Bench grinders offer a stable platform ideal for grinding, sharpening, and shaping tools with precision, making them perfect for detailed workshop tasks. Angle grinders provide versatility with their handheld design, allowing users to cut, grind, and polish various materials on-site or in tight spaces. Choosing between a bench grinder and an angle grinder depends on whether you prioritize stationary accuracy or portable flexibility for your projects.
Table of Comparison
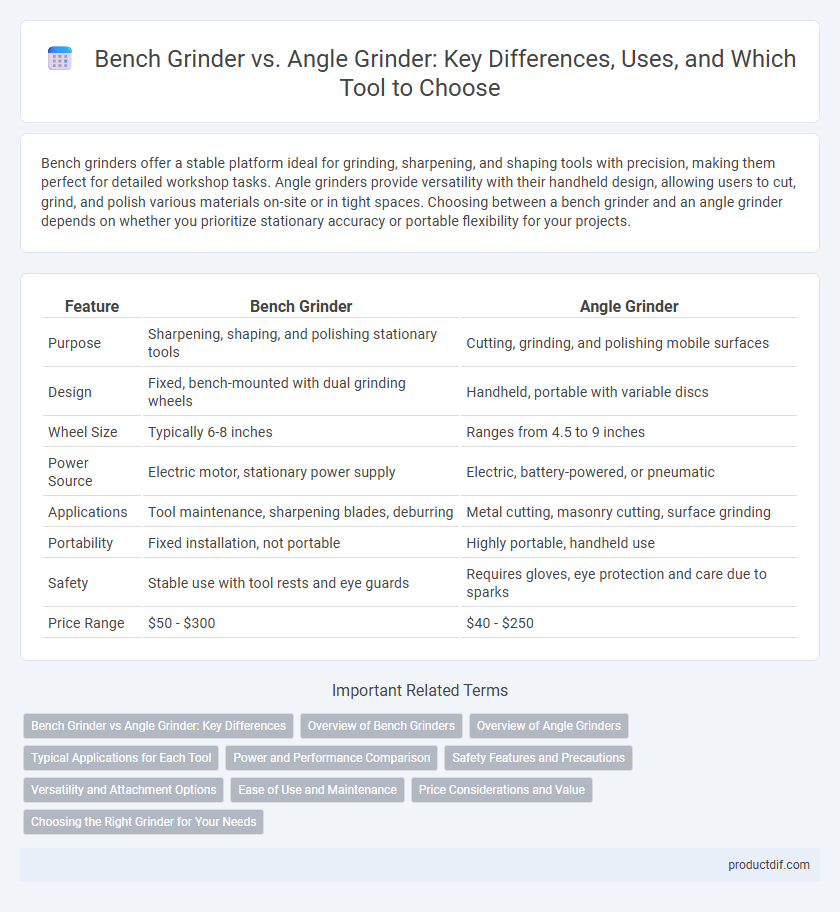
| Feature | Bench Grinder | Angle Grinder |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Sharpening, shaping, and polishing stationary tools | Cutting, grinding, and polishing mobile surfaces |
| Design | Fixed, bench-mounted with dual grinding wheels | Handheld, portable with variable discs |
| Wheel Size | Typically 6-8 inches | Ranges from 4.5 to 9 inches |
| Power Source | Electric motor, stationary power supply | Electric, battery-powered, or pneumatic |
| Applications | Tool maintenance, sharpening blades, deburring | Metal cutting, masonry cutting, surface grinding |
| Portability | Fixed installation, not portable | Highly portable, handheld use |
| Safety | Stable use with tool rests and eye guards | Requires gloves, eye protection and care due to sparks |
| Price Range | $50 - $300 | $40 - $250 |
Bench Grinder vs Angle Grinder: Key Differences
Bench grinders offer stability and precision for sharpening and shaping tasks with adjustable tool rests, while angle grinders provide portability and versatility for cutting, grinding, and polishing various materials using different disc attachments. Bench grinders typically operate at lower speeds, ideal for detailed work on metals and tools, whereas angle grinders spin at higher speeds for more aggressive material removal. The fixed position of bench grinders contrasts with the handheld design of angle grinders, influencing their suitability based on the task requirements and workspace constraints.
