Gas detectors specialize in identifying the presence of hazardous gases in the environment, providing critical alerts to prevent poisoning or explosions. Vapor monitors specifically measure volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other harmful vapors, ensuring air quality and safety in industrial or confined spaces. Choosing between a gas detector and a vapor monitor depends on the specific type of contaminant risk and the sensitivity required for effective pet safety.
Table of Comparison
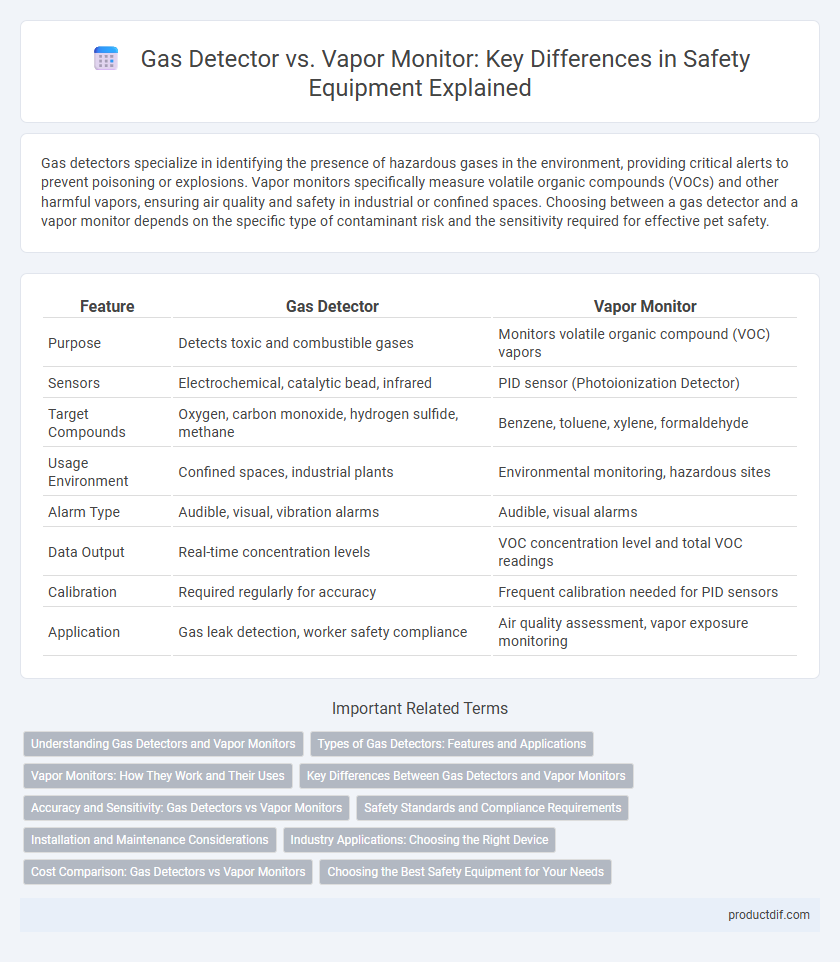
| Feature | Gas Detector | Vapor Monitor |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detects toxic and combustible gases | Monitors volatile organic compound (VOC) vapors |
| Sensors | Electrochemical, catalytic bead, infrared | PID sensor (Photoionization Detector) |
| Target Compounds | Oxygen, carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, methane | Benzene, toluene, xylene, formaldehyde |
| Usage Environment | Confined spaces, industrial plants | Environmental monitoring, hazardous sites |
| Alarm Type | Audible, visual, vibration alarms | Audible, visual alarms |
| Data Output | Real-time concentration levels | VOC concentration level and total VOC readings |
| Calibration | Required regularly for accuracy | Frequent calibration needed for PID sensors |
| Application | Gas leak detection, worker safety compliance | Air quality assessment, vapor exposure monitoring |
Understanding Gas Detectors and Vapor Monitors
Gas detectors are designed to identify and measure the concentration of hazardous gases in the environment, such as oxygen, carbon monoxide, and combustible gases, providing real-time alerts for potentially dangerous conditions. Vapor monitors specifically detect and quantify volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other vapors that may pose health risks, often using photoionization or flame ionization sensors for precise readings. Both devices play critical roles in industrial safety by preventing toxic exposures and ensuring compliance with occupational health standards.
