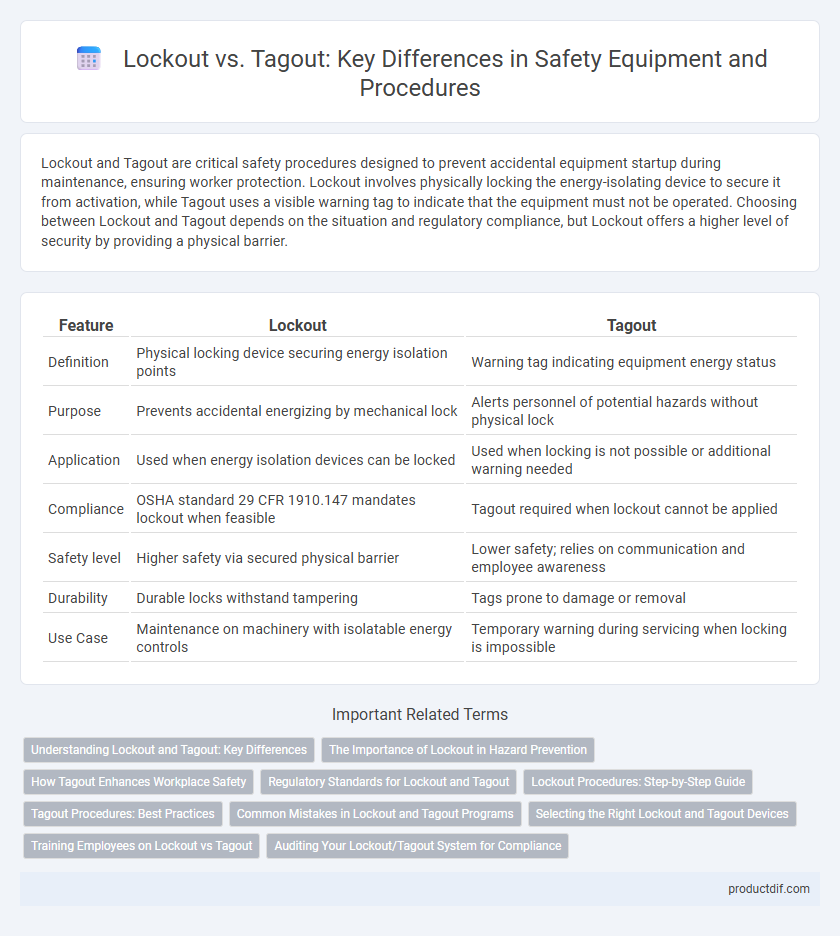
Lockout and Tagout are critical safety procedures designed to prevent accidental equipment startup during maintenance, ensuring worker protection. Lockout involves physically locking the energy-isolating device to secure it from activation, while Tagout uses a visible warning tag to indicate that the equipment must not be operated. Choosing between Lockout and Tagout depends on the situation and regulatory compliance, but Lockout offers a higher level of security by providing a physical barrier.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lockout | Tagout |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical locking device securing energy isolation points | Warning tag indicating equipment energy status |
| Purpose | Prevents accidental energizing by mechanical lock | Alerts personnel of potential hazards without physical lock |
| Application | Used when energy isolation devices can be locked | Used when locking is not possible or additional warning needed |
| Compliance | OSHA standard 29 CFR 1910.147 mandates lockout when feasible | Tagout required when lockout cannot be applied |
| Safety level | Higher safety via secured physical barrier | Lower safety; relies on communication and employee awareness |
| Durability | Durable locks withstand tampering | Tags prone to damage or removal |
| Use Case | Maintenance on machinery with isolatable energy controls | Temporary warning during servicing when locking is impossible |
Understanding Lockout and Tagout: Key Differences
Lockout involves physically isolating energy sources by applying locks to equipment controls, ensuring machinery cannot be energized during maintenance. Tagout uses warning tags to inform personnel that equipment should not be operated but does not provide a physical barrier to prevent activation. Understanding these distinctions is critical for compliance with OSHA standards and enhancing workplace safety protocols.
