Solder mask provides a protective coating over the PCB surface to prevent oxidation and solder bridging during assembly, enhancing durability and reliability. Silkscreen consists of printed labels and markings that identify component locations and reference designators, improving assembly accuracy and troubleshooting. Both layers are essential for optimized PCB functionality but serve distinct roles in the manufacturing process.
Table of Comparison
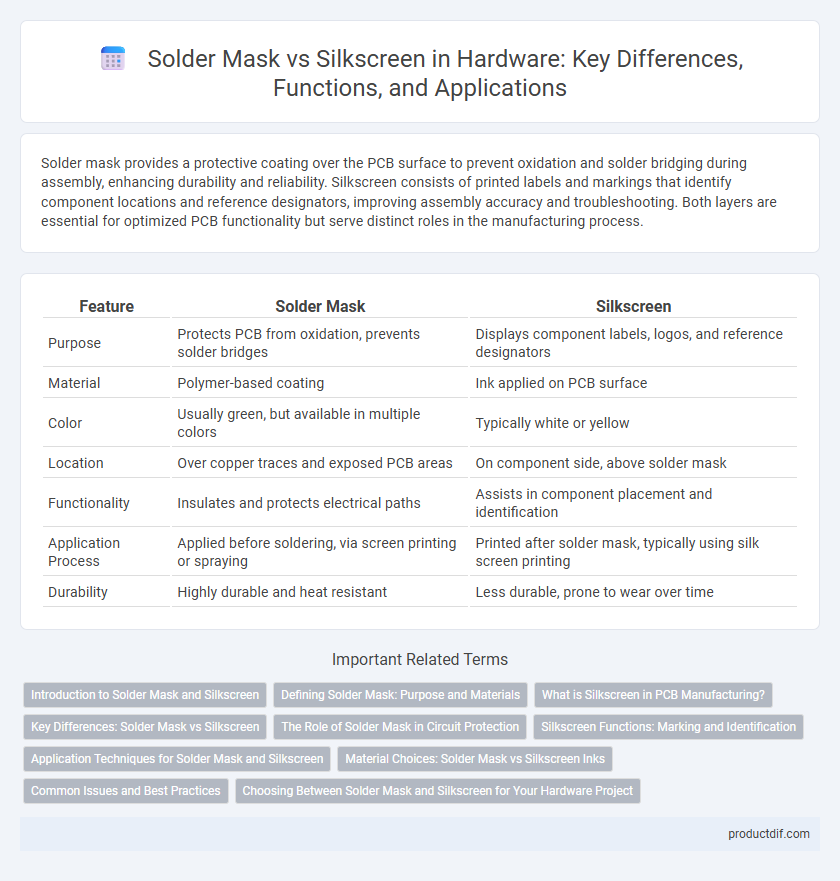
| Feature | Solder Mask | Silkscreen |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects PCB from oxidation, prevents solder bridges | Displays component labels, logos, and reference designators |
| Material | Polymer-based coating | Ink applied on PCB surface |
| Color | Usually green, but available in multiple colors | Typically white or yellow |
| Location | Over copper traces and exposed PCB areas | On component side, above solder mask |
| Functionality | Insulates and protects electrical paths | Assists in component placement and identification |
| Application Process | Applied before soldering, via screen printing or spraying | Printed after solder mask, typically using silk screen printing |
| Durability | Highly durable and heat resistant | Less durable, prone to wear over time |
Introduction to Solder Mask and Silkscreen
Solder mask is a protective layer applied to printed circuit boards (PCBs) that prevents solder bridges between closely spaced components and protects copper traces from oxidation. Silkscreen refers to the layer of ink used to print labels, symbols, and component identifiers directly onto the PCB surface, aiding in assembly and troubleshooting. Both solder mask and silkscreen are critical for PCB durability, functionality, and ease of maintenance in electronics manufacturing.
