Reusable medical devices offer cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits by reducing waste through sterilization and multiple uses. Single-use devices ensure sterility and reduce infection risks but generate more medical waste and incur higher recurring costs. Healthcare providers balance patient safety, economic factors, and sustainability when choosing between reusable and single-use medical tools.
Table of Comparison
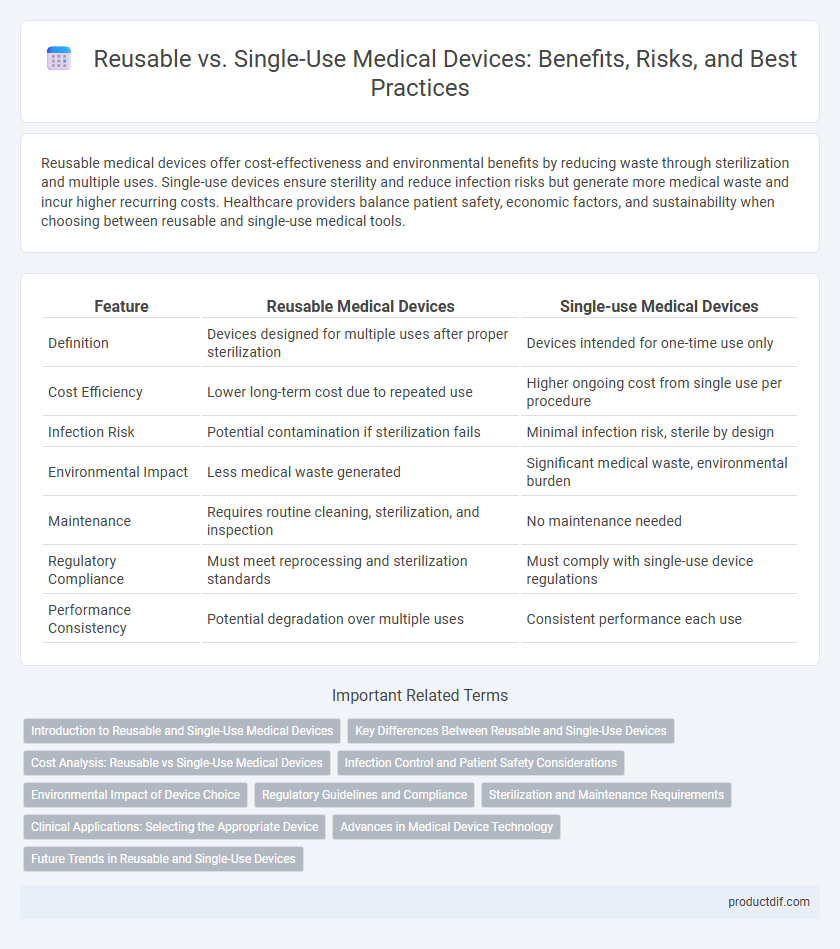
| Feature | Reusable Medical Devices | Single-use Medical Devices |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Devices designed for multiple uses after proper sterilization | Devices intended for one-time use only |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower long-term cost due to repeated use | Higher ongoing cost from single use per procedure |
| Infection Risk | Potential contamination if sterilization fails | Minimal infection risk, sterile by design |
| Environmental Impact | Less medical waste generated | Significant medical waste, environmental burden |
| Maintenance | Requires routine cleaning, sterilization, and inspection | No maintenance needed |
| Regulatory Compliance | Must meet reprocessing and sterilization standards | Must comply with single-use device regulations |
| Performance Consistency | Potential degradation over multiple uses | Consistent performance each use |
Introduction to Reusable and Single-Use Medical Devices
Reusable medical devices are designed for multiple uses with proper sterilization, offering cost-efficiency and environmental benefits by reducing medical waste. Single-use devices are intended for one-time application, minimizing the risk of cross-contamination and infection transmission in clinical settings. The choice between reusable and single-use medical devices depends on factors such as patient safety, device complexity, sterilization capabilities, and healthcare facility protocols.
