Lockout tagout provides a more comprehensive safety approach by physically isolating energy sources to prevent accidental machine startup, whereas tagout only uses warning tags without physical locking mechanisms. Lockout tagout is generally mandatory in higher-risk environments to ensure maximum protection for workers during maintenance. Tagout alone offers limited protection and is typically used when lockout devices cannot be applied safely or effectively.
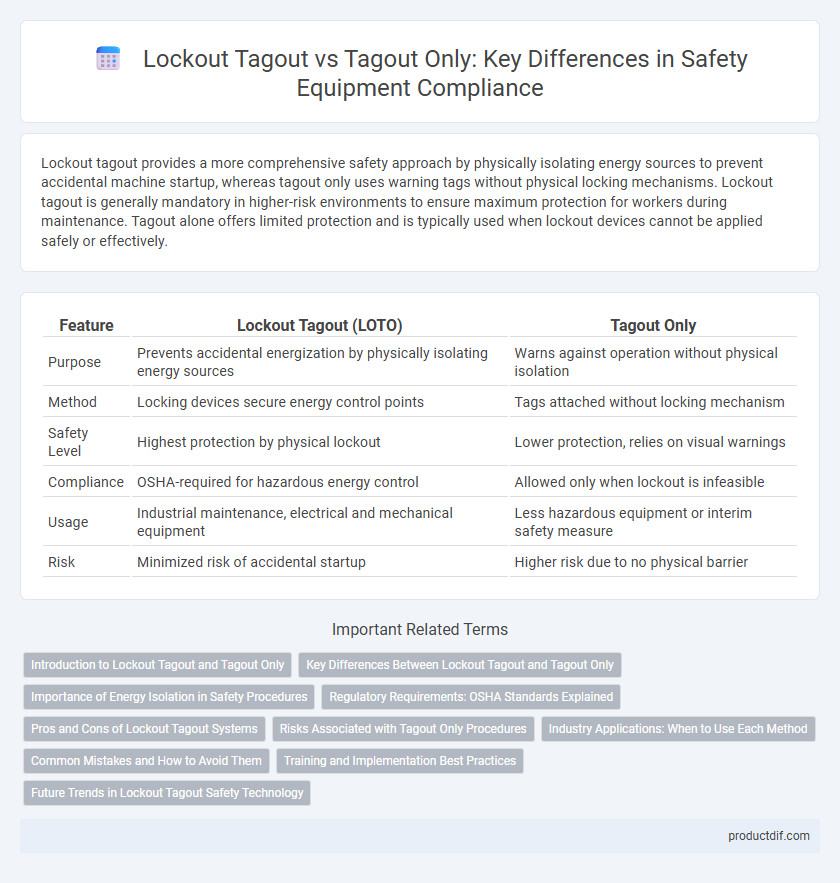
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lockout Tagout (LOTO) | Tagout Only |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents accidental energization by physically isolating energy sources | Warns against operation without physical isolation |
| Method | Locking devices secure energy control points | Tags attached without locking mechanism |
| Safety Level | Highest protection by physical lockout | Lower protection, relies on visual warnings |
| Compliance | OSHA-required for hazardous energy control | Allowed only when lockout is infeasible |
| Usage | Industrial maintenance, electrical and mechanical equipment | Less hazardous equipment or interim safety measure |
| Risk | Minimized risk of accidental startup | Higher risk due to no physical barrier |
Introduction to Lockout Tagout and Tagout Only
Lockout Tagout (LOTO) procedures involve physically isolating energy sources using locks and tags to prevent accidental machine startup, ensuring maximum worker safety during maintenance. Tagout Only systems rely solely on warning tags without the use of locks, which can be less secure and increase the risk of unintended energization. OSHA regulations prioritize Lockout Tagout for controlling hazardous energy, emphasizing its critical role in comprehensive workplace safety programs.
