Point-of-care devices deliver rapid, on-site diagnostic results, enabling immediate clinical decisions and reducing patient wait times. Lab-based devices offer comprehensive, high-throughput testing with greater analytical accuracy but require specialized personnel and longer processing periods. Choosing between these devices depends on the clinical setting's need for speed, accuracy, and resource availability.
Table of Comparison
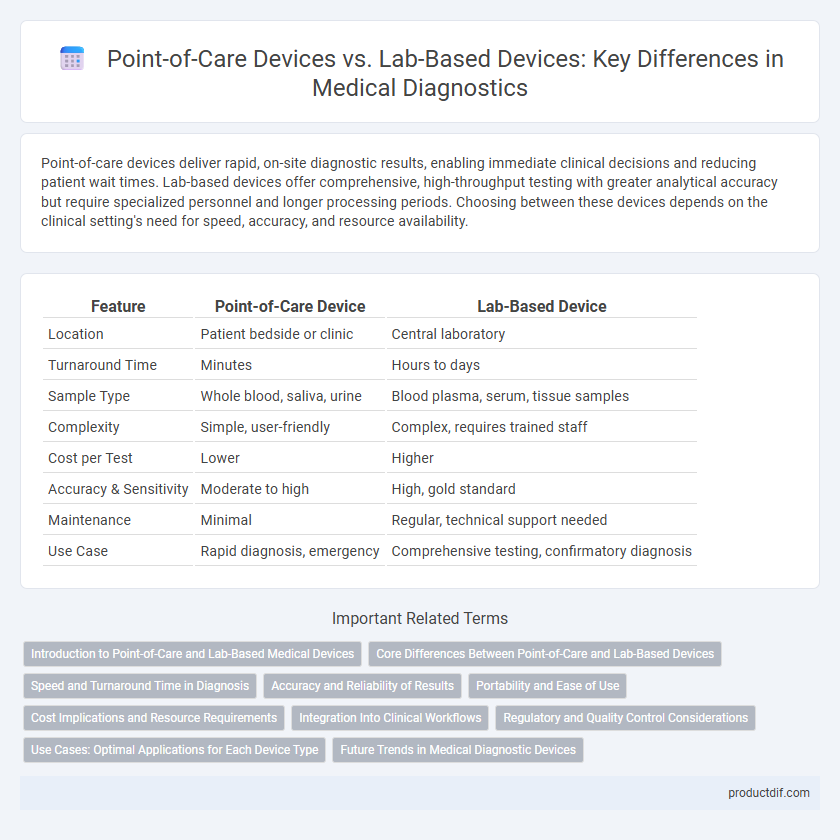
| Feature | Point-of-Care Device | Lab-Based Device |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Patient bedside or clinic | Central laboratory |
| Turnaround Time | Minutes | Hours to days |
| Sample Type | Whole blood, saliva, urine | Blood plasma, serum, tissue samples |
| Complexity | Simple, user-friendly | Complex, requires trained staff |
| Cost per Test | Lower | Higher |
| Accuracy & Sensitivity | Moderate to high | High, gold standard |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Regular, technical support needed |
| Use Case | Rapid diagnosis, emergency | Comprehensive testing, confirmatory diagnosis |
Introduction to Point-of-Care and Lab-Based Medical Devices
Point-of-care (POC) devices enable rapid diagnostic testing at or near the patient, facilitating immediate clinical decisions without the need for centralized laboratory infrastructure. Lab-based medical devices, in contrast, offer comprehensive, high-throughput analysis with advanced detection capabilities but require specialized facilities and longer turnaround times. The evolving landscape of medical diagnostics increasingly integrates POC technologies to complement traditional lab-based systems, enhancing overall healthcare efficiency and patient outcomes.
Core Differences Between Point-of-Care and Lab-Based Devices
Point-of-care devices deliver rapid diagnostic results at or near the patient site, enabling immediate clinical decisions, whereas lab-based devices operate within centralized laboratories, requiring longer turnaround times due to sample transport and batch processing. Point-of-care devices typically emphasize portability, user-friendliness, and real-time data output, while lab-based systems prioritize higher throughput, advanced analytic capabilities, and comprehensive testing panels. The core differences lie in speed, accessibility, and operational complexity, impacting clinical workflow, patient management, and healthcare delivery models.
