Biocompatibility testing evaluates the overall compatibility of a medical device with human tissue, ensuring it does not cause harmful effects when implanted or in contact with the body. Cytotoxicity testing specifically measures the potential of the device's materials to cause cell damage or death, serving as an initial screening for biocompatibility. These tests are critical in the regulatory approval process to guarantee patient safety and device efficacy.
Table of Comparison
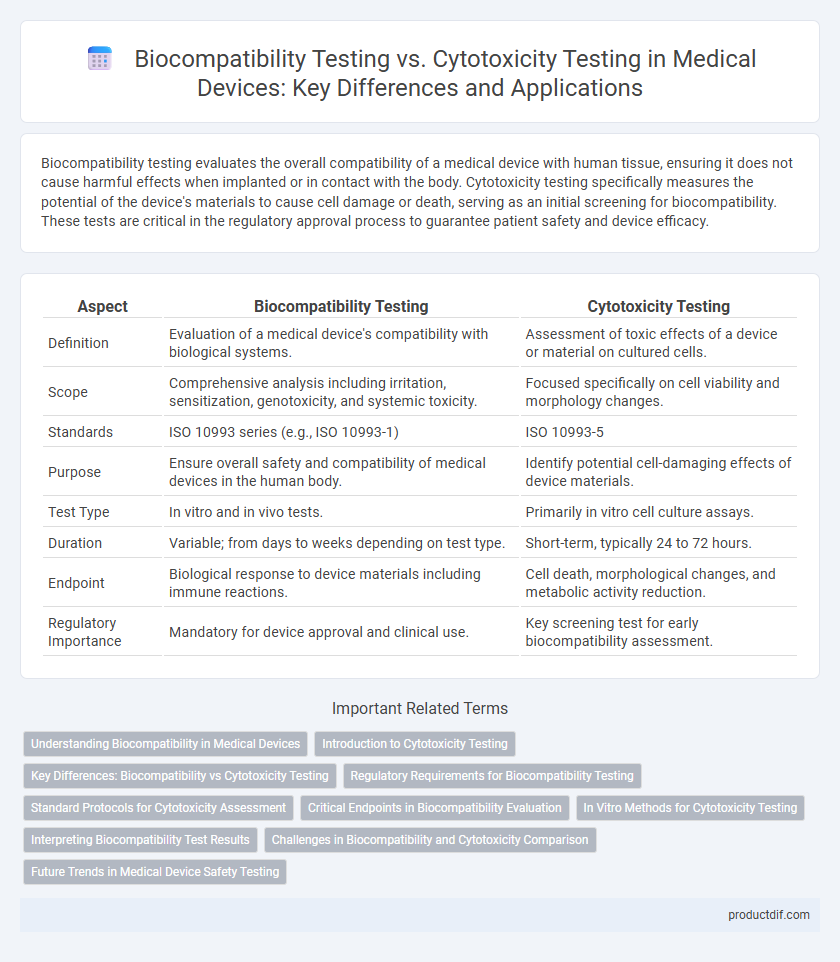
| Aspect | Biocompatibility Testing | Cytotoxicity Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluation of a medical device's compatibility with biological systems. | Assessment of toxic effects of a device or material on cultured cells. |
| Scope | Comprehensive analysis including irritation, sensitization, genotoxicity, and systemic toxicity. | Focused specifically on cell viability and morphology changes. |
| Standards | ISO 10993 series (e.g., ISO 10993-1) | ISO 10993-5 |
| Purpose | Ensure overall safety and compatibility of medical devices in the human body. | Identify potential cell-damaging effects of device materials. |
| Test Type | In vitro and in vivo tests. | Primarily in vitro cell culture assays. |
| Duration | Variable; from days to weeks depending on test type. | Short-term, typically 24 to 72 hours. |
| Endpoint | Biological response to device materials including immune reactions. | Cell death, morphological changes, and metabolic activity reduction. |
| Regulatory Importance | Mandatory for device approval and clinical use. | Key screening test for early biocompatibility assessment. |
Understanding Biocompatibility in Medical Devices
Biocompatibility testing evaluates how medical devices interact with biological systems to ensure safety and functionality, encompassing various assessments such as cytotoxicity, sensitization, and irritation tests. Cytotoxicity testing specifically measures the potential of a device or its materials to cause cell damage or death, serving as an initial screening step within the broader biocompatibility evaluation. Understanding biocompatibility is crucial for regulatory compliance and patient safety, as it ensures that devices will not elicit adverse biological responses when implanted or in contact with tissues.
