A chemical splash suit provides protection against hazardous liquid chemicals by preventing skin exposure and contamination, making it essential for handling corrosive substances. A flame-resistant suit is designed to resist ignition and self-extinguish, reducing burn injuries in environments with fire hazards or electrical arcs. Choosing between the two depends on the specific risk factors, with chemical splash suits suited for chemical exposure and flame-resistant suits ideal for fire-related dangers.
Table of Comparison
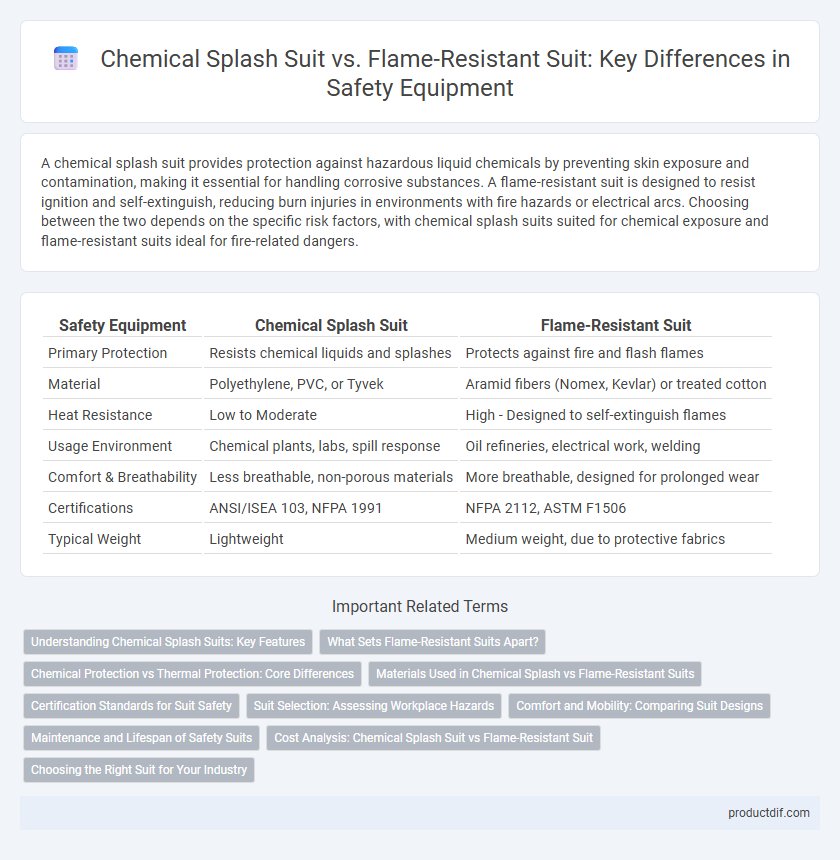
| Safety Equipment | Chemical Splash Suit | Flame-Resistant Suit |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Protection | Resists chemical liquids and splashes | Protects against fire and flash flames |
| Material | Polyethylene, PVC, or Tyvek | Aramid fibers (Nomex, Kevlar) or treated cotton |
| Heat Resistance | Low to Moderate | High - Designed to self-extinguish flames |
| Usage Environment | Chemical plants, labs, spill response | Oil refineries, electrical work, welding |
| Comfort & Breathability | Less breathable, non-porous materials | More breathable, designed for prolonged wear |
| Certifications | ANSI/ISEA 103, NFPA 1991 | NFPA 2112, ASTM F1506 |
| Typical Weight | Lightweight | Medium weight, due to protective fabrics |
Understanding Chemical Splash Suits: Key Features
Chemical splash suits provide critical protection against hazardous liquid exposure, featuring impermeable materials like polyethylene or PVC to prevent chemical penetration. These suits often include sealed seams, adjustable closures, and integrated hoods to ensure comprehensive coverage and resistance to splashes from acids, solvents, and other corrosive substances. Flame-resistant suits, by contrast, are designed to resist ignition and reduce burn injuries but lack the chemical impermeability essential in splash protection.
What Sets Flame-Resistant Suits Apart?
