Dust masks provide basic protection against airborne particles like dust and pollen, making them suitable for low-risk environments. Gas masks offer comprehensive defense against toxic gases, vapors, and airborne pathogens, ideal for hazardous or contaminated settings. Choosing the right safety equipment for pets depends on the specific environmental threats and required level of respiratory protection.
Table of Comparison
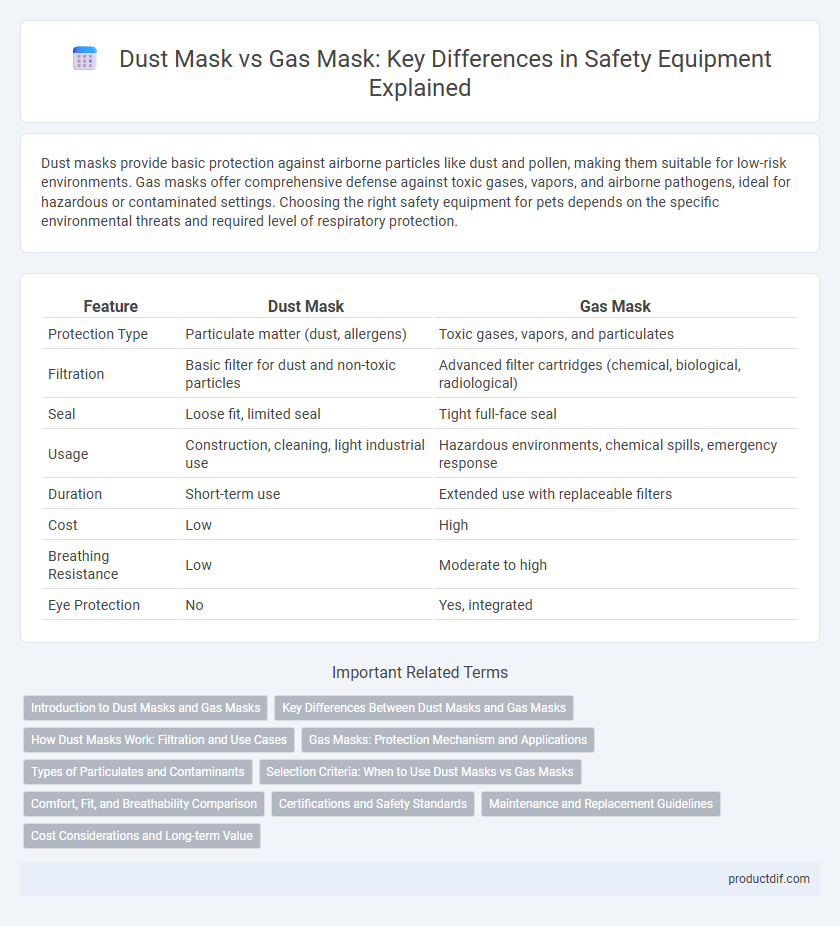
| Feature | Dust Mask | Gas Mask |
|---|---|---|
| Protection Type | Particulate matter (dust, allergens) | Toxic gases, vapors, and particulates |
| Filtration | Basic filter for dust and non-toxic particles | Advanced filter cartridges (chemical, biological, radiological) |
| Seal | Loose fit, limited seal | Tight full-face seal |
| Usage | Construction, cleaning, light industrial use | Hazardous environments, chemical spills, emergency response |
| Duration | Short-term use | Extended use with replaceable filters |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Breathing Resistance | Low | Moderate to high |
| Eye Protection | No | Yes, integrated |
Introduction to Dust Masks and Gas Masks
Dust masks are designed primarily to protect the wearer from particulate matter such as dust, allergens, and other non-toxic airborne particles, commonly used in construction, woodworking, and cleaning environments. Gas masks provide a higher level of protection by filtering out toxic gases, vapors, and airborne pathogens through specialized filters, making them essential in hazardous chemical, biological, and industrial settings. Both masks serve distinct purposes in respiratory protection, with dust masks offering basic filtration and gas masks equipped for comprehensive defense against chemical and biological threats.