Key Differences Between Lockout Tagout and Tagout Only
Lockout Tagout (LOTO) involves physically locking energy-isolating devices to prevent machinery startup during maintenance, ensuring maximum safety by requiring a key or combination for removal. Tagout only uses warning tags to indicate hazardous energy isolation but does not physically restrain equipment, posing a higher risk if tags are ignored or removed prematurely. The key difference lies in Lockout Tagout providing a positive mechanical barrier, while Tagout relies solely on communication and compliance to prevent accidental energization.
Importance of Energy Isolation in Safety Procedures
Energy isolation is critical in safety procedures to prevent accidental startup or release of hazardous energy during maintenance. Lockout tagout (LOTO) ensures complete de-energization by physically locking energy sources, while tagout only relies on warning tags without physical locks, increasing risk. Proper energy isolation minimizes workplace injuries, ensuring compliance with OSHA regulations and safeguarding workers from electric shocks, mechanical hazards, and unexpected equipment activation.
Regulatory Requirements: OSHA Standards Explained
OSHA standards 29 CFR 1910.147 mandate lockout/tagout procedures to control hazardous energy during equipment maintenance, emphasizing the use of lockout to ensure physical isolation. Tagout-only programs are permitted only when lockout devices are not feasible but require stringent additional safety measures and employee training. Compliance with these regulations reduces workplace injuries and ensures adherence to federal safety laws.
Pros and Cons of Lockout Tagout Systems
Lockout tagout systems provide a more reliable method of energy isolation by physically locking machinery, reducing the risk of accidental startup and enhancing worker safety during maintenance. Tagout-only systems rely solely on warning tags without physically preventing equipment activation, which can lead to higher chances of human error and unintended energization. However, lockout tagout systems require additional hardware and training, potentially increasing costs and complexity compared to tagout-only procedures.
Risks Associated with Tagout Only Procedures
Tagout only procedures pose significant risks due to the absence of physical locks securing energy-isolating devices, increasing the likelihood of accidental equipment re-energization during maintenance. The reliance solely on tags, which serve as warnings but lack mechanical restraint, elevates the chances of human error and inadvertent machine startup, potentially causing severe injuries. Comprehensive lockout tagout protocols effectively mitigate these risks by combining physical lockout devices with visible tags, ensuring both mechanical isolation and clear communication of hazards.
Industry Applications: When to Use Each Method
Lockout tagout (LOTO) is essential in industries involving complex machinery and electrical systems where complete energy isolation is critical, such as manufacturing, construction, and utilities, to prevent accidental machine startup during maintenance. Tagout only is appropriate in low-risk applications with less complex equipment, commonly used in scenarios where energy isolation cannot be physically secured but warning tags serve as a visual deterrent, such as in service or inspection tasks. Understanding specific industry requirements and hazard risk levels ensures compliance with OSHA standards and maximizes worker safety during equipment servicing.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Common mistakes in Lockout Tagout (LOTO) procedures include failing to fully isolate energy sources and improperly securing locks and tags, leading to accidental machine startups. Tagout only systems often rely on tags without physical locks, increasing the risk of unauthorized removal and employee injury. To avoid these errors, implement comprehensive training on energy control protocols, ensure the use of durable, standardized tags and locks, and conduct regular audits to verify compliance with OSHA's LOTO requirements.
Training and Implementation Best Practices
Effective lockout/tagout (LOTO) training emphasizes hands-on practice with energy control devices to ensure workers understand the complete isolation process, including both locking and tagging mechanisms. Training programs should integrate scenario-based drills that highlight the risks of incomplete tagout-only procedures, reinforcing why physical locks are critical for preventing accidental machine startup. Implementation best practices involve clear communication, standardized procedures, and regular audit checks to verify compliance and competency in both lockout/tagout protocols.
Future Trends in Lockout Tagout Safety Technology
Emerging lockout tagout safety technology increasingly incorporates IoT-enabled devices that provide real-time monitoring and remote verification to enhance compliance and reduce human error. Advanced biometric authentication systems are being developed to ensure only authorized personnel can perform lockout tagout procedures, minimizing risks associated with tagout-only methods. Integration of augmented reality (AR) for training and maintenance support is transforming traditional lockout tagout practices, enabling safer, more efficient workflows.
Lockout tagout vs Tagout only Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com