Injection molding offers high-volume production with consistent part quality and complex shapes at a lower per-unit cost. CNC machining excels in producing precise, low-volume prototypes and custom parts with tight tolerances from a variety of materials. Selecting between injection molding and CNC machining depends on factors like production volume, design complexity, and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
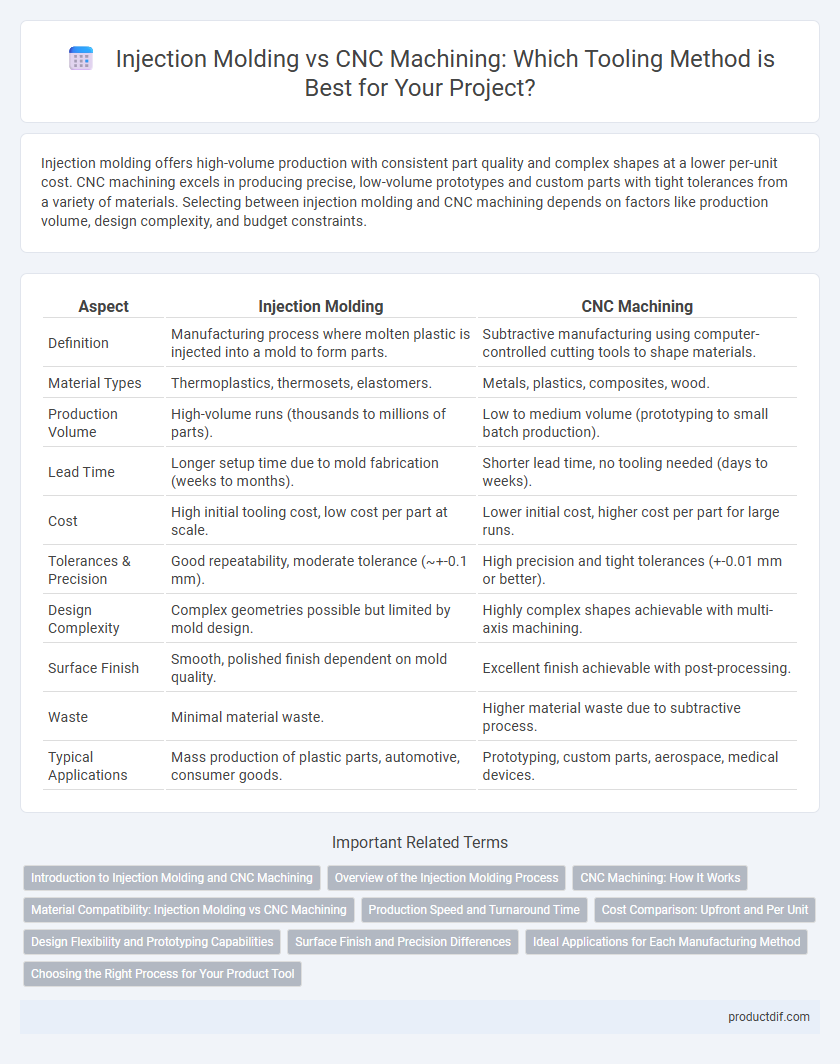
| Aspect | Injection Molding | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturing process where molten plastic is injected into a mold to form parts. | Subtractive manufacturing using computer-controlled cutting tools to shape materials. |
| Material Types | Thermoplastics, thermosets, elastomers. | Metals, plastics, composites, wood. |
| Production Volume | High-volume runs (thousands to millions of parts). | Low to medium volume (prototyping to small batch production). |
| Lead Time | Longer setup time due to mold fabrication (weeks to months). | Shorter lead time, no tooling needed (days to weeks). |
| Cost | High initial tooling cost, low cost per part at scale. | Lower initial cost, higher cost per part for large runs. |
| Tolerances & Precision | Good repeatability, moderate tolerance (~+-0.1 mm). | High precision and tight tolerances (+-0.01 mm or better). |
| Design Complexity | Complex geometries possible but limited by mold design. | Highly complex shapes achievable with multi-axis machining. |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, polished finish dependent on mold quality. | Excellent finish achievable with post-processing. |
| Waste | Minimal material waste. | Higher material waste due to subtractive process. |
| Typical Applications | Mass production of plastic parts, automotive, consumer goods. | Prototyping, custom parts, aerospace, medical devices. |
Introduction to Injection Molding and CNC Machining
Injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material, typically plastic, into a mold cavity to produce complex and high-volume parts with precise dimensions and surface finishes. CNC machining, on the other hand, uses computer-controlled cutting tools to remove material from a solid block, enabling high precision and flexibility for low to medium volume production runs. Both methods offer distinct advantages depending on the project requirements, with injection molding excelling in mass production and CNC machining providing rapid prototyping and customization options.
