Class G helmets provide limited impact protection with low-voltage electrical insulation up to 2,200 volts, making them suitable for general construction work where electrical hazards are minimal. Class E helmets offer higher electrical insulation, protecting against high-voltage hazards up to 20,000 volts, which is essential for electricians and workers exposed to significant electrical risks. Choosing between Class G and Class E helmets depends on the specific work environment and the level of electrical hazard present.
Table of Comparison
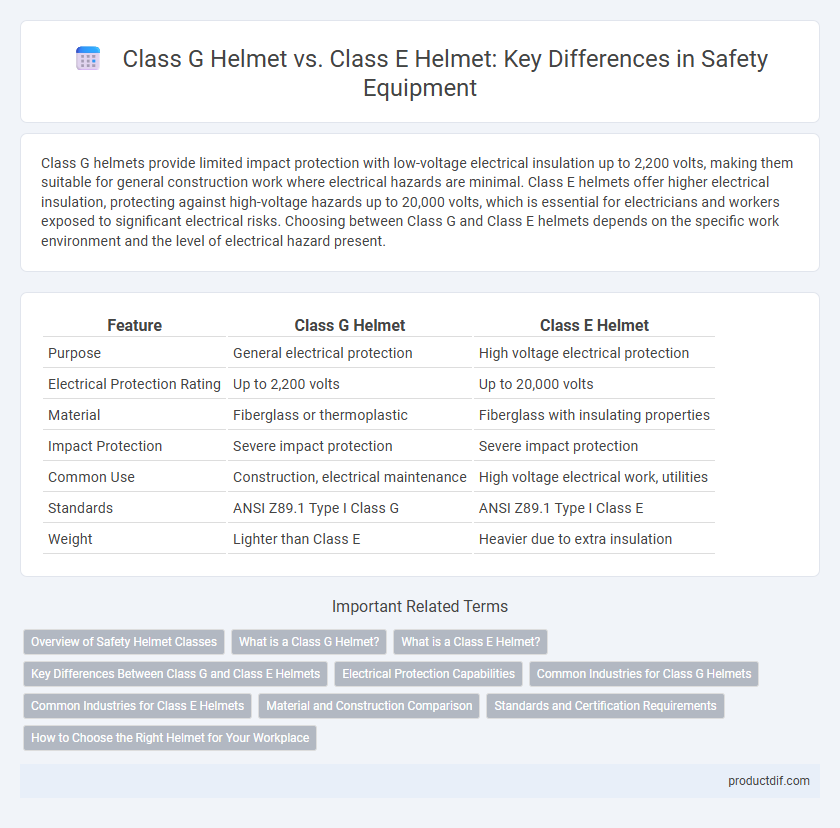
| Feature | Class G Helmet | Class E Helmet |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | General electrical protection | High voltage electrical protection |
| Electrical Protection Rating | Up to 2,200 volts | Up to 20,000 volts |
| Material | Fiberglass or thermoplastic | Fiberglass with insulating properties |
| Impact Protection | Severe impact protection | Severe impact protection |
| Common Use | Construction, electrical maintenance | High voltage electrical work, utilities |
| Standards | ANSI Z89.1 Type I Class G | ANSI Z89.1 Type I Class E |
| Weight | Lighter than Class E | Heavier due to extra insulation |
Overview of Safety Helmet Classes
Class G helmets are designed to provide low-voltage electrical protection up to 2,200 volts, commonly used in utility and construction industries, whereas Class E helmets offer high-voltage protection up to 20,000 volts, ideal for electrical workers exposed to higher voltage hazards. Both helmets meet specific ANSI/ISEA Z89.1 standards, ensuring impact resistance and penetration protection tailored to different electrical environments. Choosing the appropriate helmet class depends on the voltage risk level and job site safety requirements to minimize electrical shock and head injury.
What is a Class G Helmet?