Defining Solder Mask: Purpose and Materials
Solder mask is a protective layer applied to printed circuit boards (PCBs) to prevent solder bridges and corrosion, enhancing electrical isolation between conductive traces. Typically made from epoxy liquid or dry film materials, it ensures durability and heat resistance during soldering processes. This coating also improves PCB reliability by safeguarding delicate components from environmental contaminants.
What is Silkscreen in PCB Manufacturing?
Silkscreen in PCB manufacturing refers to the layer of ink applied on the circuit board surface to display text, symbols, and component labels for assembly and troubleshooting purposes. It is typically printed using epoxy ink and provides visual guidance, ensuring accurate component placement and identification. Unlike solder masks, which protect copper traces and prevent solder bridging, silkscreens serve purely informational and aesthetic functions on the PCB.
Key Differences: Solder Mask vs Silkscreen
Solder mask is a protective layer applied on printed circuit boards (PCBs) that prevents solder bridging during assembly and protects copper traces from oxidation, whereas silkscreen is a layer used to print text and symbols, providing component identification and assembly instructions. Solder mask typically appears as a green (or other color) coating over the PCB surface, while silkscreen is printed in contrasting colors like white or black for readability. The primary function of solder mask is electrical insulation and protection, while silkscreen aids in PCB assembly and troubleshooting by labeling parts and connections.
The Role of Solder Mask in Circuit Protection
Solder mask serves as a vital protective layer on printed circuit boards (PCBs), preventing oxidation and solder bridging during assembly. This polymer coating insulates the copper traces, reducing the risk of short circuits and enhancing the board's durability against environmental factors like moisture and dust. Unlike silkscreen, which provides component labeling, the solder mask primarily ensures electrical isolation and physical protection of the circuitry.
Silkscreen Functions: Marking and Identification
Silkscreen on PCBs serves critical functions in marking and identification, providing clear labels for component placement, test points, and polarity indicators essential for assembly accuracy. Unlike the solder mask, which protects PCB traces from oxidation and prevents solder bridging, silkscreen enhances visual guidance, improving troubleshooting and maintenance efficiency. This layer uses non-conductive ink to ensure readability without interfering with electrical performance, making it vital for precise hardware fabrication and repair processes.
Application Techniques for Solder Mask and Silkscreen
Solder mask is applied through a photolithographic process where a liquid epoxy layer is exposed to UV light and then developed to protect PCB traces from oxidation and solder bridges. Silkscreen uses screen printing or inkjet technology to deposit component designators and labels onto the PCB surface for easy identification during assembly. Precise application of solder mask ensures electrical isolation, while accurate silkscreen placement improves assembly accuracy and troubleshooting.
Material Choices: Solder Mask vs Silkscreen Inks
Solder mask materials typically consist of epoxy liquid photoimageable inks that provide corrosion resistance and electrical insulation on PCB surfaces. Silkscreen inks are composed of epoxy or acrylic-based materials designed for high contrast markings and readability, ensuring component identification and assembly accuracy. The distinct chemical compositions influence adhesion, durability, and resistance to thermal and chemical stress during PCB manufacturing and operation.
Common Issues and Best Practices
Common issues with solder mask include improper curing leading to delamination and short circuits caused by mask misalignment, while silkscreen problems often involve poor adhesion and smudging during assembly. Best practices for solder mask application emphasize precise registration, thorough curing processes, and selecting compatible materials to ensure durability. For silkscreen, using high-contrast, heat-resistant inks and verifying print alignment improves readability and maintains clarity throughout PCB lifespan.
Choosing Between Solder Mask and Silkscreen for Your Hardware Project
Solder mask provides essential protection by insulating the PCB surface and preventing solder bridges during assembly, while silkscreen offers valuable component labeling and orientation guidance. Selecting solder mask is crucial for ensuring electrical insulation and reliability, whereas silkscreen enhances clarity and aids troubleshooting through visible markings. Prioritize solder mask for functional protection and silkscreen for effective communication in your hardware design.
Solder mask vs Silkscreen Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com