Class G helmets offer limited protection against electrical hazards and moderate impact, making them suitable for general construction and utility work, while Class C helmets prioritize comfort and ventilation but provide no electrical protection, ideal for non-electrical environments. Choosing between Class G and Class C helmets depends on the specific safety requirements of the job site, especially regarding electrical exposure risks. Proper helmet selection ensures optimum safety for workers handling potentially hazardous conditions.
Table of Comparison
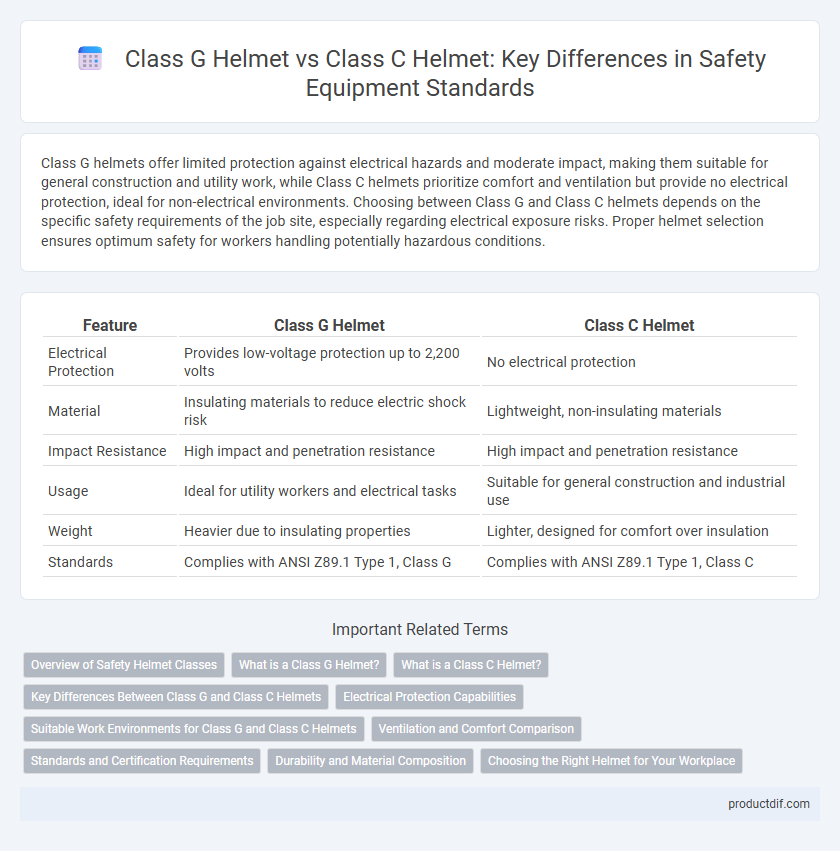
| Feature | Class G Helmet | Class C Helmet |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Protection | Provides low-voltage protection up to 2,200 volts | No electrical protection |
| Material | Insulating materials to reduce electric shock risk | Lightweight, non-insulating materials |
| Impact Resistance | High impact and penetration resistance | High impact and penetration resistance |
| Usage | Ideal for utility workers and electrical tasks | Suitable for general construction and industrial use |
| Weight | Heavier due to insulating properties | Lighter, designed for comfort over insulation |
| Standards | Complies with ANSI Z89.1 Type 1, Class G | Complies with ANSI Z89.1 Type 1, Class C |
Overview of Safety Helmet Classes
Class G helmets provide limited voltage protection up to 2,200 volts and offer impact resistance for general construction and utility work, making them suitable for electrical and mechanical environments. Class C helmets lack electrical insulation but deliver lightweight comfort and ventilation, ideal for environments with minimal electrical hazards. Understanding these distinctions ensures proper safety compliance and optimal protection tailored to workplace requirements.
What is a Class G Helmet?
A Class G helmet, also known as General helmet, is designed to provide impact protection and limited voltage protection up to 2,200 volts. It is commonly used in industries such as construction, electrical work, and utility services where there is a risk of electrical shock and falling objects. Class G helmets are tested to meet the ANSI/ISEA Z89.1 standard requirements for electrical insulation and impact resistance, making them suitable for moderate voltage environments.
What is a Class C Helmet?
A Class C helmet is a lightweight safety helmet designed primarily for impact protection without electrical insulation, commonly used in construction and manufacturing environments. Unlike Class G helmets, which provide limited voltage protection up to 2,200 volts, Class C helmets are made from aluminum or other metals that do not offer electrical resistance. These helmets excel in protecting the head from falling objects and bumps but should not be used in environments with electrical hazards.
Key Differences Between Class G and Class C Helmets
Class G helmets are designed to provide general impact protection and limited voltage protection up to 2,200 volts, making them suitable for electrical work environments. Class C helmets offer lightweight comfort and ventilation but do not provide electrical insulation, focusing primarily on impact and penetration resistance. The key difference lies in Class G helmets' electrical protection, which is absent in Class C helmets, making Class G essential for workers exposed to electrical hazards.
Electrical Protection Capabilities
Class G helmets provide impact protection and limited voltage protection up to 2,200 volts, making them suitable for electrical workers exposed to low-voltage environments. Class C helmets lack electrical insulation and do not offer any voltage protection, focusing primarily on impact and penetration resistance. Choosing a Class G helmet is essential for jobs involving potential contact with energized circuits, while Class C helmets are better suited for non-electrical work environments.
Suitable Work Environments for Class G and Class C Helmets
Class G helmets are designed for electric utility workers, providing impact protection and limited voltage protection up to 2,200 volts, making them suitable for electrical and construction environments where contact with low-voltage conductors is possible. Class C helmets offer lightweight comfort without electrical insulation, ideal for environments like manufacturing or general construction where impact protection is necessary but electrical hazards are minimal. Choosing between Class G and Class C helmets depends on the specific workplace electrical risks and required safety standards.
Ventilation and Comfort Comparison
Class G helmets provide limited ventilation with a focus on impact protection and electrical insulation, resulting in moderate comfort for extended wear. Class C helmets feature enhanced ventilation systems with multiple air vents, promoting better airflow and increased comfort in hot or strenuous environments. Workers prioritizing breathability and heat dissipation often prefer Class C helmets for improved comfort during long shifts.
Standards and Certification Requirements
Class G helmets comply with ANSI/ISEA Z89.1 standards, providing impact and penetration protection with limited electrical protection up to 2,200 volts. Class C helmets meet the same ANSI Z89.1 standard but lack electrical protection, focusing primarily on impact resistance and lightweight comfort. Both classes require rigorous testing for impact absorption, penetration resistance, and electrical insulation criteria where applicable to ensure workplace safety compliance.
Durability and Material Composition
Class G helmets are made from fiberglass or reinforced plastic, providing robust durability against impact and penetration, and are designed to reduce electrical exposure up to 2,200 volts. Class C helmets, typically composed of lightweight aluminum or plastic, offer less durability and minimal electrical protection but excel in comfort and ventilation. Durability-wise, Class G helmets outperform Class C helmets due to their more resilient material composition and higher safety standards for electrical insulation.
Choosing the Right Helmet for Your Workplace
Class G helmets provide impact protection and limited voltage resistance up to 2,200 volts, making them ideal for electrical and construction environments where low-voltage hazards exist. Class C helmets offer lightweight comfort with impact protection but lack electrical insulation, suitable for industries prioritizing physical safety without electrical exposure, such as manufacturing or warehousing. Selecting the right helmet depends on evaluating workplace hazards, ensuring compliance with ANSI/ISEA Z89.1 standards, and prioritizing both head protection and electrical safety requirements.
Class G helmet vs Class C helmet Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com