Key Differences Between Reusable and Single-Use Devices
Reusable medical devices undergo rigorous sterilization processes to ensure safety and cost-efficiency across multiple uses, while single-use devices prioritize sterility and convenience by being disposed of after one patient interaction. Material composition and design differ significantly, with reusable devices crafted for durability and resistance to repeated sterilization, whereas single-use devices emphasize lightweight, cost-effective materials to maintain hygiene standards. Regulatory compliance varies as well, with single-use devices facing stringent packaging and disposal requirements, contrasting with the maintenance and inspection protocols mandatory for reusable devices.
Cost Analysis: Reusable vs Single-Use Medical Devices
Cost analysis of reusable versus single-use medical devices reveals significant differences in long-term expenditure and resource allocation. Reusable devices often incur higher initial acquisition costs but lower per-use expenses due to sterilization and maintenance processes, making them cost-effective in high-volume settings. Single-use devices eliminate reprocessing costs and reduce infection risks but may lead to greater cumulative expenses over time, particularly in institutions with frequent procedures.
Infection Control and Patient Safety Considerations
Reusable medical devices require stringent sterilization protocols to prevent cross-contamination and reduce infection risks, emphasizing thorough cleaning and validation processes. Single-use devices eliminate the risk of pathogen transmission associated with inadequate sterilization but generate more medical waste, raising environmental concerns. Patient safety is enhanced by selecting the appropriate device type based on procedure risk, infection control standards, and healthcare setting capabilities.
Environmental Impact of Device Choice
Choosing reusable medical devices over single-use alternatives significantly reduces medical waste volume, lowering environmental pollution and landfill burden. Reusable devices decrease resource consumption by minimizing the need for frequent manufacturing, thus cutting carbon emissions and raw material extraction. Life cycle assessments demonstrate that sustainable sterilization practices can mitigate environmental impacts, making reusable options a greener choice for healthcare facilities aiming to improve eco-efficiency.
Regulatory Guidelines and Compliance
Regulatory guidelines for reusable medical devices emphasize stringent protocols for cleaning, sterilization, and validation to ensure patient safety and infection control, as outlined by agencies like the FDA and EMA. Single-use devices, governed by distinct compliance measures, mandate rigorous manufacturing standards and clear labeling to prevent reuse, thereby minimizing contamination risks. Compliance with ISO 13485 and FDA's Quality System Regulation (QSR) is critical for both types to meet market approval and maintain patient safety standards.
Sterilization and Maintenance Requirements
Reusable medical devices require stringent sterilization protocols such as autoclaving or chemical disinfection to ensure patient safety and prevent cross-contamination. Single-use devices eliminate the need for sterilization, reducing maintenance efforts and risk of infection but increasing medical waste. Proper sterilization of reusable devices demands rigorous validation and routine maintenance to maintain functionality and compliance with regulatory standards.
Clinical Applications: Selecting the Appropriate Device
Clinical applications dictate the choice between reusable and single-use medical devices based on infection control, cost-efficiency, and procedural requirements. Reusable devices offer durability and cost savings in high-volume settings but require rigorous sterilization protocols to prevent cross-contamination. Single-use devices enhance patient safety by eliminating reprocessing risks, making them ideal for sterile environments and procedures with strict infection prevention standards.
Advances in Medical Device Technology
Advances in medical device technology have significantly improved the durability and sterilization methods for reusable devices, enhancing patient safety and reducing healthcare costs. Innovations in materials science, such as antimicrobial coatings and biocompatible polymers, extend the lifespan and reduce infection risk during multiple uses. Single-use devices benefit from cutting-edge manufacturing techniques like 3D printing, enabling precise, sterile, and cost-effective production tailored for specific medical procedures.
Future Trends in Reusable and Single-Use Devices
Advancements in materials science and sterilization technology are driving the future of reusable medical devices, enhancing durability and reducing infection risks. Single-use devices are evolving with eco-friendly biodegradable materials and smart sensors for real-time patient monitoring. Integration of digital health technologies will increasingly blur the line between disposable and reusable, offering personalized treatment and improved clinical outcomes.
Reusable vs Single-use Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com