Manual tools offer precise control and simplicity, making them ideal for detailed tasks and low-volume work. Pneumatic tools deliver higher power and efficiency, suitable for repetitive or heavy-duty applications, reducing user fatigue. Choosing between manual and pneumatic depends on the specific job requirements, tool durability, and available resources.
Table of Comparison
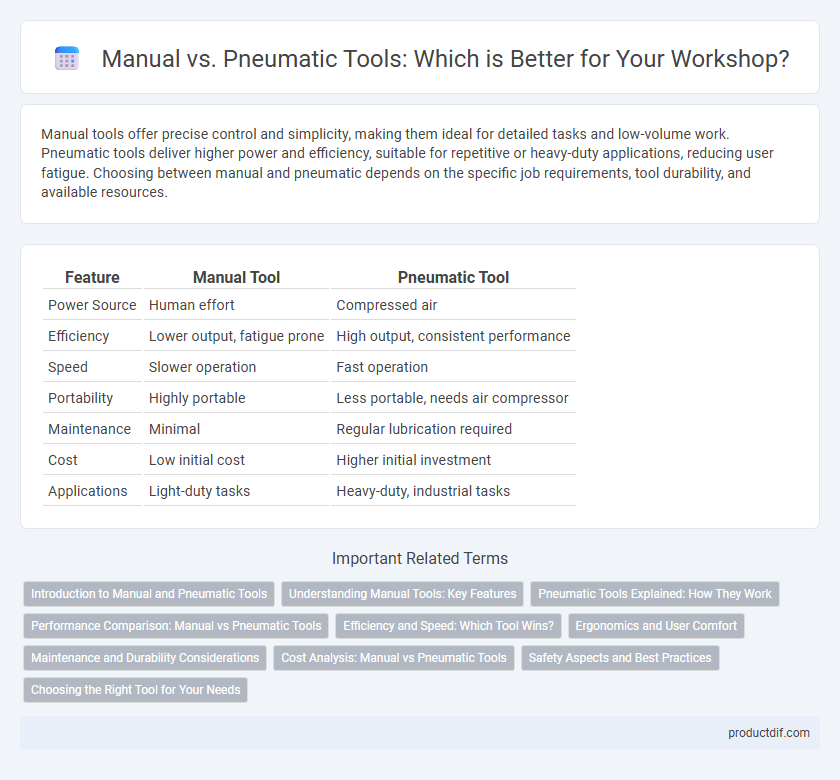
| Feature | Manual Tool | Pneumatic Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Human effort | Compressed air |
| Efficiency | Lower output, fatigue prone | High output, consistent performance |
| Speed | Slower operation | Fast operation |
| Portability | Highly portable | Less portable, needs air compressor |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Regular lubrication required |
| Cost | Low initial cost | Higher initial investment |
| Applications | Light-duty tasks | Heavy-duty, industrial tasks |
Introduction to Manual and Pneumatic Tools
Manual tools rely on human power for operation, offering precision and control in tasks such as cutting, shaping, and fastening. Pneumatic tools use compressed air to generate high force and speed, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications like drilling, grinding, and impact driving. Understanding the basic differences in power sources and typical uses helps in selecting the right tool for efficiency and effectiveness in industrial or construction settings.
Understanding Manual Tools: Key Features
Manual tools rely on human physical effort without external power sources, offering precise control and simplicity in operation. Key features include durability, ease of maintenance, and versatility for various tasks such as cutting, fastening, or measuring. These tools excel in tasks requiring fine motor skills, reducing fatigue and increasing accuracy in detailed work.
Pneumatic Tools Explained: How They Work
Pneumatic tools operate using compressed air stored in a tank or supplied from an air compressor, converting this energy into mechanical motion for tasks like drilling, hammering, or fastening. These tools are favored for their high power-to-weight ratio, durability, and safety since they generate less heat compared to electric tools. Their efficiency relies on consistent air pressure and proper maintenance, making them ideal for industrial and heavy-duty applications.
Performance Comparison: Manual vs Pneumatic Tools
Pneumatic tools consistently outperform manual tools in terms of speed and power, delivering higher torque and enabling faster task completion in industrial settings. Manual tools require greater user effort and are less efficient for repetitive or heavy-duty tasks, making pneumatic tools preferable for sustained performance. The durability and precision of pneumatic tools also contribute to improved consistency and reduced operator fatigue compared to manual alternatives.
Efficiency and Speed: Which Tool Wins?
Pneumatic tools deliver higher efficiency and speed compared to manual tools by utilizing compressed air to perform rapid, powerful actions with minimal user effort. Manual tools, while offering precision and control, generally require more time and physical exertion, making them less suitable for high-volume or repetitive tasks. In industrial and professional settings focused on productivity, pneumatic tools dominate due to their ability to accelerate workflows and reduce fatigue.
Ergonomics and User Comfort
Manual tools demand more physical effort and repetitive motion, increasing the risk of user fatigue and strain injuries over extended use. Pneumatic tools reduce muscle exertion by utilizing compressed air, enhancing ergonomics through lighter weight and reduced vibration levels, thereby improving user comfort and productivity. Ergonomic designs in pneumatic tools also promote better wrist and hand positioning, minimizing discomfort during prolonged tasks.
Maintenance and Durability Considerations
Manual tools require minimal maintenance, mainly occasional cleaning and lubrication, resulting in longer durability under normal usage conditions. Pneumatic tools demand regular maintenance, including air filter checks, oiling, and hose inspections to prevent wear and ensure optimal performance. The durability of pneumatic tools heavily relies on consistent maintenance, while manual tools generally withstand rough handling with less frequent upkeep.
Cost Analysis: Manual vs Pneumatic Tools
Manual tools typically have lower upfront costs and minimal maintenance expenses, making them cost-effective for small-scale or occasional tasks. Pneumatic tools require higher initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs such as air compressor upkeep but offer faster operation and increased productivity in high-volume or continuous use scenarios. Evaluating total cost of ownership involves balancing purchase price, maintenance, energy consumption, and labor efficiency based on application requirements.
Safety Aspects and Best Practices
Manual tools offer greater control and reduce the risk of operator fatigue, minimizing accidents from repetitive strain injuries. Pneumatic tools require strict adherence to safety protocols such as wearing protective gear and ensuring proper maintenance to prevent high-pressure air hazards and accidental activation. Best practices include regular training, secure workspace organization, and routine inspection of all tool components to enhance safety during operation.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs
Choosing the right tool depends on the task's precision, power, and efficiency requirements. Manual tools offer greater control and cost-effectiveness for detailed, small-scale work, while pneumatic tools provide superior power and speed for repetitive or heavy-duty applications. Evaluating factors such as job frequency, material hardness, and budget ensures optimal tool selection for maximum productivity.
Manual vs Pneumatic Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com