocks, pump housings, and heavy equipment components, where intricate detail is less critical but strength and flexibility in material choice are important. Both methods serve distinct roles in manufacturing, with die casting excelling in mass production and fine detail, while sand casting offers versatility for custom and oversized items.
Durability and Mechanical Properties
Die casting produces parts with superior mechanical properties and higher durability due to its fine-grained metal structure and reduced porosity. Sand casting typically results in coarser grain and more surface imperfections, which can compromise strength and wear resistance. The precision of die casting also enhances dimensional accuracy, contributing to the overall performance and longevity of the components.
Choosing the Right Casting Method for Your Product
Die casting offers superior precision and surface finish, making it ideal for high-volume production of complex metal parts, especially aluminum and zinc alloys. Sand casting provides greater flexibility for larger, intricate components and lower initial tooling costs, suitable for small batches or prototypes. Selecting the appropriate casting method depends on factors like production volume, part complexity, material type, and cost efficiency.
Die Casting vs Sand Casting Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com