Speed and Turnaround Time in Diagnosis
Point-of-care devices deliver rapid diagnostic results within minutes at the patient's location, significantly reducing turnaround time compared to lab-based devices that require sample transport and processing, often taking hours to days. The immediate feedback from point-of-care testing enhances clinical decision-making and accelerates treatment initiation. In contrast, lab-based devices offer comprehensive analysis but involve longer delays due to centralized processing and batch testing workflows.
Accuracy and Reliability of Results
Point-of-care devices offer rapid diagnostics with moderate accuracy, making them suitable for immediate clinical decisions but sometimes limited by environmental factors and operator variability. Lab-based devices provide higher accuracy and reliability due to controlled conditions, standardized protocols, and advanced equipment, ensuring precise and reproducible results. The choice between point-of-care and lab-based testing depends on the clinical need for speed versus the demand for diagnostic precision and consistency.
Portability and Ease of Use
Point-of-care devices offer superior portability with compact designs that enable bedside testing and immediate diagnostic results, unlike lab-based devices which are bulky and stationary. Their user-friendly interfaces require minimal training, facilitating faster decision-making in clinical settings. Lab-based devices, while highly accurate, necessitate specialized personnel and longer processing times, limiting their convenience and accessibility outside central laboratories.
Cost Implications and Resource Requirements
Point-of-care devices typically offer lower upfront costs and reduced need for specialized personnel compared to lab-based devices, making them cost-effective for decentralized settings. Lab-based devices, while more expensive to acquire and maintain, provide higher throughput and more comprehensive testing capabilities, demanding significant infrastructure and trained laboratory technicians. Resource allocation must consider the balance between immediate accessibility and long-term operational expenses to optimize healthcare delivery.
Integration Into Clinical Workflows
Point-of-care devices enhance clinical workflows by providing rapid diagnostic results directly at the patient's bedside, minimizing delays associated with sample transport and laboratory processing. Lab-based devices offer high-throughput testing and complex analyses that require centralized facilities but may introduce workflow interruptions due to longer turnaround times. Integration of point-of-care devices into electronic health records (EHR) streamlines data management and supports real-time clinical decision-making, optimizing patient care efficiency.
Regulatory and Quality Control Considerations
Point-of-care devices must comply with stringent regulatory standards such as FDA's 21 CFR Part 820 and ISO 13485 to ensure safety and effectiveness in diverse clinical settings, while lab-based devices often follow more comprehensive validation protocols due to controlled environments. Quality control for point-of-care devices emphasizes ease of use, rapid calibration, and robust error detection to maintain accuracy during decentralized testing, whereas lab-based devices rely on extensive quality assurance programs including proficiency testing and instrument maintenance. Both device types require adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and regular audits to meet regulatory compliance and ensure consistent diagnostic performance.
Use Cases: Optimal Applications for Each Device Type
Point-of-care devices excel in emergency settings, remote locations, and outpatient care by delivering rapid diagnostic results directly at the patient's side, facilitating timely treatment decisions. Lab-based devices are optimal for comprehensive testing, complex analyses, and high-throughput workflows in centralized laboratories, ensuring high accuracy and detailed data output. Each device type supports distinct clinical scenarios, with point-of-care devices enhancing accessibility and speed, while lab-based devices provide extensive diagnostic capabilities and reliability.
Future Trends in Medical Diagnostic Devices
Point-of-care devices are evolving with enhanced portability, rapid processing, and user-friendly interfaces, enabling immediate diagnosis outside traditional laboratory settings. Lab-based devices continue to integrate advanced automation, high-throughput capabilities, and artificial intelligence to improve precision and complex biomarker analysis. Future trends emphasize hybrid models combining the speed of point-of-care testing with the comprehensive data output of lab-based diagnostics, driving personalized medicine and real-time health monitoring.
Point-of-care device vs Lab-based device Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com