EEPROM offers byte-level erase and write capabilities, allowing for precise data modification with slower write speeds, while Flash memory erases data in larger blocks, providing faster write and erase cycles suitable for bulk storage. Flash memory is generally preferred for high-capacity applications due to its cost-effectiveness and speed, whereas EEPROM is ideal for storing small amounts of non-volatile data that require frequent updates. Both technologies retain data without power, but their structural and operational differences dictate their optimal usage scenarios in embedded hardware systems.
Table of Comparison
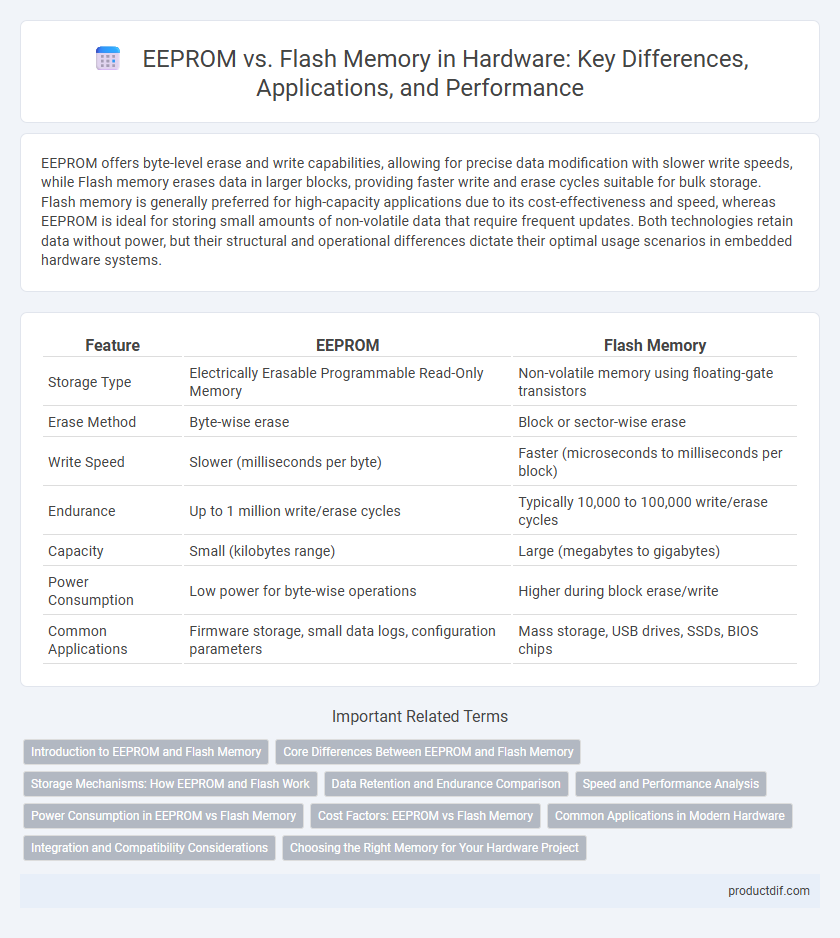
| Feature | EEPROM | Flash Memory |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Type | Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory | Non-volatile memory using floating-gate transistors |
| Erase Method | Byte-wise erase | Block or sector-wise erase |
| Write Speed | Slower (milliseconds per byte) | Faster (microseconds to milliseconds per block) |
| Endurance | Up to 1 million write/erase cycles | Typically 10,000 to 100,000 write/erase cycles |
| Capacity | Small (kilobytes range) | Large (megabytes to gigabytes) |
| Power Consumption | Low power for byte-wise operations | Higher during block erase/write |
| Common Applications | Firmware storage, small data logs, configuration parameters | Mass storage, USB drives, SSDs, BIOS chips |
Introduction to EEPROM and Flash Memory
EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) and Flash Memory are both non-volatile storage technologies used in hardware for data retention without power. EEPROM allows byte-level erasing and reprogramming, making it suitable for small data storage with frequent updates, while Flash Memory erases data in larger blocks, providing faster write and erase cycles ideal for mass storage. These differences impact their applications in embedded systems, firmware updates, and memory-intensive devices.
