PoP (Package on Package) technology stacks memory chips directly on top of the processor to save space and improve performance, while SoC (System on Chip) integrates all components, including CPU, GPU, and memory, onto a single silicon chip. PoP offers flexibility for upgrading memory independently, whereas SoC provides a more compact design with potentially lower power consumption and improved data transfer efficiency. Choosing between PoP and SoC depends on the specific requirements for device size, performance, and manufacturing complexity.
Table of Comparison
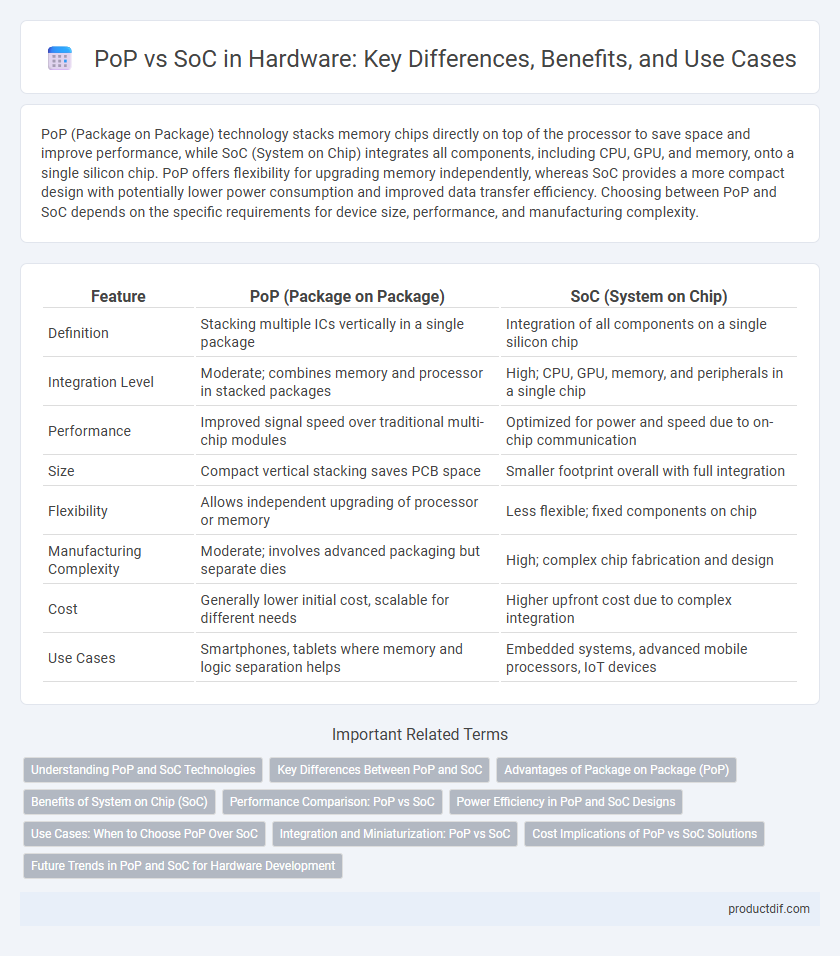
| Feature | PoP (Package on Package) | SoC (System on Chip) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Stacking multiple ICs vertically in a single package | Integration of all components on a single silicon chip |
| Integration Level | Moderate; combines memory and processor in stacked packages | High; CPU, GPU, memory, and peripherals in a single chip |
| Performance | Improved signal speed over traditional multi-chip modules | Optimized for power and speed due to on-chip communication |
| Size | Compact vertical stacking saves PCB space | Smaller footprint overall with full integration |
| Flexibility | Allows independent upgrading of processor or memory | Less flexible; fixed components on chip |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Moderate; involves advanced packaging but separate dies | High; complex chip fabrication and design |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost, scalable for different needs | Higher upfront cost due to complex integration |
| Use Cases | Smartphones, tablets where memory and logic separation helps | Embedded systems, advanced mobile processors, IoT devices |
Understanding PoP and SoC Technologies
PoP (Package on Package) technology stacks multiple integrated circuits vertically, enhancing space efficiency and improving signal transmission for mobile devices. SoC (System on Chip) integrates all essential components, including CPU, GPU, memory, and I/O interfaces, onto a single semiconductor chip, optimizing performance and power consumption. Understanding the differences between PoP and SoC technologies helps in selecting the appropriate hardware solution for compact design and high integration requirements.