Types of Gas Detectors: Features and Applications
Photoionization detectors (PIDs) and catalytic bead sensors are common types of gas detectors, each offering distinct features to detect volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and combustible gases, respectively. Infrared (IR) sensors provide selective detection of gases like carbon dioxide and methane with high accuracy and low maintenance. Applications range from industrial safety and environmental monitoring to hazardous material handling, ensuring effective detection tailored to specific gas properties and environments.
Vapor Monitors: How They Work and Their Uses
Vapor monitors detect airborne chemical vapors by using photoionization detectors (PIDs) or flame ionization detectors (FIDs) to measure the concentration of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in real-time. These devices are essential in industrial safety for identifying hazardous organic vapors in environments like chemical plants, refineries, and hazardous waste sites. Vapor monitors help prevent exposure to toxic vapors, ensuring worker safety and regulatory compliance through continuous air quality assessment.
Key Differences Between Gas Detectors and Vapor Monitors
Gas detectors identify and measure the concentration of hazardous gases, such as carbon monoxide or hydrogen sulfide, providing real-time alerts to prevent toxic exposure or explosions. Vapor monitors specifically target volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and combustible vapors, with high sensitivity to substances like gasoline or solvents in industrial or environmental settings. Key differences include the gas type detected, detection technology, and application focus, where gas detectors prioritize toxic or explosive gases and vapor monitors emphasize combustible vapor detection for leak or spill control.
Accuracy and Sensitivity: Gas Detectors vs Vapor Monitors
Gas detectors exhibit higher accuracy in identifying individual toxic or combustible gases by utilizing specific sensors calibrated for target gas concentrations, ensuring precise hazard detection. Vapor monitors generally measure total volatile organic compounds (VOCs) presence, offering broader sensitivity to complex mixtures but with less specificity for individual gas identification. The superior sensitivity of gas detectors to particular gases makes them essential for environments requiring exact concentration measurements, whereas vapor monitors provide valuable real-time screening of general vapor presence.
Safety Standards and Compliance Requirements
Gas detectors and vapor monitors must adhere to rigorous safety standards such as OSHA, ATEX, and IECEx to ensure accurate detection and employee protection in hazardous environments. Certified devices undergo stringent testing for sensitivity, response time, and environmental resilience to comply with regulatory requirements, ensuring reliable performance in detecting toxic gases or combustible vapors. Compliance with these standards minimizes workplace accidents and enhances safety protocols across industries handling volatile substances.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Gas detectors require strategic placement near potential gas leak sources and regular calibration to maintain accuracy, with sensor replacements typically scheduled every 6 to 12 months. Vapor monitors, often designed for portable use, need less complex installation but demand routine battery checks and sensor calibration based on manufacturer guidelines. Both devices benefit from consistent maintenance to ensure reliable detection in hazardous environments.
Industry Applications: Choosing the Right Device
Gas detectors are essential in industries such as oil and gas, mining, and chemical manufacturing where monitoring toxic or combustible gases is critical for worker safety and regulatory compliance. Vapor monitors are specifically designed for detecting volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous vapors in environments like painting booths, pharmaceutical plants, and environmental cleanup sites. Selecting the appropriate device depends on the specific gases or vapors present, industry regulations, and the sensitivity required for early leak detection to prevent accidents and exposures.
Cost Comparison: Gas Detectors vs Vapor Monitors
Gas detectors generally have higher upfront costs compared to vapor monitors due to their advanced sensor technology and broader detection capabilities. Vapor monitors tend to be more affordable initially but may require more frequent maintenance and calibration, impacting long-term expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including purchase price, calibration frequency, and sensor lifespan, is crucial for selecting the most cost-effective safety equipment.
Choosing the Best Safety Equipment for Your Needs
Selecting the right safety equipment requires understanding the differences between gas detectors and vapor monitors, each designed for specific hazard detection. Gas detectors identify the presence of combustible or toxic gases such as methane or carbon monoxide, providing critical alerts to prevent poisoning or explosions. Vapor monitors, on the other hand, specialize in detecting volatile organic compounds (VOCs) like solvents and chemical vapors, ensuring protection in industrial and environmental settings where inhalation risks are prevalent.
Gas detector vs Vapor monitor Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com