Hearing protection for pets reduces noise-induced stress and potential hearing damage during loud events like fireworks or thunderstorms, using earmuffs or noise-canceling devices tailored for animals. Eye protection shields pets from debris, UV rays, and harsh environmental elements with goggles or protective eyewear designed to fit comfortably. Both types of safety equipment are essential for protecting sensory health, but choosing between hearing protection and eye protection depends on the specific environmental risks and activities the pet will encounter.
Table of Comparison
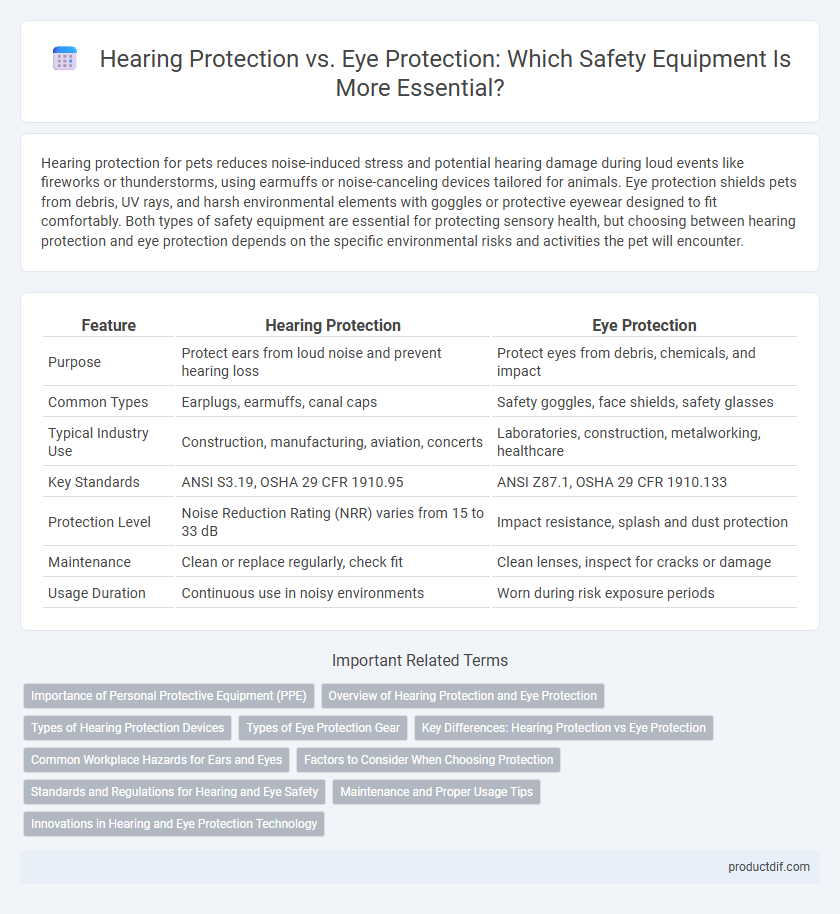
| Feature | Hearing Protection | Eye Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protect ears from loud noise and prevent hearing loss | Protect eyes from debris, chemicals, and impact |
| Common Types | Earplugs, earmuffs, canal caps | Safety goggles, face shields, safety glasses |
| Typical Industry Use | Construction, manufacturing, aviation, concerts | Laboratories, construction, metalworking, healthcare |
| Key Standards | ANSI S3.19, OSHA 29 CFR 1910.95 | ANSI Z87.1, OSHA 29 CFR 1910.133 |
| Protection Level | Noise Reduction Rating (NRR) varies from 15 to 33 dB | Impact resistance, splash and dust protection |
| Maintenance | Clean or replace regularly, check fit | Clean lenses, inspect for cracks or damage |
| Usage Duration | Continuous use in noisy environments | Worn during risk exposure periods |
Importance of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is essential for safeguarding workers from hazards in noisy and high-risk environments, with hearing protection preventing noise-induced hearing loss and eye protection guarding against flying debris and chemical splashes. Proper selection and consistent use of PPE reduce workplace injuries, ensuring compliance with OSHA regulations and enhancing overall safety. Employers must prioritize training and enforcement to maximize the effectiveness of hearing and eye protection in industrial settings.
