Regulatory approval and CE marking are critical steps for medical devices to enter the European market, but they serve different purposes. Regulatory approval involves comprehensive evaluation by national authorities to ensure safety and efficacy, while CE marking signifies compliance with EU health, safety, and environmental requirements, allowing free market access. Manufacturers must navigate both processes to achieve legal marketing and distribution within the EU.
Table of Comparison
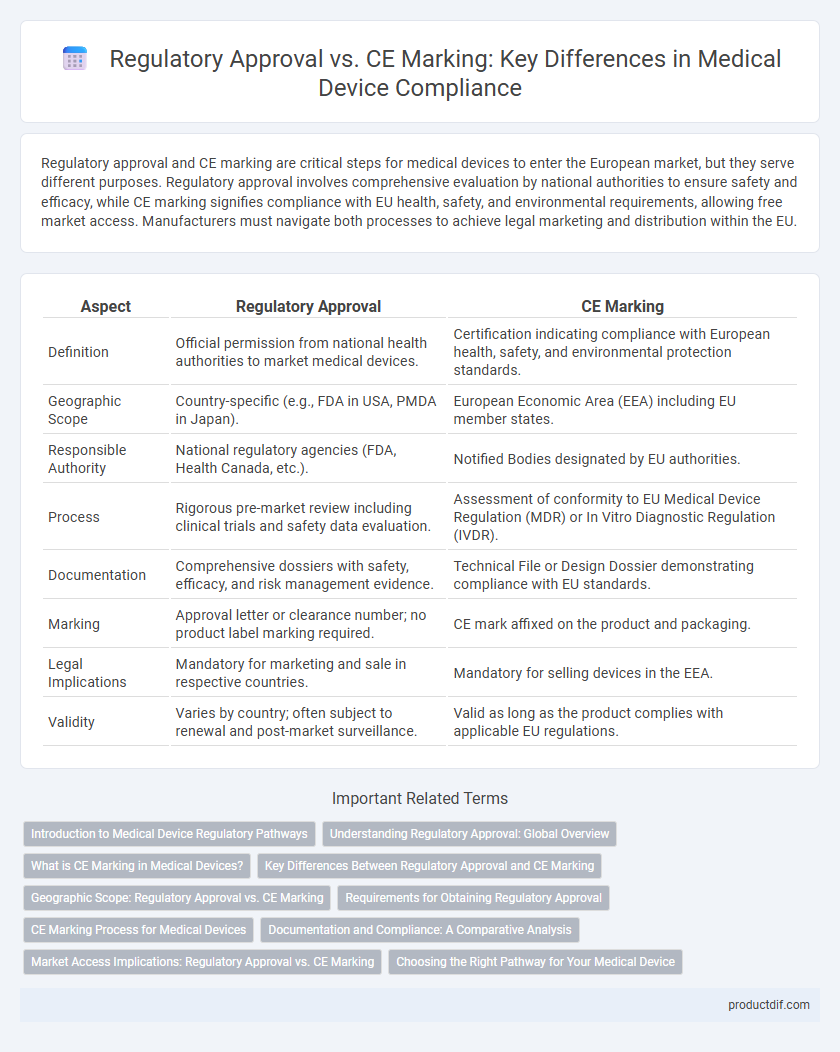
| Aspect | Regulatory Approval | CE Marking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official permission from national health authorities to market medical devices. | Certification indicating compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. |
| Geographic Scope | Country-specific (e.g., FDA in USA, PMDA in Japan). | European Economic Area (EEA) including EU member states. |
| Responsible Authority | National regulatory agencies (FDA, Health Canada, etc.). | Notified Bodies designated by EU authorities. |
| Process | Rigorous pre-market review including clinical trials and safety data evaluation. | Assessment of conformity to EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) or In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR). |
| Documentation | Comprehensive dossiers with safety, efficacy, and risk management evidence. | Technical File or Design Dossier demonstrating compliance with EU standards. |
| Marking | Approval letter or clearance number; no product label marking required. | CE mark affixed on the product and packaging. |
| Legal Implications | Mandatory for marketing and sale in respective countries. | Mandatory for selling devices in the EEA. |
| Validity | Varies by country; often subject to renewal and post-market surveillance. | Valid as long as the product complies with applicable EU regulations. |
Introduction to Medical Device Regulatory Pathways
Medical device regulatory pathways vary significantly between regions, with regulatory approval typically referring to the formal authorization process by government agencies like the FDA in the United States, ensuring safety and efficacy before market entry. CE marking represents conformity with European Union directives, allowing devices to be sold within the EU by demonstrating compliance with essential health and safety requirements. Understanding these pathways is critical for manufacturers to navigate compliance, market access, and post-market surveillance obligations effectively.