Flame-resistant suits are specifically designed to protect against heat and fire hazards, utilizing materials like Nomex or Kevlar that self-extinguish when exposed to flames. Unlike chemical splash suits, which provide a barrier against hazardous liquids and chemicals, flame-resistant suits prioritize thermal protection and minimize burn injuries. Their durability under extreme heat and compliance with industry safety standards set them apart in environments with fire and electrical risks.
Chemical Protection vs Thermal Protection: Core Differences
Chemical splash suits provide essential protection against hazardous liquid chemicals by using impermeable materials that prevent skin contact and contamination. Flame-resistant suits are designed to resist ignition and self-extinguish, offering crucial thermal protection against heat, flames, and flash fires. Understanding the core differences between chemical protection and thermal protection is vital for selecting the appropriate safety equipment in hazardous environments.
Materials Used in Chemical Splash vs Flame-Resistant Suits
Chemical splash suits are typically made from non-porous materials such as PVC, rubber, or neoprene, designed to prevent hazardous liquid penetration. Flame-resistant suits utilize fabrics like Nomex, Kevlar, or treated cotton that resist ignition and self-extinguish when exposed to high temperatures. The material choice directly influences protective capabilities against chemical splashes or fire hazards in industrial environments.
Certification Standards for Suit Safety
Chemical splash suits are typically certified under standards such as ASTM F903 or EN 14605, focusing on resistance to hazardous liquid penetration and splash protection. Flame-resistant suits comply with certifications like NFPA 2112 or ISO 11612, ensuring protection against heat and flame exposure. Proper certification guarantees that each suit type meets specific safety performance criteria crucial for occupational hazard mitigation.
Suit Selection: Assessing Workplace Hazards
Selecting the right safety suit requires a thorough assessment of workplace hazards, considering chemical exposure levels and fire risks. Chemical splash suits provide protection against hazardous liquid splashes and corrosive substances, while flame-resistant suits are designed to withstand heat and open flames without igniting. Evaluating the specific environmental dangers ensures optimal protection, minimizing injury and enhancing worker safety compliance.
Comfort and Mobility: Comparing Suit Designs
Chemical splash suits are typically made from lightweight, flexible materials like polyethylene or PVC, enhancing comfort and mobility during extended wear. Flame-resistant suits use heavier, often layered fabrics such as Nomex or Kevlar to provide thermal protection, which can restrict movement and increase heat retention. Workers needing high dexterity and freedom often prefer chemical splash suits, while flame-resistant suits prioritize protective performance over wearability.
Maintenance and Lifespan of Safety Suits
Chemical splash suits require thorough rinsing with water and decontamination after each use to prevent chemical degradation, while flame-resistant suits need regular inspection for thermal damage and cleaning according to manufacturer guidelines to maintain fabric integrity. The lifespan of chemical splash suits varies depending on exposure frequency and chemical concentration, typically lasting several months to a year, whereas flame-resistant suits can last up to five years with proper care and limited exposure to harsh environments. Proper maintenance extends the service life of both suit types and ensures optimal protection against chemical splashes or fire hazards.
Cost Analysis: Chemical Splash Suit vs Flame-Resistant Suit
Chemical splash suits typically cost less due to simpler materials designed for liquid protection, while flame-resistant suits involve advanced fibers like Nomex or Kevlar, increasing their price. Maintenance expenses are generally higher for flame-resistant suits, requiring specialized cleaning to preserve fire-retardant properties, contrasting with the easier maintenance of chemical splash suits. When budgeting for safety gear, organizations must weigh initial purchase prices against long-term care costs and the specific hazard risks present in their work environment.
Choosing the Right Suit for Your Industry
Selecting the correct safety suit depends on industry-specific hazards; chemical splash suits are designed with impermeable materials to protect against hazardous liquid exposures in industries like pharmaceuticals and laboratories. Flame-resistant suits use heat-resistant fibers to provide critical protection against thermal and flash fire risks, making them essential for industries such as oil and gas, electrical utilities, and welding operations. Assessing workplace exposure to chemicals or fire hazards and reviewing compliance with OSHA and NFPA standards ensures the optimal safety gear choice for industrial environments.
Chemical splash suit vs Flame-resistant suit Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com