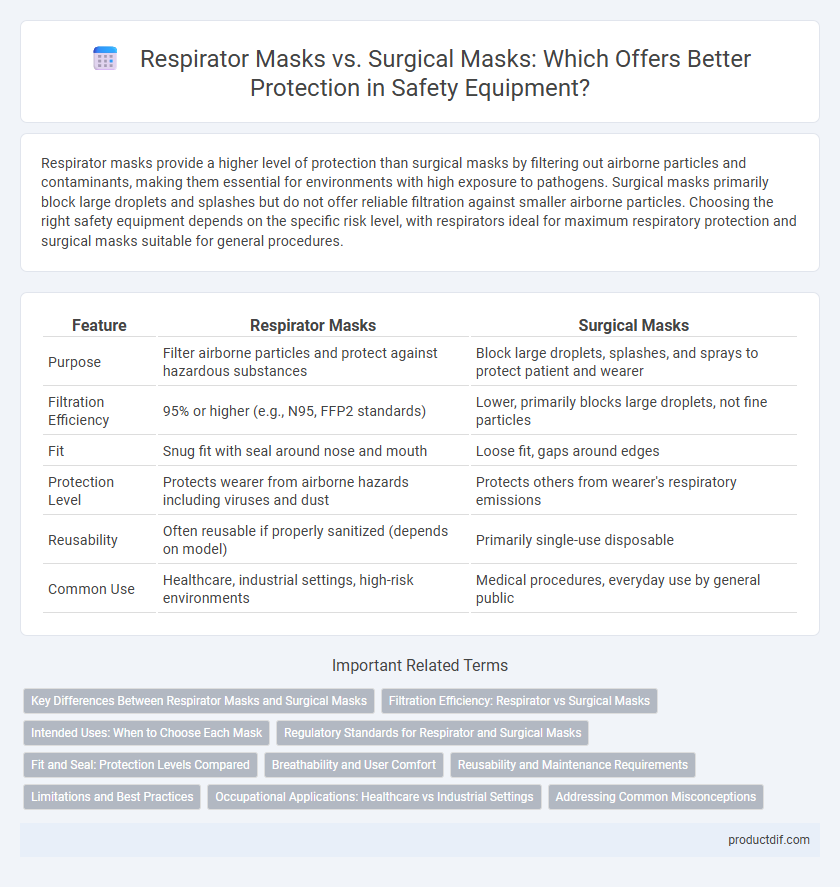
Respirator masks provide a higher level of protection than surgical masks by filtering out airborne particles and contaminants, making them essential for environments with high exposure to pathogens. Surgical masks primarily block large droplets and splashes but do not offer reliable filtration against smaller airborne particles. Choosing the right safety equipment depends on the specific risk level, with respirators ideal for maximum respiratory protection and surgical masks suitable for general procedures.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Respirator Masks | Surgical Masks |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Filter airborne particles and protect against hazardous substances | Block large droplets, splashes, and sprays to protect patient and wearer |
| Filtration Efficiency | 95% or higher (e.g., N95, FFP2 standards) | Lower, primarily blocks large droplets, not fine particles |
| Fit | Snug fit with seal around nose and mouth | Loose fit, gaps around edges |
| Protection Level | Protects wearer from airborne hazards including viruses and dust | Protects others from wearer's respiratory emissions |
| Reusability | Often reusable if properly sanitized (depends on model) | Primarily single-use disposable |
| Common Use | Healthcare, industrial settings, high-risk environments | Medical procedures, everyday use by general public |
Key Differences Between Respirator Masks and Surgical Masks
Respirator masks, such as N95 and FFP2, provide a tight seal and filter at least 95% of airborne particles, offering protection against airborne contaminants including viruses and fine dust. Surgical masks are loose-fitting barriers primarily designed to protect others from the wearer's respiratory emissions and provide limited filtration of large droplets or splashes. Respirators meet strict regulatory standards for filtration efficiency and fit testing, while surgical masks are primarily intended for fluid resistance and source control in medical settings.