Introduction to Cytotoxicity Testing
Cytotoxicity testing evaluates the toxic effects of medical device materials on living cells to ensure biocompatibility and patient safety. It provides a rapid and cost-effective screening method to detect potential cell damage or death caused by device extracts or direct contact. This test serves as an essential initial step in the overall biocompatibility assessment following international standards like ISO 10993-5.
Key Differences: Biocompatibility vs Cytotoxicity Testing
Biocompatibility testing evaluates the overall compatibility of a medical device with biological systems, including factors like toxicity, sensitization, and irritation, to ensure patient safety and regulatory compliance. Cytotoxicity testing specifically measures the potential of a device or material to cause cell damage or death, serving as an initial screening step within the broader biocompatibility assessment. Key differences lie in the scope and purpose: cytotoxicity focuses on direct cellular response, while biocompatibility encompasses a comprehensive evaluation of biological interactions.
Regulatory Requirements for Biocompatibility Testing
Biocompatibility testing for medical devices is mandated by regulatory agencies such as the FDA and ISO 10993 series to ensure device safety and patient compatibility. Unlike cytotoxicity testing, which primarily assesses cell toxicity in vitro, biocompatibility testing encompasses a broader evaluation including sensitization, irritation, and systemic toxicity. Compliance with these regulatory requirements is essential for device approval, risk management, and successful market access.
Standard Protocols for Cytotoxicity Assessment
Cytotoxicity testing of medical devices follows ISO 10993-5 standards, which specify procedures to evaluate the potential toxic effects of device materials on cultured mammalian cells. The standard protocol involves direct contact, extract dilution, or agar diffusion methods to assess cell viability, morphology, and proliferation. Accurate compliance with ISO 10993-5 ensures reliable assessment of cytotoxicity, distinct from broader biocompatibility testing that encompasses systemic and long-term effects.
Critical Endpoints in Biocompatibility Evaluation
Critical endpoints in biocompatibility evaluation focus on assessing the overall safety and compatibility of medical devices with biological tissues, including sensitization, irritation, systemic toxicity, and genotoxicity. Cytotoxicity testing specifically measures cell viability and membrane integrity to detect adverse cellular responses induced by material extracts, serving as an initial screening method within the broader biocompatibility assessment. Comprehensive biocompatibility testing integrates multiple endpoints to ensure the medical device does not elicit harmful biological effects during clinical use.
In Vitro Methods for Cytotoxicity Testing
In vitro methods for cytotoxicity testing are essential components of biocompatibility testing for medical devices, ensuring materials do not induce cell death or dysfunction. These assays, including MTT, XTT, and LIVE/DEAD staining, provide rapid, sensitive, and quantitative evaluation of material toxicity on cultured cells. Cytotoxicity testing in vitro helps predict potential adverse cellular responses, guiding safer medical device development and regulatory compliance.
Interpreting Biocompatibility Test Results
Interpreting biocompatibility test results requires a comprehensive understanding of how medical devices interact with biological systems, ensuring safety and regulatory compliance. Biocompatibility testing evaluates multiple endpoints such as sensitization, irritation, and systemic toxicity, while cytotoxicity testing specifically assesses cellular damage and viability. Accurate interpretation integrates both test outcomes to predict clinical performance and identify potential adverse reactions, guiding risk management and device optimization.
Challenges in Biocompatibility and Cytotoxicity Comparison
Biocompatibility testing presents challenges due to its comprehensive evaluation of a medical device's interaction with biological systems, requiring assessment of multiple endpoints such as irritation, sensitization, and systemic toxicity, whereas cytotoxicity testing primarily focuses on detecting cell-level toxicity. Variability in test methods, sample preparation, and interpretation of results often complicate direct comparisons between biocompatibility and cytotoxicity outcomes. Regulatory standards like ISO 10993 emphasize the importance of tailored testing strategies to address these challenges, ensuring safer and more effective medical device evaluation.
Future Trends in Medical Device Safety Testing
Biocompatibility testing is expanding to incorporate advanced in vitro models and omics technologies, providing a more comprehensive assessment of medical device safety beyond traditional cytotoxicity testing, which primarily evaluates cell viability and membrane integrity. Emerging trends emphasize the integration of predictive computational models and high-throughput screening to enhance the accuracy and speed of material-tissue interaction evaluations. The convergence of these innovative approaches aims to reduce reliance on animal testing and support regulatory frameworks with more reliable and mechanistic safety data.
Biocompatibility testing vs Cytotoxicity testing Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com