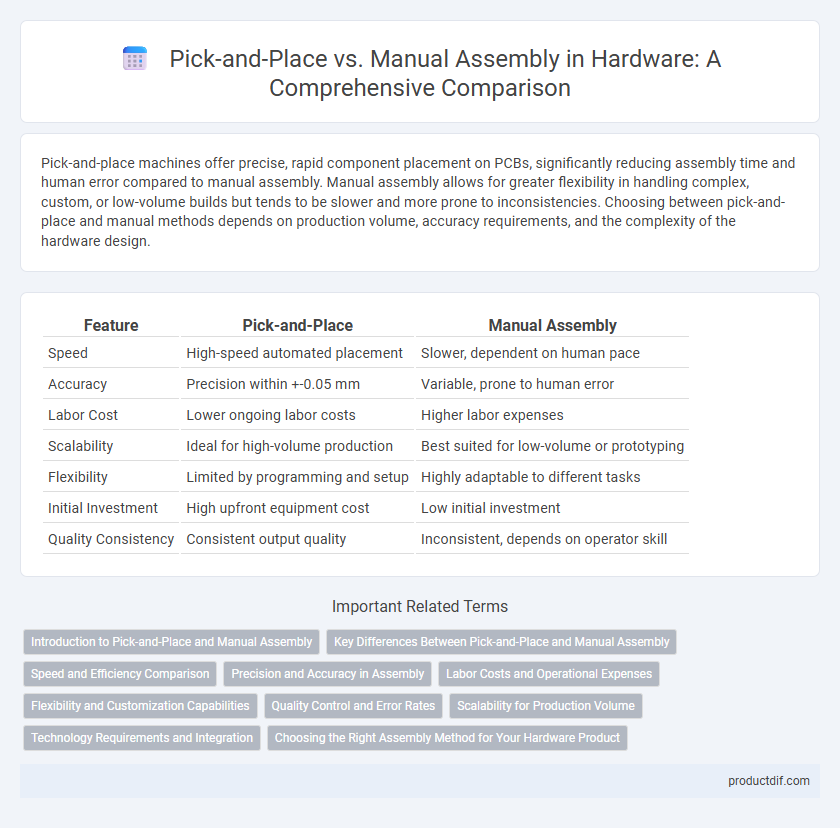
Pick-and-place machines offer precise, rapid component placement on PCBs, significantly reducing assembly time and human error compared to manual assembly. Manual assembly allows for greater flexibility in handling complex, custom, or low-volume builds but tends to be slower and more prone to inconsistencies. Choosing between pick-and-place and manual methods depends on production volume, accuracy requirements, and the complexity of the hardware design.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pick-and-Place | Manual Assembly |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | High-speed automated placement | Slower, dependent on human pace |
| Accuracy | Precision within +-0.05 mm | Variable, prone to human error |
| Labor Cost | Lower ongoing labor costs | Higher labor expenses |
| Scalability | Ideal for high-volume production | Best suited for low-volume or prototyping |
| Flexibility | Limited by programming and setup | Highly adaptable to different tasks |
| Initial Investment | High upfront equipment cost | Low initial investment |
| Quality Consistency | Consistent output quality | Inconsistent, depends on operator skill |
Introduction to Pick-and-Place and Manual Assembly
Pick-and-place machines automate the precise placement of surface-mount devices onto printed circuit boards, significantly enhancing production speed and accuracy compared to manual assembly. Manual assembly relies on skilled technicians to position and solder components by hand, which can introduce variability and slower throughput. The integration of pick-and-place technology is essential for meeting high-volume manufacturing demands while maintaining consistent quality.
Key Differences Between Pick-and-Place and Manual Assembly
Pick-and-place machines offer high precision and speed by automatically positioning components on circuit boards, significantly reducing human error compared to manual assembly. Manual assembly relies on skilled technicians to place parts, which can be time-consuming and less consistent but allows for flexibility in handling complex or customized tasks. The key differences include automation level, efficiency, scalability, and accuracy, with pick-and-place excelling in mass production and manual assembly favored for prototyping or small batches.
Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Pick-and-place machines significantly outperform manual assembly in speed, capable of placing thousands of components per hour with high precision and repeatability. Manual assembly's slower pace and susceptibility to human error reduce overall efficiency, especially in high-volume production environments. Automation using pick-and-place technology leads to consistent quality and shorter production cycles, maximizing throughput and minimizing labor costs.
Precision and Accuracy in Assembly
Pick-and-place machines deliver superior precision and accuracy in assembly by automating component placement with consistent repeatability and micron-level alignment, reducing human error inherent in manual assembly. Manual assembly relies heavily on the skill and steadiness of technicians, leading to variability in placement accuracy and higher risk of misalignment or component damage. Industrial studies show pick-and-place systems improve assembly accuracy by up to 30%, enhancing product reliability in high-density electronic manufacturing.
Labor Costs and Operational Expenses
Pick-and-place machines significantly reduce labor costs by automating component placement with high precision and speed compared to manual assembly, which requires intensive human labor and increases operational expenses. Automated systems improve production efficiency and minimize errors, leading to lower rework and material waste costs. Although initial investment for pick-and-place equipment is high, long-term operational expenses decline due to reduced staffing needs and faster throughput.
Flexibility and Customization Capabilities
Pick-and-place machines offer high precision and speed while allowing limited flexibility in handling diverse component types and board layouts, making them ideal for mass production with consistent quality. Manual assembly provides unparalleled customization capabilities, enabling technicians to adapt to complex or unique designs that automated systems may struggle with, though it often sacrifices scalability and speed. Balancing pick-and-place efficiency with manual assembly customization optimizes production workflows for electronics manufacturing demanding both flexibility and precision.
Quality Control and Error Rates
Pick-and-place machines significantly enhance quality control by ensuring consistent component placement with minimal error rates, often achieving accuracy within +-0.01 mm. Manual assembly, however, is prone to variability due to human factors, resulting in higher defect rates and increased risk of misplaced or damaged parts. Automated pick-and-place systems reduce rework costs and improve overall product reliability compared to manual processes.
Scalability for Production Volume
Pick-and-place machines offer unparalleled scalability for high production volumes, enabling rapid, precise component placement with minimal human intervention, which significantly reduces errors and increases throughput. Manual assembly, while flexible for low-volume or prototype runs, struggles to maintain consistency and speed as production scales, leading to increased labor costs and potential quality variability. Automated hardware assembly systems optimize manufacturing efficiency by supporting scalable output without sacrificing accuracy or reliability.
Technology Requirements and Integration
Pick-and-place machines demand advanced robotics, vision systems, and precise control software for automated component placement, ensuring high accuracy and speed. Manual assembly relies on skilled labor with minimal technology, emphasizing flexibility but limited scalability and consistency. Integration of pick-and-place systems requires seamless communication between CAD data, feeders, and conveyors, enabling efficient workflow automation in manufacturing lines.
Choosing the Right Assembly Method for Your Hardware Product
Pick-and-place machines deliver precise, high-speed component placement ideal for mass production of complex hardware, reducing human error and increasing throughput. Manual assembly offers flexibility for low-volume, customized, or prototype hardware products requiring intricate handling and adjustments. Selecting the optimal assembly method depends on production volume, component complexity, cost constraints, and desired manufacturing speed.
Pick-and-Place vs Manual Assembly Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com