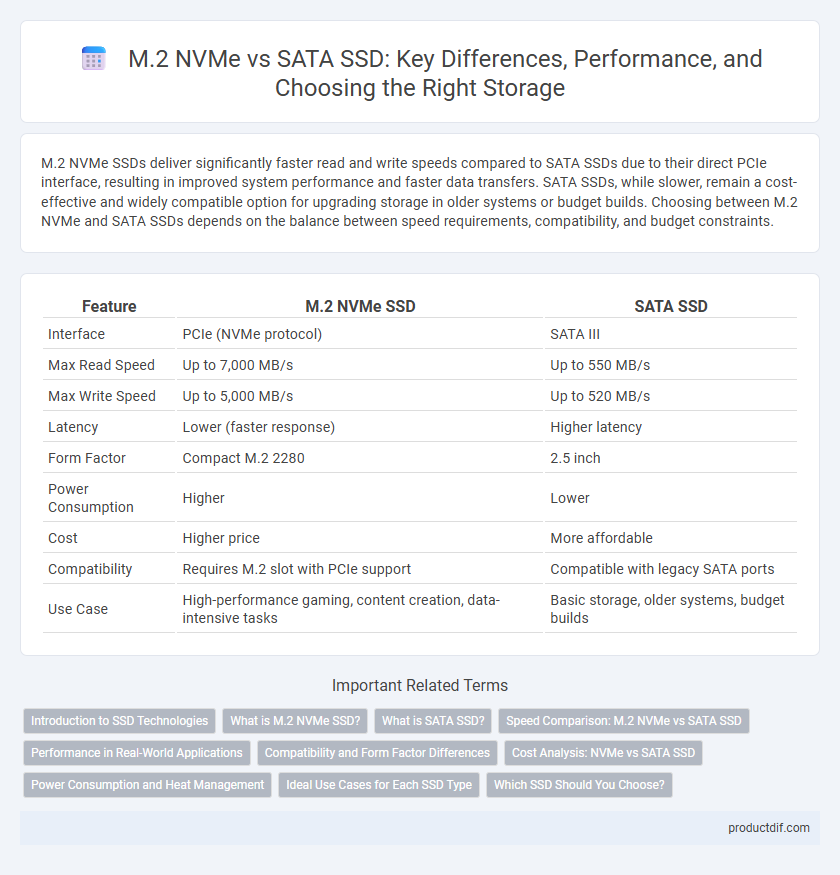
M.2 NVMe SSDs deliver significantly faster read and write speeds compared to SATA SSDs due to their direct PCIe interface, resulting in improved system performance and faster data transfers. SATA SSDs, while slower, remain a cost-effective and widely compatible option for upgrading storage in older systems or budget builds. Choosing between M.2 NVMe and SATA SSDs depends on the balance between speed requirements, compatibility, and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | M.2 NVMe SSD | SATA SSD |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | PCIe (NVMe protocol) | SATA III |
| Max Read Speed | Up to 7,000 MB/s | Up to 550 MB/s |
| Max Write Speed | Up to 5,000 MB/s | Up to 520 MB/s |
| Latency | Lower (faster response) | Higher latency |
| Form Factor | Compact M.2 2280 | 2.5 inch |
| Power Consumption | Higher | Lower |
| Cost | Higher price | More affordable |
| Compatibility | Requires M.2 slot with PCIe support | Compatible with legacy SATA ports |
| Use Case | High-performance gaming, content creation, data-intensive tasks | Basic storage, older systems, budget builds |
Introduction to SSD Technologies
M.2 NVMe SSDs leverage the PCIe interface, offering significantly faster data transfer speeds compared to SATA SSDs, which use the older SATA III interface limited to 6 Gbps. NVMe technology reduces latency and improves IOPS performance by enabling direct communication between storage and the CPU through the PCIe bus. SATA SSDs remain compatible with a wider range of devices but are outperformed by NVMe SSDs in speed-intensive applications like gaming and professional video editing.
What is M.2 NVMe SSD?
M.2 NVMe SSDs utilize the Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) protocol to deliver significantly faster data transfer speeds compared to traditional SATA SSDs, leveraging the PCIe interface for direct communication with the CPU. These drives are compact M.2 form factor modules, designed to optimize performance in ultrabooks, gaming PCs, and workstations by reducing latency and increasing input/output operations per second (IOPS). M.2 NVMe SSDs offer enhanced bandwidth, typically reaching speeds up to 3500 MB/s or higher, far surpassing the 600 MB/s limit of SATA SSDs, making them ideal for demanding applications and rapid data access.
