Surface mount assembly offers faster production speeds and higher precision for placing tiny components on PCBs, significantly improving manufacturing efficiency compared to hand soldering. Hand soldering provides greater flexibility for prototyping and repairs but is more time-consuming and prone to human error, especially with intricate circuits. Automated surface mount assembly ensures consistent quality and repeatability, making it ideal for large-scale hardware production.
Table of Comparison
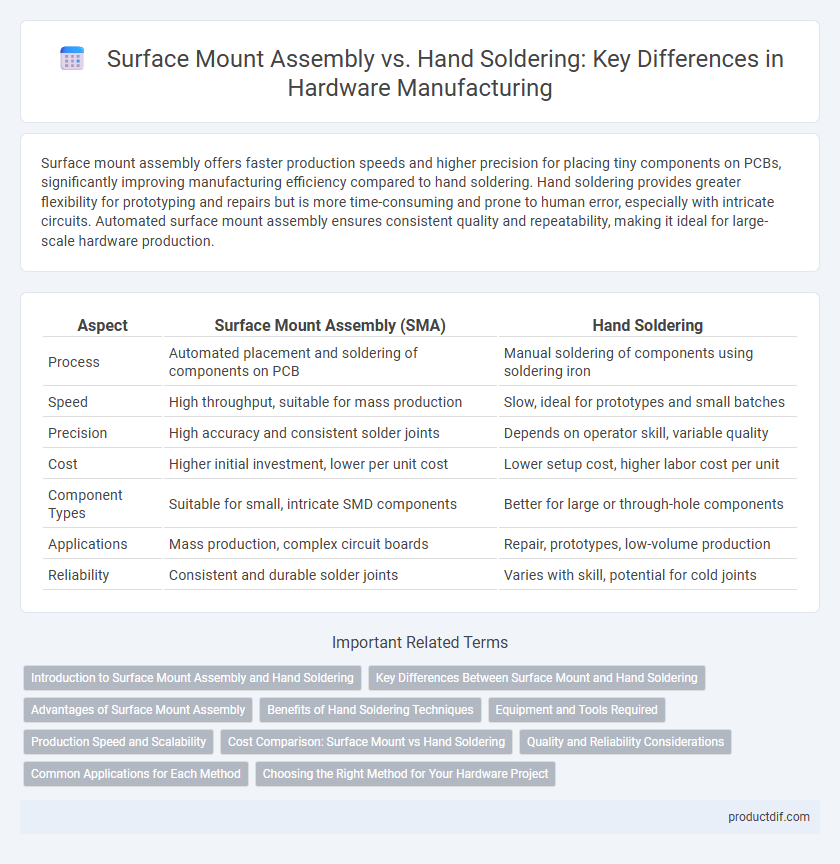
| Aspect | Surface Mount Assembly (SMA) | Hand Soldering |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Automated placement and soldering of components on PCB | Manual soldering of components using soldering iron |
| Speed | High throughput, suitable for mass production | Slow, ideal for prototypes and small batches |
| Precision | High accuracy and consistent solder joints | Depends on operator skill, variable quality |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower per unit cost | Lower setup cost, higher labor cost per unit |
| Component Types | Suitable for small, intricate SMD components | Better for large or through-hole components |
| Applications | Mass production, complex circuit boards | Repair, prototypes, low-volume production |
| Reliability | Consistent and durable solder joints | Varies with skill, potential for cold joints |
Introduction to Surface Mount Assembly and Hand Soldering
Surface Mount Assembly (SMA) involves placing and soldering electronic components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs) using automated machinery, optimizing precision and production speed for complex designs. Hand soldering is the manual process of attaching components to PCBs with a soldering iron, commonly used for prototyping, repairs, and low-volume production due to its flexibility and control. Understanding the differences in application, efficiency, and component compatibility between Surface Mount Assembly and Hand Soldering is crucial for selecting the appropriate method in electronics manufacturing.
Key Differences Between Surface Mount and Hand Soldering
Surface mount assembly uses automated processes to place and solder components directly onto the PCB surface, enabling high precision and faster production rates compared to hand soldering. Hand soldering relies on manual application of solder to component leads, which can lead to inconsistencies and slower throughput but offers greater flexibility for prototyping and repair work. The key differences include automation level, production speed, precision, and suitability for complex, high-density circuits in surface mount assembly versus the tactile control and adaptability of hand soldering.
Advantages of Surface Mount Assembly
Surface Mount Assembly offers higher precision and consistency in component placement compared to hand soldering, resulting in improved product reliability. Automated processes enable faster production rates and reduced labor costs, making it ideal for large-scale manufacturing. The ability to accommodate smaller and more complex components enhances overall device miniaturization and performance.
Benefits of Hand Soldering Techniques
Hand soldering offers precise control over component placement and solder joint quality, making it ideal for complex or prototype electronic assemblies. This technique enables quick adjustments and corrections without the need for specialized machinery, reducing setup time and cost. Skilled technicians can ensure reliable electrical connections and minimize the risk of thermal damage to sensitive components during soldering.
Equipment and Tools Required
Surface Mount Assembly requires specialized equipment such as pick-and-place machines, reflow ovens, and automated inspection systems to achieve high precision and efficiency in mounting components. Hand Soldering primarily relies on manual tools including soldering irons, tweezers, magnifying glasses, and flux dispensers, suitable for prototyping or repair work. Automated machinery in Surface Mount Assembly enhances consistency and throughput, whereas hand soldering offers flexibility for complex or low-volume tasks.
Production Speed and Scalability
Surface mount assembly significantly outperforms hand soldering in production speed, enabling rapid placement of components through automated machinery that can handle thousands of units per hour. Scalability is inherently greater with surface mount assembly, as automated processes allow easy adjustment for large-scale manufacturing without compromising consistency or quality. Hand soldering remains slower and less scalable due to its labor-intensive nature, limiting throughput and increasing variability in mass production environments.
Cost Comparison: Surface Mount vs Hand Soldering
Surface mount assembly offers significant cost advantages over hand soldering due to automation and higher throughput, reducing labor expenses and minimizing human error. Hand soldering incurs increased labor costs with longer production times and potential rework, making it less economical for large-scale manufacturing. For small production runs or prototypes, hand soldering may have lower initial setup costs but lacks the scalability and overall cost efficiency of surface mount assembly.
Quality and Reliability Considerations
Surface mount assembly offers higher precision and consistency in solder joints compared to hand soldering, reducing the risk of defects such as cold joints and bridging. Automated processes ensure uniform heat application, enhancing component integrity and long-term reliability in high-volume production. Hand soldering, while flexible for prototyping or repair, introduces greater variability and potential for human error, impacting overall quality and durability of the final hardware product.
Common Applications for Each Method
Surface mount assembly excels in producing high-density electronic circuits commonly found in smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices due to its precision and automation capabilities. Hand soldering is preferred for repair work, prototyping, and low-volume production where flexibility and precision on individual components, such as connectors or discrete components, are crucial. Both methods play key roles in electronics manufacturing, balancing efficiency and customization.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Hardware Project
Surface mount assembly offers high precision and efficiency for complex hardware projects with dense circuit layouts, ensuring consistent solder joints and scalability. Hand soldering is ideal for prototypes, small batches, or repairs where flexibility and accessibility to components are crucial. Selecting the right soldering method depends on project volume, component type, and desired production quality to optimize performance and cost-effectiveness.
Surface Mount Assembly vs Hand Soldering Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com