Overview of Hearing Protection and Eye Protection
Hearing protection devices, such as earplugs and earmuffs, are designed to reduce noise exposure and prevent hearing loss in noisy environments, while eye protection, including safety glasses and goggles, safeguards against chemical splashes, debris, and impact hazards. Both types of protective equipment are essential in industrial, construction, and laboratory settings to ensure worker safety by addressing distinct sensory risks. Proper selection and use of hearing and eye protection depend on the specific environmental hazards to effectively minimize injury.
Types of Hearing Protection Devices
Hearing protection devices include earmuffs, earplugs, and custom-molded inserts designed to reduce exposure to harmful noise levels. Earmuffs cover the entire ear and provide a consistent noise reduction rating (NRR), while earplugs are inserted into the ear canal for portability and comfort in various work environments. Custom-molded inserts offer tailored protection for long-term use, ensuring a secure fit and effective attenuation of hazardous noise frequencies.
Types of Eye Protection Gear
Types of eye protection gear include safety glasses, goggles, face shields, and welding helmets, each designed to guard against specific hazards like impact, chemical splashes, or intense light. Safety glasses provide basic protection with impact-resistant lenses, while goggles create a seal to prevent liquid or dust exposure. Face shields offer full-face coverage from flying debris, and welding helmets protect from harmful UV and infrared radiation during welding processes.
Key Differences: Hearing Protection vs Eye Protection
Hearing protection primarily guards against noise-induced hearing loss by using earplugs or earmuffs to reduce sound exposure, while eye protection shields against physical, chemical, and biological hazards through safety goggles or face shields. The materials and design of hearing protection target auditory risk mitigation, whereas eye protection focuses on preventing injuries like splashes, debris, or impact to the eyes. Both are essential in industrial environments but serve distinct protective functions based on the type of hazard encountered.
Common Workplace Hazards for Ears and Eyes
Common workplace hazards for ears include prolonged exposure to loud machinery, which can lead to noise-induced hearing loss, while hazardous eye conditions often arise from flying debris, chemical splashes, and intense light exposure such as welding arcs. Hearing protection devices like earmuffs and earplugs reduce the risk of auditory damage by dampening harmful noise levels, whereas safety goggles and face shields prevent eye injuries by providing a barrier against physical and chemical hazards. Proper selection and consistent use of hearing and eye protection tailored to specific workplace risks significantly decrease the incidence of occupational hearing and eye injuries.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Protection
Choosing between hearing protection and eye protection depends on the specific hazards present in the work environment, such as exposure to loud noise levels above 85 decibels or the risk of flying debris and chemical splashes. Comfort, fit, and compliance with industry safety standards like OSHA and ANSI play critical roles in ensuring consistent use and effectiveness of the protective gear. The duration of exposure and compatibility with other personal protective equipment (PPE) also influence the optimal selection of hearing or eye protection.
Standards and Regulations for Hearing and Eye Safety
Hearing protection devices must comply with standards such as ANSI S3.19 and OSHA regulations 29 CFR 1910.95, ensuring attenuation of harmful noise levels above 85 decibels. Eye protection equipment follows ANSI Z87.1 standards and OSHA 29 CFR 1910.133 regulations, specifying impact resistance, coverage, and optical clarity essential for preventing eye injuries. Both hearing and eye safety require adherence to these regulatory frameworks to maintain workplace compliance and protect workers from sensory damage.
Maintenance and Proper Usage Tips
Regularly clean hearing protection devices with mild soap and water to prevent ear infections and ensure clear sound attenuation, while replacing worn ear cushions or filters to maintain effectiveness. For eye protection, disinfect lenses with approved solutions to avoid scratches and fogging, and inspect frames for cracks or damage that compromise safety. Proper storage in a clean, dry place prolongs the lifespan of both hearing and eye protection equipment, ensuring consistent performance during use.
Innovations in Hearing and Eye Protection Technology
Innovations in hearing protection technology feature advanced noise-canceling materials and smart sensors that adapt to sound levels, enhancing user comfort and situational awareness. Eye protection advancements include impact-resistant lenses with anti-fog and blue light filtering capabilities, improving safety and visual clarity in diverse environments. Both fields integrate lightweight, ergonomic designs and connectivity features for real-time monitoring and improved user interaction on worksites.
Hearing protection vs Eye protection Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com