Key Differences Between Dust Masks and Gas Masks
Dust masks primarily protect against airborne particles such as dust, pollen, and other non-toxic particulates by filtering physical matter from the air. Gas masks provide a higher level of protection by filtering out hazardous gases, vapors, and chemical agents using activated carbon or specialized filters. Key differences include the type of contaminants filtered, the filtration technology employed, and the intended use environments, with gas masks being essential for chemical exposure and dust masks suitable for general particle filtration.
How Dust Masks Work: Filtration and Use Cases
Dust masks work by filtering out airborne particles through layers of non-woven fabric designed to trap dust, pollen, and other particulates, providing respiratory protection in environments with non-toxic dust. They rely primarily on mechanical filtration to block larger particles and electrostatic attraction to capture smaller particles, making them suitable for construction sites, woodworking, and general dust exposure. Dust masks are not designed to filter harmful gases or vapors, which distinguishes their use cases from gas masks that protect against toxic chemical hazards.
Gas Masks: Protection Mechanism and Applications
Gas masks provide protection by filtering out chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear (CBRN) contaminants through activated charcoal and specialized filter cartridges, preventing harmful particles and gases from entering the respiratory system. These masks create a sealed environment around the face, ensuring contaminants do not bypass the filtration system. Commonly used in industrial settings, military operations, and hazardous material handling, gas masks are essential for safeguarding against airborne toxins and respiratory hazards.
Types of Particulates and Contaminants
Dust masks are designed to filter out non-toxic particulates such as dust, pollen, and other airborne particles commonly found in construction and woodworking environments. Gas masks provide protection against toxic gases, vapors, and chemical contaminants by using activated charcoal filters and are essential in industrial, chemical spill, or hazardous material scenarios. Choosing between a dust mask and a gas mask depends on the specific types of particulates and airborne contaminants present in the environment.
Selection Criteria: When to Use Dust Masks vs Gas Masks
Dust masks are suitable for protection against non-toxic dust particles, allergens, and limited airborne particulates commonly found in construction, woodworking, or cleaning tasks. Gas masks are essential in environments with hazardous gases, chemical vapors, or toxic fumes, such as industrial settings, chemical handling, or emergency response situations. Selecting the right mask depends on the nature of airborne hazards, required filtration efficiency, and specific exposure risks to ensure optimal respiratory protection.
Comfort, Fit, and Breathability Comparison
Dust masks offer lightweight comfort and a looser fit, making them suitable for short-term use in low-hazard environments, but their breathability may be limited under heavy particulate loads. Gas masks provide a tighter seal essential for protection against toxic gases and vapors, but this secure fit can reduce comfort during extended wear and increase breathing resistance due to activated carbon filters. Optimal selection depends on balancing the need for airtight protection with the user's ability to tolerate reduced breathability and fit constraints.
Certifications and Safety Standards
Dust masks generally comply with standards such as NIOSH N95 or EN 149 FFP2, providing filtration against non-oil-based particles and offering protection primarily from dust and allergens. Gas masks, certified under more stringent conditions like NIOSH CBRN (Chemical, Biological, Radiological, and Nuclear) standards or EN 136/EN 14387, are designed to protect against hazardous gases, vapors, and particulates through specialized cartridges and filters. Choosing the correct mask requires understanding these certifications to ensure compliance with safety regulations and effective protection based on environmental hazards.
Maintenance and Replacement Guidelines
Dust masks require frequent replacement after exposure to high particulate levels or when breathing becomes difficult, typically every 8 hours of use. Gas masks need thorough maintenance including filter replacement based on manufacturer guidelines, often every 6 months or after contamination exposure, and regular inspections of seals and valves to ensure airtight protection. Proper cleaning and storage in a dry, cool environment prolong the lifespan and effectiveness of both dust and gas masks.
Cost Considerations and Long-term Value
Dust masks generally have a lower initial cost compared to gas masks, making them more affordable for short-term use in environments with minimal particulate hazards. Gas masks, though more expensive upfront, provide superior protection against a broader range of contaminants and offer greater long-term value in hazardous environments due to their durability and replaceable filters. Investing in gas masks reduces the need for frequent replacements and enhances safety, ultimately proving cost-effective for sustained exposure scenarios.
Dust mask vs Gas mask Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com