Overview of Bench Grinders
Bench grinders are stationary power tools designed for precision grinding, shaping, and sharpening tasks, typically featuring two grinding wheels of different grit sizes mounted on a workbench. Commonly used in metalworking and woodworking, bench grinders provide stability and consistent speed for accurate material removal, making them ideal for sharpening blades, deburring, and tool maintenance. Their robust construction allows for extended use, with adjustable tool rests and eye shields enhancing safety and control during operation.
Overview of Angle Grinders
Angle grinders feature a versatile design equipped with a rotating abrasive disc capable of cutting, grinding, and polishing various materials such as metal, stone, and ceramics. Their compact, handheld structure enables precision work in tight spaces and surface preparation tasks, making them indispensable in construction, metalworking, and automotive industries. High-speed motors ranging from 5,000 to 10,000 RPM enhance efficiency, while adjustable guard and side handles improve safety and control during operation.
Typical Applications for Each Tool
Bench grinders excel at sharpening cutting tools, shaping metal parts, and removing rust or burrs on stationary workpieces in workshops. Angle grinders are versatile for cutting, grinding, and polishing metal, concrete, or tile surfaces in construction, fabrication, and maintenance tasks. Each tool's design aligns with its applications: bench grinders provide stability for precision work, while angle grinders offer mobility for on-site versatility.
Power and Performance Comparison
Bench grinders typically feature motors ranging from 1/2 to 2 horsepower, delivering consistent power for heavy-duty sharpening and shaping tasks. Angle grinders, equipped with high-speed motors between 5 to 15 amps, offer versatile performance suitable for cutting, grinding, and polishing various materials. Power output in angle grinders translates to faster material removal, while bench grinders provide stable rotational speed for precision work.
Safety Features and Precautions
Bench grinders feature adjustable eye shields, spark guards, and tool rests to minimize accidents during use, ensuring stable grinding and effective debris containment. Angle grinders incorporate safety aspects like side handles for better control, safety switches to prevent accidental starts, and guard covers tailored for specific cutting or grinding discs. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, maintain clear workspaces, and regularly inspect tool guards and components to uphold optimal safety standards.
Versatility and Attachment Options
Bench grinders offer limited versatility but excel in precise sharpening and shaping tasks with fixed grinding wheels, while angle grinders provide extensive versatility through a variety of attachments like cutting discs, wire brushes, and sanding pads. The wide range of compatible attachments for angle grinders makes them suitable for cutting, grinding, polishing, and even metal brushing, surpassing the specialized function of bench grinders. Users seeking multifunctional tools often prefer angle grinders due to their adaptability in various applications and ease of switching attachments.
Ease of Use and Maintenance
Bench grinders offer greater stability and user control due to their stationary design, making them easier for precise grinding tasks. Angle grinders provide more versatility in tight spaces but require careful handling and periodic disc replacements, slightly increasing maintenance complexity. Regular lubrication and cleaning extend the lifespan of both tools, but bench grinders typically demand less frequent upkeep.
Price Considerations and Value
Bench grinders generally have a higher upfront cost, ranging from $50 to $300 depending on power and features, while angle grinders are often more affordable, priced between $30 and $150. The value of a bench grinder lies in its stability and precision for sharpening and shaping tasks, making it ideal for workshops, whereas angle grinders offer versatility and portability suitable for cutting, grinding, and polishing. Choosing between the two depends on specific project needs and budget constraints, balancing cost with tool functionality and durability.
Choosing the Right Grinder for Your Needs
Choosing the right grinder depends on the specific tasks you need to perform; a bench grinder excels at precision sharpening, shaping, and polishing with its stationary design, making it ideal for workshop use. In contrast, an angle grinder offers versatility and portability, suitable for cutting, grinding, and sanding various materials on-site due to its handheld nature and multiple disc options. Assessing your project requirements, workspace, and material type will help determine whether the bench grinder's stable, focused grinding or the angle grinder's dynamic, multi-functional capabilities best fit your needs.
Bench grinder vs Angle grinder Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com