Overview of the Injection Molding Process
Injection molding is a manufacturing process where molten material, typically plastic or metal, is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure to form precise and complex shapes. The process involves clamping the mold, injecting the material, cooling it until solidified, and then ejecting the finished part, enabling high-volume production with consistent quality. This method is especially efficient for producing large quantities of identical components with intricate designs and tight tolerances compared to CNC machining.
CNC Machining: How It Works
CNC machining operates by precisely removing material from a solid block using computer-controlled rotary cutters, enabling the creation of complex and highly accurate parts. This subtractive manufacturing process relies on CAD/CAM software to guide multi-axis machines in shaping metals, plastics, or composites with tight tolerances. The capability to produce intricate geometries and fine surface finishes makes CNC machining ideal for prototyping and low-to-medium volume production runs.
Material Compatibility: Injection Molding vs CNC Machining
Injection molding excels in processing thermoplastics and thermosetting polymers, allowing high-volume production with consistent material properties. CNC machining offers greater versatility across metals, plastics, and composites, making it ideal for low-volume runs or prototypes requiring precise tolerances. Material compatibility depends on project requirements, with injection molding favoring plastic parts and CNC machining accommodating a broader range of materials including aluminum, steel, and engineering plastics.
Production Speed and Turnaround Time
Injection molding offers significantly faster production speeds compared to CNC machining, especially for high-volume manufacturing with cycle times often under a minute per part. CNC machining provides more flexibility for low to medium production runs but typically has longer turnaround times due to its subtractive process and setup requirements. Manufacturers choose injection molding to optimize efficiency and reduce lead times when producing large quantities of consistent parts.
Cost Comparison: Upfront and Per Unit
Injection molding requires a higher upfront cost due to expensive mold creation, making it more cost-effective at large production volumes where the per unit cost decreases significantly. CNC machining involves lower initial setup costs but has higher per unit expenses, making it ideal for low to medium production runs. Evaluating volume requirements helps determine whether the fixed mold cost of injection molding or the variable machining expenses dominate overall project cost.
Design Flexibility and Prototyping Capabilities
Injection molding offers limited design flexibility due to the high cost and time required for mold creation, making it more suitable for high-volume production runs. CNC machining provides greater prototyping capabilities with rapid adjustments and the ability to produce complex, custom parts without extensive setup costs. Both methods serve distinct needs: injection molding excels in mass production efficiency, while CNC machining enables agile design iterations during the prototyping phase.
Surface Finish and Precision Differences
Injection molding offers smooth surface finishes with consistent texture due to the mold's polished cavity, ideal for high-volume production of complex shapes. CNC machining provides superior precision and tighter tolerances, allowing for intricate details and customized surface finishes through precise tool paths. While injection molding excels in repeatability and speed, CNC machining ensures enhanced dimensional accuracy and versatility in surface texture options.
Ideal Applications for Each Manufacturing Method
Injection molding is ideal for high-volume production of complex plastic parts with consistent precision and intricate geometries, especially in industries like automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. CNC machining excels in low- to medium-volume manufacturing, offering superior material versatility and tight tolerances for metal or plastic components, making it suitable for prototyping and custom parts. Selecting between injection molding and CNC machining depends on factors such as production volume, material type, dimensional accuracy, and design complexity.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Product Tool
Injection molding offers high-volume production with consistent precision, ideal for complex shapes and plastic materials, while CNC machining provides superior accuracy and flexibility for prototypes and low-volume runs, especially with metals and harder materials. Selecting the right process depends on factors like production volume, material type, design complexity, and budget constraints. For fast, cost-effective mass production of intricate plastic parts, injection molding is preferred; for detailed, customizable metal components, CNC machining is the optimal choice.
Injection Molding vs CNC Machining Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com