Understanding Regulatory Approval: Global Overview
Regulatory approval for medical devices involves rigorous evaluation by governmental bodies such as the FDA in the United States and the PMDA in Japan, ensuring safety and efficacy before market entry. CE marking, required for products sold within the European Economic Area, signifies conformity with EU health, safety, and environmental protection standards but is not an approval in itself. Understanding the global landscape requires recognizing that while CE marking facilitates market access in Europe, regulatory approval processes vary significantly across countries, each with distinct requirements and timelines.
What is CE Marking in Medical Devices?
CE marking in medical devices signifies compliance with the European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR), allowing manufacturers to legally market their products within the European Economic Area (EEA). It demonstrates that the device meets essential safety, health, and environmental protection requirements through conformity assessment procedures. Achieving CE marking involves rigorous documentation, clinical evaluation, and quality management system implementation to ensure device reliability and patient safety.
Key Differences Between Regulatory Approval and CE Marking
Regulatory approval is a comprehensive process ensuring medical devices meet safety and efficacy standards set by specific national authorities like the FDA in the US, while CE marking indicates conformity with European Union safety, health, and environmental requirements, allowing free market access within the EU. Regulatory approval often requires clinical trials and extensive documentation demonstrating product safety and performance, whereas CE marking relies on compliance with harmonized European standards and assessment procedures, sometimes involving a notified body. The scope of regulatory approval is typically more stringent and country-specific, whereas CE marking facilitates a unified regulatory pathway across multiple European countries.
Geographic Scope: Regulatory Approval vs. CE Marking
Regulatory approval for medical devices varies significantly by geographic scope, with each country or region enforcing its own standards and requirements, such as the FDA in the United States and Health Canada in Canada. CE marking specifically applies to the European Economic Area (EEA) and demonstrates compliance with the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR), allowing free market access across member states. Manufacturers targeting global markets must navigate distinct regulatory pathways to meet the specific criteria of each jurisdiction.
Requirements for Obtaining Regulatory Approval
Obtaining regulatory approval for medical devices requires comprehensive clinical data demonstrating safety and efficacy, strict adherence to quality management standards such as ISO 13485, and submission of detailed technical documentation to regulatory bodies like the FDA or MHRA. This process often includes rigorous premarket evaluations, risk assessments, and post-market surveillance commitments to ensure ongoing compliance. Regulatory approval timelines and requirements vary significantly by region, necessitating tailored strategies for markets such as the US, EU, and emerging economies.
CE Marking Process for Medical Devices
The CE marking process for medical devices involves a thorough assessment to ensure compliance with the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) or In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR). Manufacturers must conduct clinical evaluations, implement a quality management system, and prepare a technical documentation file demonstrating safety and performance. Notified Bodies review the documentation and audit manufacturing processes before granting CE certification, allowing the device to be marketed within the European Economic Area.
Documentation and Compliance: A Comparative Analysis
Regulatory approval for medical devices involves rigorous documentation including clinical evaluation reports, risk management files, and quality management system certificates to meet the specific requirements of authorities like the FDA or Health Canada. CE marking documentation requires a comprehensive technical file and conformity assessment demonstrating compliance with the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR), focusing on safety and performance standards. Both processes demand thorough evidence of compliance, but regulatory approval often requires more detailed clinical data while CE marking emphasizes ongoing post-market surveillance and risk management.
Market Access Implications: Regulatory Approval vs. CE Marking
Regulatory approval, such as FDA clearance in the United States, is mandatory for medical devices to enter the U.S. market, ensuring safety and efficacy through rigorous pre-market evaluation. CE marking indicates compliance with the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR), allowing devices to be marketed across the European Economic Area, facilitating access to one of the largest global healthcare markets. Differences in regulatory frameworks impact market entry speed, post-market surveillance requirements, and reimbursement eligibility, making strategic planning essential for global market access.
Choosing the Right Pathway for Your Medical Device
Regulatory approval and CE marking represent distinct pathways for medical device market access, with regulatory approval required in markets like the United States through the FDA, while CE marking is mandatory for European Economic Area countries. Selecting the appropriate pathway depends on the target market, device classification, and specific regulatory requirements such as premarket submissions or conformity assessments. Understanding these differences ensures compliance, accelerates time-to-market, and mitigates the risk of legal and financial penalties.
Regulatory Approval vs CE Marking Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com