Build-to-Order hardware offers customization and flexibility, enabling manufacturers to tailor products to specific customer needs while minimizing inventory costs. Mass production emphasizes high volume and standardized components, driving economies of scale and reducing per-unit cost but sacrificing personalization. Choosing between these approaches depends on demand variability, production speed requirements, and cost considerations.
Table of Comparison
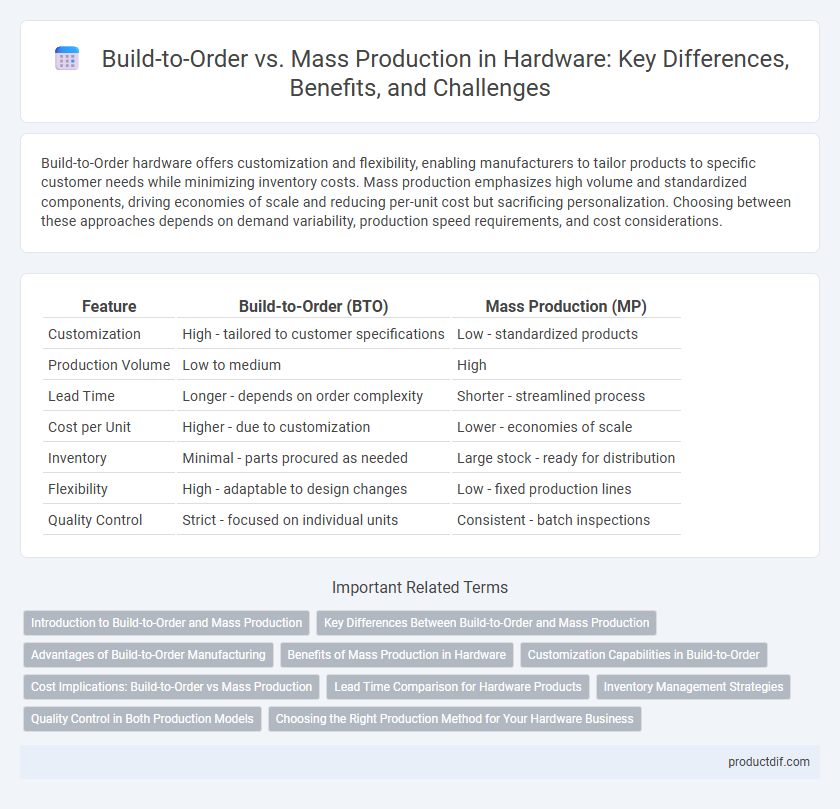
| Feature | Build-to-Order (BTO) | Mass Production (MP) |
|---|---|---|
| Customization | High - tailored to customer specifications | Low - standardized products |
| Production Volume | Low to medium | High |
| Lead Time | Longer - depends on order complexity | Shorter - streamlined process |
| Cost per Unit | Higher - due to customization | Lower - economies of scale |
| Inventory | Minimal - parts procured as needed | Large stock - ready for distribution |
| Flexibility | High - adaptable to design changes | Low - fixed production lines |
| Quality Control | Strict - focused on individual units | Consistent - batch inspections |
Introduction to Build-to-Order and Mass Production
Build-to-Order (BTO) manufacturing customizes hardware products based on specific customer requirements, allowing flexibility in design and features while minimizing inventory costs. Mass Production involves producing large quantities of standardized hardware units using assembly lines, optimizing economies of scale and reducing per-unit cost. BTO suits niche markets with unique demands, whereas mass production fits high-volume markets prioritizing cost efficiency and uniformity.
Key Differences Between Build-to-Order and Mass Production
Build-to-Order (BTO) hardware manufacturing customizes products to individual specifications, reducing inventory costs and allowing greater flexibility, while Mass Production focuses on high-volume output with standardized components to maximize efficiency and minimize per-unit cost. BTO typically results in longer lead times and higher unit costs but offers enhanced product personalization, whereas Mass Production delivers faster delivery and economies of scale at the expense of customization. The choice between BTO and Mass Production depends on the balance between market demand for tailored hardware solutions and the need for cost-effective, rapid deployment.
Advantages of Build-to-Order Manufacturing
Build-to-Order manufacturing enables customized hardware solutions tailored to specific customer needs, reducing inventory costs and minimizing waste. This approach enhances flexibility, allowing rapid adaptation to market changes and technological advancements. Improved customer satisfaction and higher profit margins are achieved through personalized products and efficient resource utilization.
Benefits of Mass Production in Hardware
Mass production in hardware manufacturing significantly reduces unit costs through economies of scale, enabling affordable pricing for consumers and increased profit margins for companies. Standardized processes and automation enhance product consistency and quality control, minimizing defects and returns. High-volume output meets large market demands efficiently, ensuring faster delivery and availability across global distribution channels.
Customization Capabilities in Build-to-Order
Build-to-Order (BTO) hardware offers superior customization capabilities by allowing customers to select specific components such as CPUs, GPUs, memory size, and cooling systems tailored to their needs. This approach supports unique configurations for specialized applications, enhancing performance efficiency and user satisfaction. In contrast, mass production focuses on uniformity and cost reduction, limiting customization options significantly.
Cost Implications: Build-to-Order vs Mass Production
Build-to-order manufacturing typically incurs higher per-unit costs due to customized components and lower economies of scale, impacting overall production expenses. Mass production benefits from bulk purchasing, standardized processes, and streamlined assembly lines, significantly reducing the cost per unit. Companies must weigh these cost implications against demand predictability and inventory risks when choosing between build-to-order and mass production models.
Lead Time Comparison for Hardware Products
Build-to-order hardware products typically have longer lead times ranging from several days to weeks due to customized assembly and components sourcing. Mass production hardware benefits from significantly shorter lead times, often measured in hours to days, due to standardized processes and bulk inventory availability. Efficient supply chain management and just-in-time manufacturing further reduce lead times in mass production compared to the more flexible yet slower build-to-order model.
Inventory Management Strategies
Build-to-order hardware manufacturing minimizes inventory holding costs by producing items based on actual customer demand, reducing excess stock and obsolescence risks. Mass production relies on forecasting and maintaining large inventory levels to achieve economies of scale, which can lead to higher storage expenses and potential inventory write-downs if demand fluctuates. Effective inventory management strategies in build-to-order systems emphasize just-in-time procurement and dynamic supply chain coordination, whereas mass production focuses on demand forecasting accuracy and inventory turnover optimization.
Quality Control in Both Production Models
Build-to-Order production enables stringent quality control by allowing customization and inspection at each assembly stage, reducing defects through tailored component selection. Mass production benefits from standardized quality control protocols and automated testing systems that ensure consistency across large volumes. Both models utilize statistical process control methods to monitor production quality, but Build-to-Order emphasizes flexibility while Mass Production prioritizes efficiency and uniformity.
Choosing the Right Production Method for Your Hardware Business
Build-to-order manufacturing offers customized hardware solutions tailored to specific customer requirements, enhancing product uniqueness and reducing inventory costs. Mass production excels in generating large volumes of standardized hardware with economies of scale, lowering per-unit costs and accelerating delivery times. Hardware businesses must evaluate factors like market demand, customization needs, production costs, and lead times to determine the optimal production method that aligns with their strategic goals.
Build-to-Order vs Mass Production Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com