Manual tools require direct human operation, offering precision and control for detailed tasks but often demanding more time and effort. Automated tools enhance efficiency by performing repetitive or complex functions with minimal human intervention, reducing errors and increasing productivity. Choosing between manual and automated tools depends on the task complexity, desired accuracy, and available resources.
Table of Comparison
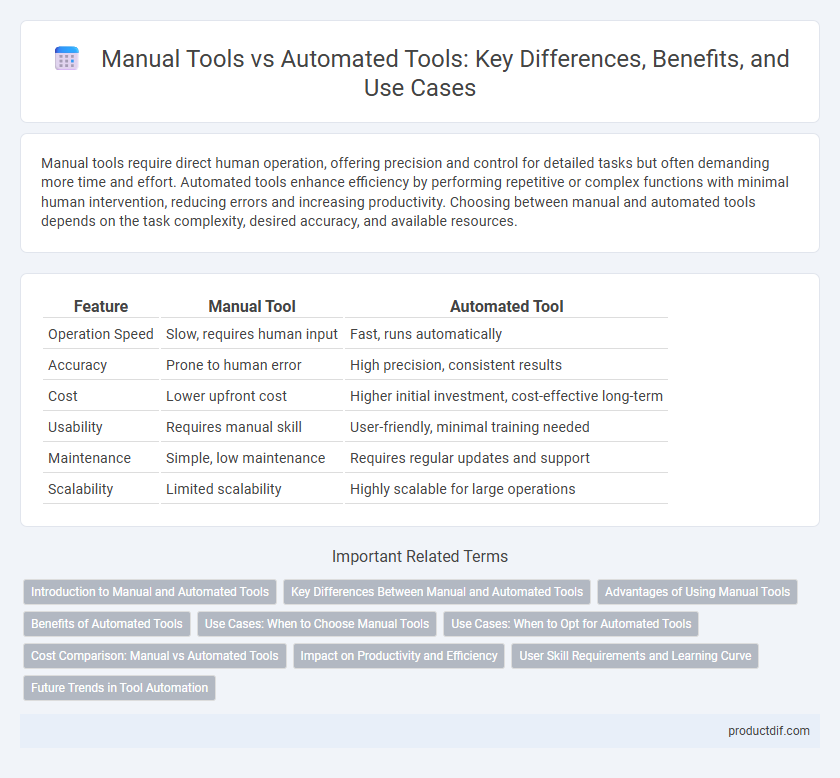
| Feature | Manual Tool | Automated Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Operation Speed | Slow, requires human input | Fast, runs automatically |
| Accuracy | Prone to human error | High precision, consistent results |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher initial investment, cost-effective long-term |
| Usability | Requires manual skill | User-friendly, minimal training needed |
| Maintenance | Simple, low maintenance | Requires regular updates and support |
| Scalability | Limited scalability | Highly scalable for large operations |
Introduction to Manual and Automated Tools
Manual tools require direct human operation, offering precise control and adaptability in various tasks such as cutting, shaping, or assembly. Automated tools utilize motorized, programmable systems powered by electricity or hydraulics, enhancing efficiency, consistency, and speed in repetitive or complex processes. Choosing between manual and automated tools depends on factors like task complexity, production volume, and desired accuracy.
Key Differences Between Manual and Automated Tools
Manual tools require human effort for operation, offering precision and control in detailed tasks but limiting speed and scalability. Automated tools use technology to perform repetitive or complex processes efficiently, increasing productivity and reducing human error. Key differences include the level of human involvement, operational speed, and consistency in task execution.
Advantages of Using Manual Tools
Manual tools offer enhanced precision and tactile feedback, allowing users to make fine adjustments and maintain greater control during intricate tasks. They require minimal power sources, making them highly reliable in remote or low-resource environments. The simplicity of manual tools often results in lower maintenance costs and increased durability compared to automated alternatives.
Benefits of Automated Tools
Automated tools enhance efficiency by performing repetitive tasks faster and with higher accuracy than manual tools, reducing human error significantly. They enable consistent results and streamline workflows, allowing teams to focus on complex problem-solving and innovation. Integration capabilities with other software systems further amplify productivity and data management in automated tooling environments.
Use Cases: When to Choose Manual Tools
Manual tools are ideal for tasks requiring high precision, customization, or when dealing with small-scale projects where automation overhead is unjustified. They excel in environments where human judgment and adaptability are crucial, such as prototyping, intricate repairs, or unique, one-off tasks. Choosing manual tools is beneficial when flexibility, immediate control, and tactile feedback outweigh the scalability and speed offered by automated alternatives.
Use Cases: When to Opt for Automated Tools
Automated tools excel in scenarios requiring repetitive tasks, high precision, and large-scale data processing, reducing human error and increasing efficiency. Industries such as software testing, manufacturing, and data analytics benefit from automation to handle complex workflows and real-time monitoring. Opting for automated tools is essential when scalability and speed are critical for project success.
Cost Comparison: Manual vs Automated Tools
Manual tools generally involve lower upfront costs but incur higher long-term expenses due to labor intensity and slower task completion rates. Automated tools require significant initial investment but reduce operational costs by increasing efficiency and minimizing human error over time. Businesses must weigh immediate budget constraints against potential savings achieved through automation when selecting between manual and automated solutions.
Impact on Productivity and Efficiency
Manual tools often require significant human effort and time, limiting productivity and increasing the likelihood of errors. Automated tools streamline processes by performing repetitive tasks quickly and accurately, significantly enhancing overall efficiency. Integrating automated tools in workflows reduces operational costs and enables teams to focus on higher-value activities.
User Skill Requirements and Learning Curve
Manual tools demand higher user skill and experience, requiring precise hand coordination and technique for effective operation, which often results in a steeper learning curve. Automated tools reduce the need for advanced user expertise by integrating pre-programmed functions and user-friendly interfaces, accelerating proficiency and minimizing errors. The learning curve for automated tools is generally shorter, enabling quicker adaptation and consistent results, especially beneficial for novice users or complex tasks.
Future Trends in Tool Automation
Future trends in tool automation emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance precision and efficiency in automated tools. Smart sensors and IoT connectivity enable real-time data collection and adaptive tool adjustments, reducing human intervention. Collaborative robots (cobots) are increasingly designed to work alongside manual tools, allowing seamless hybrid operations that maximize productivity and flexibility in manufacturing and construction.
Manual Tool vs Automated Tool Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com