What is SATA SSD?
SATA SSDs use the Serial ATA interface to connect storage devices, offering data transfer speeds up to 600 MB/s, which is significantly faster than traditional HDDs but slower compared to NVMe SSDs. SATA SSDs are widely compatible with most laptops and desktops, making them a cost-effective upgrade for improved system performance and faster boot times. Their architecture relies on AHCI protocol, which limits bandwidth compared to the PCIe interface used by NVMe drives.
Speed Comparison: M.2 NVMe vs SATA SSD
M.2 NVMe SSDs deliver significantly faster read and write speeds compared to SATA SSDs, often exceeding 3,000 MB/s versus the typical 550 MB/s of SATA drives. This performance boost results from the NVMe protocol utilizing PCIe lanes, enabling higher bandwidth and lower latency than SATA's AHCI interface. For tasks requiring rapid data access and transfer, such as gaming, video editing, or database management, M.2 NVMe offers superior speed and responsiveness.
Performance in Real-World Applications
M.2 NVMe SSDs deliver significantly faster read and write speeds compared to SATA SSDs, with typical sequential transfer rates exceeding 3000 MB/s versus SATA's 550 MB/s, enhancing boot times and file transfers. Real-world applications such as gaming, video editing, and database management experience reduced latency and quicker load times with NVMe drives due to their parallel processing capabilities and lower I/O overhead. For workflows involving large, random data access and high throughput, M.2 NVMe SSDs offer superior performance that translates into measurable productivity gains over SATA SSDs.
Compatibility and Form Factor Differences
M.2 NVMe SSDs utilize the PCIe interface, requiring compatible motherboard M.2 slots that support NVMe protocol, while SATA SSDs connect via traditional SATA ports found on virtually all motherboards. The M.2 form factor is compact and varies in size, typically 22mm wide with lengths of 30, 42, 60, 80, or 110mm, enabling direct mounting on the motherboard, whereas SATA SSDs are usually 2.5-inch drives requiring cable connections. Compatibility depends on motherboard support for NVMe PCIe lanes versus SATA interfaces, with M.2 offering faster data transfer rates but requiring modern hardware.
Cost Analysis: NVMe vs SATA SSD
M.2 NVMe SSDs generally come with higher price points compared to SATA SSDs due to advanced technology and faster data transfer speeds, typically costing around $0.10 to $0.25 per gigabyte versus SATA's $0.08 to $0.15 per gigabyte. NVMe drives deliver superior performance and lower latency, justifying the premium in environments requiring rapid data access, such as gaming or professional workloads. SATA SSDs remain a cost-effective solution for everyday computing needs where budget constraints outweigh the need for peak speed.
Power Consumption and Heat Management
M.2 NVMe SSDs typically consume more power than SATA SSDs due to their higher performance and faster data transfer rates, impacting battery life in portable devices. NVMe drives generate more heat, often requiring advanced heat sinks or thermal pads to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent throttling. SATA SSDs, while slower, generally operate with lower power consumption and heat output, making them suitable for energy-efficient systems with minimal cooling solutions.
Ideal Use Cases for Each SSD Type
M.2 NVMe SSDs excel in high-performance computing tasks like gaming, video editing, and large data transfers due to their superior speed and low latency, leveraging PCIe lanes for faster data throughput. SATA SSDs remain ideal for everyday computing needs, including web browsing, office applications, and moderate storage upgrades, offering reliability and compatibility with older systems at a lower cost. Selecting between M.2 NVMe and SATA SSDs depends on balancing budget constraints with performance requirements tailored to specific workloads.
Which SSD Should You Choose?
M.2 NVMe SSDs deliver significantly faster read and write speeds, making them ideal for gaming, video editing, and heavy multitasking, with transfer rates often exceeding 3000 MB/s compared to SATA SSDs capped around 600 MB/s. SATA SSDs, while slower, provide a cost-effective upgrade for general computing needs and are compatible with older systems lacking M.2 slots. Choosing between the two depends on your system's motherboard support, budget, and performance requirements, with M.2 NVMe being the best option for speed-critical applications.
M.2 NVMe vs SATA SSD Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com