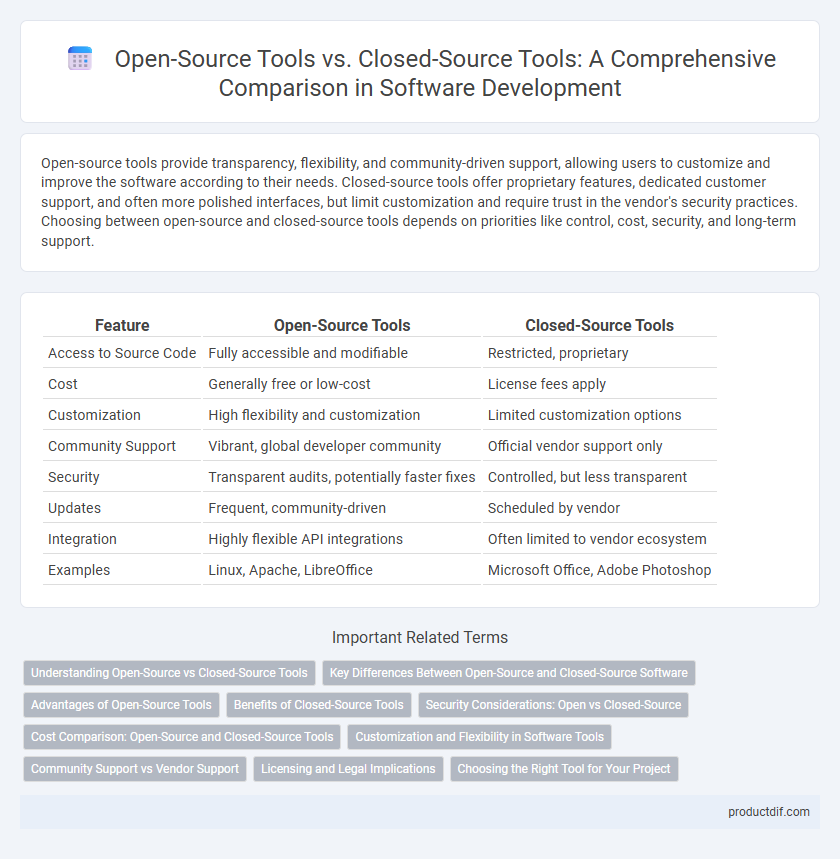
Open-source tools provide transparency, flexibility, and community-driven support, allowing users to customize and improve the software according to their needs. Closed-source tools offer proprietary features, dedicated customer support, and often more polished interfaces, but limit customization and require trust in the vendor's security practices. Choosing between open-source and closed-source tools depends on priorities like control, cost, security, and long-term support.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Open-Source Tools | Closed-Source Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Access to Source Code | Fully accessible and modifiable | Restricted, proprietary |
| Cost | Generally free or low-cost | License fees apply |
| Customization | High flexibility and customization | Limited customization options |
| Community Support | Vibrant, global developer community | Official vendor support only |
| Security | Transparent audits, potentially faster fixes | Controlled, but less transparent |
| Updates | Frequent, community-driven | Scheduled by vendor |
| Integration | Highly flexible API integrations | Often limited to vendor ecosystem |
| Examples | Linux, Apache, LibreOffice | Microsoft Office, Adobe Photoshop |
Understanding Open-Source vs Closed-Source Tools
Open-source tools provide users with access to the underlying source code, enabling customization, transparency, and community-driven development, which enhances innovation and security through collective review. Closed-source tools restrict access to source code, offering controlled environments with vendor-driven updates and support, often resulting in proprietary features and potential limitations on flexibility. Evaluating factors such as cost, customization needs, security requirements, and support availability is crucial when choosing between open-source and closed-source solutions.
Key Differences Between Open-Source and Closed-Source Software
Open-source tools provide full access to their source code, enabling customization, transparency, and community-driven improvements, which often results in faster innovation and lower costs. Closed-source tools restrict access to their source code, offering controlled environments with dedicated vendor support, enhanced security measures, and proprietary features tailored for specific business needs. The choice between open-source and closed-source software depends on factors like budget, customization requirements, security concerns, and long-term maintenance expectations.
Advantages of Open-Source Tools
Open-source tools offer unparalleled transparency, allowing users to inspect and modify source code, which enhances security and customization. They typically foster vibrant communities that drive rapid innovation and provide extensive support, reducing dependency on proprietary vendors. Cost-effectiveness is another key advantage, as open-source tools often eliminate licensing fees, making them accessible for both individuals and organizations.
Benefits of Closed-Source Tools
Closed-source tools offer enhanced security through controlled access to source code, minimizing vulnerabilities and unauthorized modifications. These tools often provide dedicated customer support and regular updates, ensuring reliability and compatibility with enterprise systems. Proprietary development allows for tailored features and optimized performance that align closely with specific business requirements.
Security Considerations: Open vs Closed-Source
Open-source tools provide transparency by allowing users to inspect, modify, and audit the source code for vulnerabilities, enhancing security through community collaboration and rapid patching. Closed-source tools rely on proprietary code, which limits external scrutiny but may reduce exposure to public exploits, placing trust in vendor-led security measures and updates. Security considerations favor open-source solutions in environments where code transparency and community vetting are critical, while closed-source tools may be preferred for controlled, proprietary security protocols.
Cost Comparison: Open-Source and Closed-Source Tools
Open-source tools typically offer significant cost savings due to free access and no licensing fees, making them ideal for budget-conscious projects. Closed-source tools often involve upfront costs, subscription fees, and ongoing expenses for updates and support, which can increase total cost of ownership. Evaluating cost comparison includes factoring in hidden expenses such as customization, integration, and training for both open-source and closed-source solutions.
Customization and Flexibility in Software Tools
Open-source tools offer unparalleled customization and flexibility, allowing developers to modify source code to tailor software features precisely to their needs. Closed-source tools, while often providing polished user experiences, limit customization options due to restricted access to proprietary code. Organizations prioritizing adaptability and control frequently prefer open-source solutions for their ability to integrate seamlessly with diverse systems and workflows.
Community Support vs Vendor Support
Open-source tools benefit from extensive community support, providing access to a broad network of developers and users who contribute to continuous improvements, troubleshooting, and documentation. In contrast, closed-source tools rely primarily on vendor support, offering dedicated customer service, regular updates, and professional assistance directly from the company. Community-driven open-source resources often enable faster innovation and collaborative problem-solving, while vendor-backed tools ensure consistent, SLA-guaranteed support tailored to enterprise needs.
Licensing and Legal Implications
Open-source tools offer licenses like GPL, MIT, or Apache that allow users to modify, distribute, and use the software freely, promoting transparency and collaboration. Closed-source tools typically come with proprietary licenses that restrict access to the source code and limit usage, redistribution, and modification rights, potentially leading to vendor lock-in. Legal implications of open-source licenses require compliance with specific terms to avoid infringement, while closed-source licenses often impose stricter control over intellectual property and liability.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Project
Open-source tools provide flexibility, customization, and community support, making them ideal for projects requiring adaptability and transparent development. Closed-source tools offer dedicated customer service, polished interfaces, and proprietary features, which benefit projects demanding stability, security, and vendor accountability. Selecting the right tool depends on evaluating project requirements, budget constraints, maintenance needs, and the desired level of innovation versus control.
Open-source tools vs Closed-source tools Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com