Core Differences Between EEPROM and Flash Memory
EEPROM provides byte-level data erasure and rewriting capabilities, making it ideal for small-scale data storage and frequent updates. Flash memory operates on block-level erasure and writing, which allows faster data transfer speeds and larger capacity, suitable for mass storage devices. The fundamental difference lies in their erasure granularity and application use cases--EEPROM serves low-density, persistent data needs, while flash memory supports high-density, large-scale storage.
Storage Mechanisms: How EEPROM and Flash Work
EEPROM stores data one byte at a time using electrical charges trapped in floating-gate transistors, allowing precise rewriting without erasing entire blocks. Flash memory operates by erasing and programming large blocks or sectors simultaneously, which enhances speed but reduces granularity compared to EEPROM. Both use floating-gate transistor technology but differ in erase cycles and data management, influencing their applications in embedded systems and data retention.
Data Retention and Endurance Comparison
EEPROM offers superior data retention, typically preserving information for over 100 years, while Flash memory generally retains data for around 10 to 20 years. Flash memory provides higher endurance in terms of write/erase cycles, supporting up to 100,000 cycles, compared to EEPROM's approximately 1 million cycles for byte-level writes but fewer cycles for block writes. This makes EEPROM more suitable for applications requiring infrequent, reliable updates, while Flash memory excels in high-volume write environments.
Speed and Performance Analysis
EEPROM offers slower write and erase speeds compared to flash memory due to its byte-level access, which increases latency during data operations. Flash memory utilizes block-level access, enabling faster write and erase cycles that enhance overall system performance in storage-intensive applications. Performance benchmarks indicate flash memory can achieve write speeds up to 100 times faster than EEPROM in typical embedded systems.
Power Consumption in EEPROM vs Flash Memory
EEPROM typically consumes less power during read operations compared to Flash memory due to its byte-level access and lower voltage requirements. However, Flash memory excels in energy efficiency during bulk data writes and erasures because it operates on larger data blocks, reducing total write cycles. Optimizing power consumption in hardware design involves selecting EEPROM for frequent small writes and Flash for high-capacity storage with less frequent updates.
Cost Factors: EEPROM vs Flash Memory
EEPROM typically incurs higher manufacturing costs per megabyte compared to flash memory due to its byte-level erase and write capabilities, which require more complex circuitry. Flash memory's block-based architecture enables lower production costs and higher storage densities, making it more economical for larger data storage applications. Cost efficiency makes flash memory the preferred choice for mass storage, while EEPROM is favored for smaller, frequent write operations despite its higher price.
Common Applications in Modern Hardware
EEPROM is commonly used in modern hardware for storing firmware, configuration settings, and small amounts of non-volatile data in embedded systems and microcontrollers. Flash memory, with its higher storage capacity and faster write speeds, is widely implemented in solid-state drives (SSDs), USB drives, and memory cards for consumer electronics. Both technologies support reliable data retention without power, but flash memory dominates applications requiring large-scale storage and frequent updates.
Integration and Compatibility Considerations
EEPROM typically offers byte-level read and write capabilities, making it highly compatible with low-density microcontrollers requiring frequent data updates. Flash memory provides block-level access and higher storage density, favoring integration in applications needing large firmware storage and fast read speeds. Compatibility depends on system architecture; EEPROM interfaces seamlessly with simpler systems, while Flash requires controllers capable of managing erase-write cycles and higher voltage operations.
Choosing the Right Memory for Your Hardware Project
EEPROM offers byte-level data erase and write capabilities, making it ideal for settings that require frequent updates and small data storage in hardware projects. Flash memory provides higher density and faster write speeds, suited for larger data storage and firmware updates but requires block-level erasing. Selecting the right memory depends on project needs for write cycles, data size, and update frequency, balancing cost and performance for optimal hardware functionality.
EEPROM vs Flash Memory Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com