Filtration Efficiency: Respirator vs Surgical Masks
Respirator masks, such as N95 or FFP2, provide filtration efficiency of at least 95% against airborne particles, including viruses and fine dust, due to their tight fit and advanced filter materials. Surgical masks offer lower filtration efficiency, typically filtering larger respiratory droplets rather than fine aerosols, with filtration rates ranging from 60% to 80%. The superior filtration performance of respirator masks makes them essential for healthcare workers exposed to airborne pathogens, while surgical masks are primarily designed to protect others from wearer-generated droplets.
Intended Uses: When to Choose Each Mask
Respirator masks, such as N95 or FFP2, are designed for high filtration efficiency and protection against airborne particles, making them ideal in industrial settings or during exposure to contagious diseases like tuberculosis or COVID-19. Surgical masks are primarily intended to protect others from the wearer's respiratory emissions and are suitable for routine medical procedures and general public use to reduce the spread of droplets. Choosing the appropriate mask depends on the level of exposure risk, with respirators recommended for close contact with infected patients or hazardous environments, while surgical masks suffice for basic infection control in low-risk situations.
Regulatory Standards for Respirator and Surgical Masks
Respirator masks, such as N95s, must comply with rigorous regulatory standards like NIOSH certification in the United States, ensuring a minimum filtration efficiency of 95% against airborne particles. Surgical masks are regulated by the FDA and must meet ASTM standards, focusing on fluid resistance, bacterial filtration efficiency, and breathability. These distinct regulatory frameworks reflect the different protective purposes of respirators, designed for airborne hazards, and surgical masks, intended primarily for splash protection and source control.
Fit and Seal: Protection Levels Compared
Respirator masks like N95s provide a tight fit and seal around the face, effectively filtering out at least 95% of airborne particles, including viruses and fine dust. Surgical masks are looser fitting and primarily block large droplets, offering lower protection against airborne pathogens due to gaps around the edges. Proper fit testing and seal checks are critical for respirators to ensure maximum respiratory protection in high-risk environments.
Breathability and User Comfort
Respirator masks such as N95s offer superior filtration but typically have lower breathability, leading to increased heat and moisture buildup during extended wear. Surgical masks provide better breathability and user comfort by allowing more airflow, making them preferable for non-hazardous environments and longer use. Selecting masks involves balancing the need for protection against particulate matter with the wearer's endurance and comfort during prolonged periods.
Reusability and Maintenance Requirements
Respirator masks, such as N95 or KN95, are designed for multiple uses with proper cleaning and filtration replacement, offering higher durability and long-term protection compared to surgical masks. Surgical masks are typically single-use, disposable, and require no maintenance, making them less suitable for extended or repeated wear. Proper storage and periodic inspection of respirator masks ensure maintained filtration efficiency and safety during repeated use.
Limitations and Best Practices
Respirator masks, such as N95s, offer superior filtration against airborne particles, providing enhanced protection compared to surgical masks, but they require proper fit testing and can be uncomfortable for extended wear, limiting their practicality in some settings. Surgical masks primarily protect against large droplets and reduce the spread of respiratory secretions but do not provide a reliable seal against airborne pathogens, making them less effective in high-risk environments. Best practices include using respirators for high-exposure tasks with fit verification, while surgical masks are suitable for general public use and low-risk situations, combined with other preventive measures like hand hygiene.
Occupational Applications: Healthcare vs Industrial Settings
Respirator masks, such as N95 and P100, provide high-level filtration and tight sealing, making them essential in industrial settings with exposure to airborne particulates, chemicals, and hazardous dust. Surgical masks primarily protect against large droplets and fluids, primarily used in healthcare to reduce pathogen transmission during medical procedures. In occupational applications, respirators are mandated for environments with toxic exposures, while surgical masks serve as basic barrier protection in clinical settings.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Respirator masks, such as N95 or FFP2, provide a higher level of protection by filtering out at least 95% of airborne particles, while surgical masks primarily protect against large droplets and splashes. A common misconception is that surgical masks offer equivalent filtration efficiency to respirators, which is inaccurate because they lack a tight seal around the face. Proper use of respirator masks is essential in high-risk environments to effectively reduce exposure to airborne contaminants.
Respirator masks vs Surgical masks Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com