Cutting tools remove material from a workpiece through shearing, often used in processes like turning, milling, and drilling to create precise shapes and sizes. Shaping tools, on the other hand, remove material by applying force to form or contour the workpiece, commonly used in shaping, slotting, and broaching operations. Both tools are essential for manufacturing but differ in their methods of material removal and typical applications.
Table of Comparison
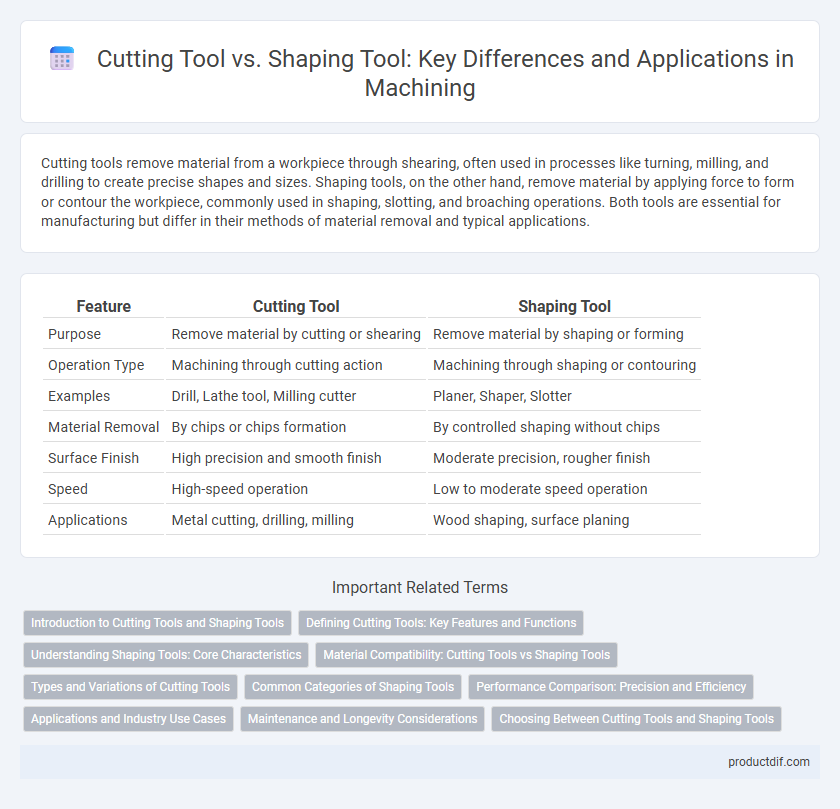
| Feature | Cutting Tool | Shaping Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Remove material by cutting or shearing | Remove material by shaping or forming |
| Operation Type | Machining through cutting action | Machining through shaping or contouring |
| Examples | Drill, Lathe tool, Milling cutter | Planer, Shaper, Slotter |
| Material Removal | By chips or chips formation | By controlled shaping without chips |
| Surface Finish | High precision and smooth finish | Moderate precision, rougher finish |
| Speed | High-speed operation | Low to moderate speed operation |
| Applications | Metal cutting, drilling, milling | Wood shaping, surface planing |
Introduction to Cutting Tools and Shaping Tools
Cutting tools remove material from a workpiece by shear deformation, commonly using edges or points made from hardened steel or carbide to achieve precision. Shaping tools, on the other hand, form or contour materials by applying force to mold or carve surfaces, typically utilizing blades or dies for metal shaping or woodworking. The distinction lies in cutting tools producing chips through material removal, while shaping tools alter the form by deformation without chip formation.
Defining Cutting Tools: Key Features and Functions
Cutting tools are designed to remove material from a workpiece through shear deformation, featuring sharp edges that facilitate precise and efficient material separation. These tools include drills, saws, and milling cutters, which operate by slicing or chipping to shape the final product. Their key functions involve enhancing surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and reducing machining time compared to shaping tools that primarily deform material without removing chips.
Understanding Shaping Tools: Core Characteristics
Shaping tools are designed to remove material by controlled linear or angular movements, producing specific geometric profiles on workpieces with high precision. These tools typically feature a single-point cutting edge and operate through reciprocating or rotary motions, making them ideal for machining flat surfaces, grooves, and complex contours. Unlike cutting tools that focus on material removal through shearing, shaping tools emphasize accuracy and surface finish in shaping metal or other materials in manufacturing processes.
Material Compatibility: Cutting Tools vs Shaping Tools
Cutting tools are designed primarily for hard materials such as metals, ceramics, and composites, utilizing sharp edges to remove material through shear deformation. Shaping tools, by contrast, are better suited for softer materials like wood, plastics, and soft metals, employing controlled displacement or removal of material with less force. Material compatibility directly influences tool selection, as cutting tools require high hardness and wear resistance, while shaping tools benefit from toughness and precision for delicate materials.
Types and Variations of Cutting Tools
Cutting tools include lathe tools, milling cutters, drills, and saw blades, each designed for material removal through processes like turning, milling, drilling, and sawing. Variations in cutting tools involve differences in geometry, material composition such as high-speed steel or carbide, and application-specific coatings that enhance durability and cutting efficiency. Shaping tools, in contrast, primarily involve tools like shaping machine cutters and gear shapers, which remove material by reciprocating motion to create precise shapes and profiles.
Common Categories of Shaping Tools
Shaping tools commonly include chisels, files, and broaches, each designed for specific material removal methods and surface finishes. Chisels enable precise cutting through manual or machine force, ideal for metal or wood shaping, while files smooth and refine surfaces with abrasive action. Broaches push or pull through workpieces to create complex internal or external profiles with high accuracy.
Performance Comparison: Precision and Efficiency
Cutting tools deliver superior precision through sharp edges designed for accurate material removal, enabling high-quality finishes with minimal waste. Shaping tools excel in efficiency by removing larger amounts of material in a single pass, making them suitable for rough shaping tasks but often sacrificing fine accuracy. The choice between cutting and shaping tools depends on whether precision or bulk material removal is the priority in the machining process.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Cutting tools such as drills, end mills, and saw blades are primarily used in industries like manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace for precise material removal to create parts and components. Shaping tools, including shaping machines and planers, are commonly applied in metalworking and woodworking industries to form shapes by removing material in controlled, repeated strokes. Both tools are essential in production lines, with cutting tools excelling in high-speed machining and shaping tools preferred for detailed contouring and finishing tasks.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Cutting tools require regular sharpening and proper coolant application to maintain edge precision and prevent overheating, which directly impacts their longevity. Shaping tools demand frequent inspection for wear on cutting edges and lubrication of moving parts to ensure consistent performance and avoid tool deformation. Proper maintenance schedules and timely replacement of worn components significantly extend the operational life of both cutting and shaping tools.
Choosing Between Cutting Tools and Shaping Tools
Choosing between cutting tools and shaping tools depends on the desired precision and material removal method. Cutting tools are ideal for high-speed operations requiring sharp edges to slice through materials, while shaping tools excel in producing intricate shapes and surfaces by removing material gradually. Understanding the specific machining requirements and material properties ensures optimal tool selection for efficiency and surface finish quality.
Cutting Tool vs Shaping Tool Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com