Key Differences Between PoP and SoC
PoP (Package on Package) stacks multiple integrated circuits vertically, optimizing space and enhancing memory bandwidth, while SoC (System on Chip) integrates all components, including CPU, GPU, and memory, into a single silicon chip for improved performance and power efficiency. PoP allows flexible memory upgrading and separate manufacturing of logic and memory dies, whereas SoC offers lower latency and reduced electrical interference due to tighter integration. Key differences lie in design flexibility, component integration, and impact on device size, power consumption, and overall system complexity.
Advantages of Package on Package (PoP)
Package on Package (PoP) technology offers significant advantages over System on Chip (SoC) designs by enabling higher integration density and improved thermal management. PoP allows separate optimization of logic and memory layers, enhancing performance flexibility and reducing design complexity. This stacking approach also shortens signal paths, resulting in faster data transfer rates and lower power consumption in compact hardware applications.
Benefits of System on Chip (SoC)
System on Chip (SoC) integrates multiple components such as CPU, GPU, memory, and input/output ports onto a single chip, significantly reducing power consumption and physical space compared to Package on Package (PoP) technology. SoC enhances performance and reliability by minimizing interconnect delays and signal losses, resulting in faster data processing and improved thermal management. The compact design of SoC also lowers manufacturing costs and simplifies device assembly, making it ideal for mobile and embedded systems demanding high efficiency.
Performance Comparison: PoP vs SoC
PoP (Package on Package) architecture allows stacking memory and logic chips vertically, enhancing data transfer speeds and reducing latency compared to traditional SoC (System on Chip) designs, which integrate components on a single silicon die. PoP can achieve higher memory bandwidth and improved thermal performance due to physical separation of components, benefiting applications requiring intensive memory access. However, SoCs typically offer lower power consumption and better integration efficiency, making them suitable for compact, energy-sensitive devices.
Power Efficiency in PoP and SoC Designs
PoP (Package on Package) designs enable improved power efficiency by allowing separate optimization of memory and processor components, which reduces power leakage and enhances thermal management compared to SoC (System on Chip) integration. SoC designs offer tight integration leading to lower overall power consumption for data transfer between components but can face challenges in balancing power efficiency across diverse functionalities. Power efficiency in PoP architectures benefits from modular upgrades and targeted power gating, while SoC designs require advanced process technologies and voltage scaling to minimize energy consumption.
Use Cases: When to Choose PoP Over SoC
PoP (Package on Package) technology is ideal for smartphones and tablets requiring compact design and high memory capacity, as it allows stacking of memory and processor in a limited space. SoC (System on Chip) is better suited for devices that require integrated components on a single chip to optimize power efficiency and reduce latency, such as embedded systems and IoT devices. Choosing PoP is advantageous when upgrading or customizing memory separately from the processor without redesigning the entire system.
Integration and Miniaturization: PoP vs SoC
PoP (Package on Package) integration stacks multiple semiconductor dies vertically, enhancing miniaturization by saving PCB space and enabling heterogeneous component combination such as DRAM and processor units. In contrast, SoC (System on Chip) integrates all components within a single silicon die, offering superior performance and power efficiency due to reduced interconnect distances. PoP provides flexibility in assembly and upgrading individual components, whereas SoC delivers compactness and optimized signal integrity essential for advanced mobile and embedded hardware applications.
Cost Implications of PoP vs SoC Solutions
PoP (Package on Package) solutions typically incur higher manufacturing costs due to the complexity of stacking multiple dies, increased testing requirements, and specialized assembly processes. SoC (System on Chip) designs, while often more expensive upfront due to extensive chip design and fabrication, reduce overall bill-of-materials and assembly expenses by integrating components into a single chip. Cost implications vary significantly depending on volume, product complexity, and functionality, with PoP being more cost-effective for moderate production runs and SoC favored in high-volume applications.
Future Trends in PoP and SoC for Hardware Development
Future trends in hardware development highlight the increasing integration and miniaturization in Package on Package (PoP) and System on Chip (SoC) technologies, driving higher performance and energy efficiency. PoP advancements focus on improved vertical stacking techniques and heterogeneous integration for enhanced memory and processing capabilities, while SoC evolution emphasizes AI acceleration, 5G connectivity, and advanced semiconductor nodes. Emerging materials and 3D packaging innovations are expected to further bridge the gap between PoP and SoC, enabling more compact, powerful, and versatile hardware solutions for next-generation devices.
PoP vs SoC Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com