The Importance of Lockout in Hazard Prevention
Lockout procedures play a critical role in hazard prevention by completely de-energizing machinery, ensuring no accidental startup during maintenance or repair. Unlike tagout, which only provides a warning, lockout physically secures energy-isolating devices, significantly reducing the risk of electrical shocks, mechanical injuries, and equipment damage. Implementing lockout protocols aligns with OSHA standards and promotes a safer work environment by preventing unintended machine activation.
How Tagout Enhances Workplace Safety
Tagout enhances workplace safety by providing clear visual warnings that equipment is not to be operated, effectively preventing accidental startup during maintenance. It ensures all employees are aware of potential hazards and respects the authority of authorized personnel to control energy sources. This communication reduces the risk of injuries and ensures compliance with OSHA safety standards.
Regulatory Standards for Lockout and Tagout
Regulatory standards for lockout and tagout are primarily governed by OSHA's Control of Hazardous Energy standard (29 CFR 1910.147), which mandates procedures to prevent accidental machine energization during maintenance. Lockout devices physically isolate energy sources, while tagout devices serve as warning tags; however, OSHA prioritizes lockout for its higher safety assurance. Compliance with these standards reduces workplace injuries by ensuring that hazardous energy is completely de-energized and equipment is clearly marked before servicing.
Lockout Procedures: Step-by-Step Guide
Lockout procedures involve systematically isolating energy sources by applying physical locks to machinery controls, ensuring equipment remains de-energized during maintenance. The step-by-step guide includes identifying energy sources, shutting down equipment, disconnecting power, applying lockout devices, releasing stored energy, and verifying isolation before work begins. Proper lockout implementation significantly reduces the risk of accidental machine startup, enhancing workplace safety.
Tagout Procedures: Best Practices
Tagout procedures require clear, standardized written instructions that specify the steps to disable machinery controls safely. Best practices include using highly visible, weather-resistant tags with detailed information such as the reason for the tagout, authorized personnel, and expected duration. Consistent training and regular audits ensure employees understand the tagout protocol, minimizing the risk of accidental equipment start-up and enhancing workplace safety.
Common Mistakes in Lockout and Tagout Programs
Common mistakes in lockout and tagout programs include inadequate employee training, failure to identify all energy sources, and improper use of lockout devices, which can lead to hazardous energy release. Overlooking routine inspections and neglecting to update procedures after equipment modifications compromise the effectiveness of these safety protocols. Ensuring comprehensive hazard assessments and maintaining strict adherence to OSHA standards significantly reduce accidents related to lockout/tagout failures.
Selecting the Right Lockout and Tagout Devices
Selecting the right lockout and tagout devices is crucial for ensuring workplace safety and regulatory compliance in energy control procedures. Lockout devices should be chosen based on specific equipment types, including circuit breakers, valves, and electrical panels, while tagout devices must provide clear, durable warnings to prevent accidental re-energization. Proper selection also involves considering device compatibility, ease of use, and compliance with OSHA standards to effectively isolate hazardous energy sources.
Training Employees on Lockout vs Tagout
Training employees on lockout vs tagout procedures ensures proper understanding of the differences between physically isolating energy sources (lockout) and placing warning tags without isolation (tagout). Effective training reduces workplace accidents by emphasizing compliance with OSHA standards and the correct application of energy control methods. Regular hands-on sessions and assessments enhance employee competency in identifying hazards and executing safe equipment shutdowns.
Auditing Your Lockout/Tagout System for Compliance
Auditing your Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) system involves systematically inspecting equipment, procedures, and employee adherence to ensure compliance with OSHA standards 29 CFR 1910.147. Regular audits identify gaps in authorized employee training, proper use of lockout devices, and accurate documentation, preventing hazardous energy release during maintenance. Implementing a thorough audit schedule reduces workplace accidents and enhances overall safety program effectiveness.
Lockout vs Tagout Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com