A Class G helmet is designed specifically for electrical work, providing impact protection and limited voltage protection up to 2,200 volts. It meets ANSI/ISEA Z89.1 standards and is commonly used by utility workers and electricians. Unlike Class E helmets, which offer higher voltage protection, Class G helmets balance electrical safety with lightweight comfort for general industrial use.
What is a Class E Helmet?
A Class E helmet is designed to provide electrical insulation and protect workers from high-voltage electrical hazards up to 20,000 volts. It is made from dielectric materials that prevent electric current from passing through, ensuring safety in environments with energized electrical components. Class E helmets are essential in industries such as electrical utility work and construction where workers face exposure to electrical shocks.
Key Differences Between Class G and Class E Helmets
Class G helmets provide impact protection and limited electrical protection up to 2,200 volts, making them suitable for general construction and utility work. Class E helmets offer higher electrical resistance, protecting against voltages up to 20,000 volts, ideal for heavy electrical tasks and utility linemen. Both helmets comply with ANSI/ISEA Z89.1 standards but vary significantly in their electrical protection capabilities.
Electrical Protection Capabilities
Class G helmets provide limited electrical protection up to 2,200 volts, suitable for low-voltage environments and general industrial use. Class E helmets offer superior electrical protection, rated for exposure to high voltage up to 20,000 volts, ideal for electrical utility work and environments with significant electrical hazards. The choice between Class G and Class E helmets depends on the specific voltage exposure risks present in the workplace.
Common Industries for Class G Helmets
Class G helmets, designed to provide limited voltage protection up to 2,200 volts, are commonly used in construction, manufacturing, and light electrical work environments where impact resistance is critical but high voltage exposure is minimal. These helmets are preferred in industries such as utilities, telecommunications, and general labor where head protection against falling objects and minor electrical hazards is essential. In contrast, Class E helmets offer higher voltage protection and are typically reserved for heavy electrical and utility work involving exposure to voltages up to 20,000 volts.
Common Industries for Class E Helmets
Class E helmets are extensively used in electrical utilities, telecommunications, and construction industries where high-voltage electrical protection is essential. These helmets provide dielectric protection up to 20,000 volts, making them a critical safety component for workers exposed to electrical hazards. Compared to Class G helmets, which offer limited electrical protection, Class E helmets ensure higher safety standards in environments with stringent electrical safety requirements.
Material and Construction Comparison
Class G helmets are constructed with a high-density polyethylene (HDPE) shell designed to provide impact protection and limited electrical insulation up to 2,200 volts, featuring a suspension system that absorbs shock. Class E helmets utilize a fiberglass or advanced thermoplastic composite shell engineered for higher electrical insulation performance, rated up to 20,000 volts, with a multi-layer construction enhancing durability and electrical resistance. The material differences in Class G and Class E helmets directly influence their electrical protection capabilities and overall durability, tailoring each to specific safety requirements in industrial environments.
Standards and Certification Requirements
Class G helmets conform to ANSI/ISEA Z89.1 standards for general industrial use, offering impact protection and limited voltage protection up to 2,200 volts. Class E helmets meet stricter ANSI/ISEA Z89.1 standards for electrical environments, providing insulation against high voltage up to 20,000 volts. Both helmet classes require rigorous testing to ensure compliance with impact resistance, penetration, and electrical insulation criteria for workplace safety.
How to Choose the Right Helmet for Your Workplace
Selecting the right helmet for your workplace depends on the specific electrical hazard levels and industry standards; Class G helmets provide protection against low-voltage electrical conductors up to 2,200 volts, ideal for general construction and utility work. In contrast, Class E helmets offer higher protection, rated for electrical exposure up to 20,000 volts, suitable for electrical linemen and workers in high-voltage environments. Evaluate the voltage exposure risk, compliance with OSHA and ANSI standards, and the nature of work tasks to determine the appropriate helmet class for optimal safety.
Class G helmet vs Class E helmet Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com