Hand tools offer precision and control for detailed tasks, making them ideal for fine craftsmanship and delicate repairs. Power tools provide increased speed and efficiency, suitable for heavy-duty projects and repetitive work. Choosing between hand tools and power tools depends on the job requirements, user skill level, and desired outcome.
Table of Comparison
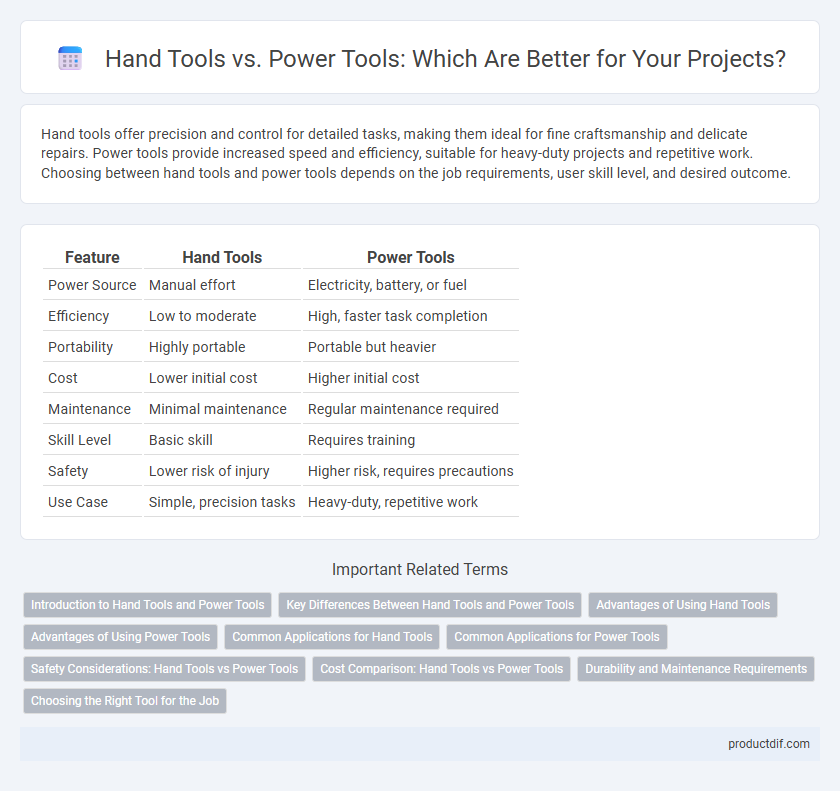
| Feature | Hand Tools | Power Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Manual effort | Electricity, battery, or fuel |
| Efficiency | Low to moderate | High, faster task completion |
| Portability | Highly portable | Portable but heavier |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance | Regular maintenance required |
| Skill Level | Basic skill | Requires training |
| Safety | Lower risk of injury | Higher risk, requires precautions |
| Use Case | Simple, precision tasks | Heavy-duty, repetitive work |
Introduction to Hand Tools and Power Tools
Hand tools encompass manual devices such as hammers, screwdrivers, and wrenches, designed for precision and control in various tasks without the need for electricity. Power tools, including drills, saws, and sanders, utilize electric motors or batteries to increase efficiency and reduce physical effort in construction and repair projects. Understanding the distinct advantages and appropriate applications of hand tools versus power tools is essential for selecting the right equipment for any job.
Key Differences Between Hand Tools and Power Tools
Hand tools rely on manual effort and are typically lightweight, portable, and require no external power source, making them ideal for precision tasks and small-scale projects. Power tools use electricity or battery power to significantly increase efficiency, speed, and power, suitable for heavy-duty applications and repetitive tasks. Key differences include the source of energy, usability complexity, and the scale of work each tool can effectively handle.
Advantages of Using Hand Tools
Hand tools provide superior precision and control, making them ideal for delicate tasks and intricate craftsmanship. They require no power source, offering portability and convenience in remote or off-grid locations. Hand tools also tend to be more durable and easier to maintain, reducing long-term costs compared to power tools.
Advantages of Using Power Tools
Power tools significantly increase efficiency and productivity by delivering higher torque and speed compared to hand tools, enabling faster completion of tasks. They reduce physical strain on users, making them ideal for repetitive or heavy-duty jobs, and often come with adjustable settings for precision and versatility. Advanced features such as battery operation and ergonomic design further enhance convenience and ease of use in various construction, woodworking, and DIY projects.
Common Applications for Hand Tools
Hand tools are commonly used for precision tasks such as measuring, cutting, tightening, and shaping materials where control and accuracy are essential. Applications include woodworking with chisels and saws, mechanical repairs using wrenches and screwdrivers, and gardening tasks like pruning with shears. These manual tools provide reliability in small-scale projects and delicate work that power tools may overdo.
Common Applications for Power Tools
Power tools excel in construction, woodworking, and metalworking by providing high-speed drilling, cutting, and fastening capabilities that increase efficiency and precision. Common applications include cordless drills for assembly, circular saws for cutting lumber, and angle grinders for shaping metal surfaces. Professionals rely on these tools to perform repetitive or heavy-duty tasks that require consistent power output and reduced manual effort.
Safety Considerations: Hand Tools vs Power Tools
Hand tools generally pose lower safety risks due to their manual operation and slower speeds, reducing the likelihood of severe injuries. Power tools require strict adherence to safety protocols, including wearing personal protective equipment (PPE) and proper maintenance, as their high speed and power increase the risk of accidents such as cuts, electrocution, and kickbacks. Employers must implement comprehensive training programs focusing on hazard identification and safe handling practices for both tool types to minimize workplace injuries.
Cost Comparison: Hand Tools vs Power Tools
Hand tools generally have a lower upfront cost compared to power tools, making them more budget-friendly for beginners or casual users. Power tools, while more expensive initially, often provide greater efficiency and speed, potentially reducing labor time and overall project costs. Maintenance and operational expenses for power tools can add up, but their increased productivity may justify the higher investment for professional use.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Hand tools typically exhibit higher durability due to their simple construction and fewer mechanical parts, resulting in lower risk of breakdowns and longer lifespan. Power tools require regular maintenance such as lubrication, battery care, and motor inspections to ensure optimal performance and prevent wear. Proper upkeep of both hand and power tools is essential, but hand tools generally demand less frequent and less complex maintenance routines.
Choosing the Right Tool for the Job
Selecting the appropriate tool depends on the task's complexity and precision requirements; hand tools offer greater control for detailed work, while power tools provide efficiency for heavy-duty projects. Consider factors such as material type, workspace accessibility, and user skill level to optimize performance and safety. Investing in the correct tool enhances productivity, reduces fatigue, and ensures quality results in any construction or repair job.
Hand tools vs Power tools Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com