DDR5 memory offers higher bandwidth and improved power efficiency compared to DDR4, making it ideal for demanding applications and future-proof systems. While DDR4 remains cost-effective and compatible with a broad range of existing hardware, DDR5's enhanced performance supports faster data transfer rates and increased module capacity. Transitioning to DDR5 enables better multitasking and gaming experiences due to its superior speed and advanced architecture.
Table of Comparison
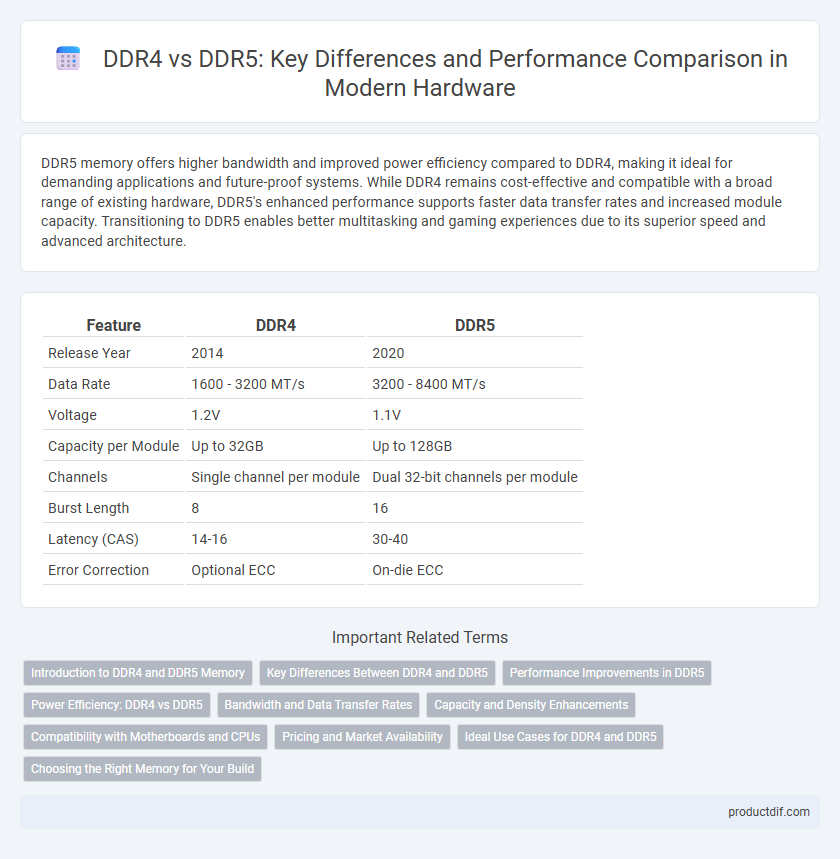
| Feature | DDR4 | DDR5 |
|---|---|---|
| Release Year | 2014 | 2020 |
| Data Rate | 1600 - 3200 MT/s | 3200 - 8400 MT/s |
| Voltage | 1.2V | 1.1V |
| Capacity per Module | Up to 32GB | Up to 128GB |
| Channels | Single channel per module | Dual 32-bit channels per module |
| Burst Length | 8 | 16 |
| Latency (CAS) | 14-16 | 30-40 |
| Error Correction | Optional ECC | On-die ECC |
Introduction to DDR4 and DDR5 Memory
DDR4 memory, introduced in 2014, offers data transfer rates ranging from 2133 MT/s to 3200 MT/s with a typical voltage of 1.2V, providing improved power efficiency and higher bandwidth compared to its predecessor DDR3. DDR5 memory, launched around 2020, significantly enhances performance with data rates starting at 4800 MT/s and potential scalability up to 8400 MT/s, operates at a lower voltage of 1.1V, and features increased memory density, enabling larger RAM capacities and improved power management. Both DDR4 and DDR5 use dual inline memory modules (DIMMs), but DDR5's architecture introduces independent subchannels and better error correction capabilities, optimizing speed and reliability for modern computing demands.
Key Differences Between DDR4 and DDR5
DDR5 memory offers double the bandwidth of DDR4, supporting speeds up to 6400 MT/s compared to DDR4's maximum of 3200 MT/s, which significantly enhances data transfer rates for high-performance computing. DDR5 modules feature increased capacity per DIMM, reaching up to 128GB, while DDR4 typically caps at 32GB, enabling better multitasking and memory-intensive applications. Improved power efficiency in DDR5 is achieved through a reduced operating voltage of 1.1V versus DDR4's 1.2V, along with on-die ECC for enhanced reliability, making DDR5 the preferred choice for future-proof systems.
Performance Improvements in DDR5
DDR5 memory delivers significant performance improvements over DDR4 by offering higher data transfer rates, starting at 4800 MT/s compared to DDR4's maximum of 3200 MT/s. It features doubled bank groups and enhanced burst lengths, enabling more efficient data handling and reduced latency during multitasking and gaming. Enhanced power management with integrated voltage regulation improves overall system stability and energy efficiency in high-performance computing environments.
Power Efficiency: DDR4 vs DDR5
DDR5 memory delivers significant improvements in power efficiency compared to DDR4, featuring a lower power supply voltage of 1.1V versus DDR4's 1.2V, which reduces overall energy consumption in computing systems. DDR5 also integrates on-die ECC (Error Correcting Code) and improved power management ICs that enable finer control of power usage, enhancing performance-per-watt ratios crucial for high-performance and mobile applications. This advanced power architecture in DDR5 results in longer battery life for laptops and lower thermal output in servers, making it a more energy-efficient choice for modern hardware environments.
Bandwidth and Data Transfer Rates
DDR5 memory significantly outperforms DDR4 in bandwidth, offering up to 51.2 GB/s compared to DDR4's maximum of around 25.6 GB/s per module, effectively doubling data transfer capabilities. DDR5 achieves higher data transfer rates starting at 4800 MT/s, scaling up sequentially to 8400 MT/s and beyond, whereas DDR4 typically ranges from 2133 to 3200 MT/s. These enhancements in DDR5 enhance overall system performance, particularly in data-intensive applications like gaming, AI processing, and high-frequency trading.
Capacity and Density Enhancements
DDR5 memory modules offer significantly higher capacity and density enhancements compared to DDR4, with individual DIMMs reaching up to 128GB, doubling DDR4's maximum of 64GB. This increase is facilitated by improved bank group architecture and the use of higher-density chips supporting greater storage per module. These advancements enable better performance in data-intensive applications and future-proof systems requiring larger memory footprints.
Compatibility with Motherboards and CPUs
DDR5 memory requires compatible motherboards with updated chipsets such as Intel 600 series or AMD 600 series, unlike DDR4 which supports older platforms like Intel 300 series and AMD 400/500 series. CPUs must also support DDR5 for optimal performance, with Intel Alder Lake and newer processors or AMD Ryzen 7000 series being compatible. Using DDR5 on incompatible motherboards or CPUs may lead to system instability or failure to boot.
Pricing and Market Availability
DDR4 memory modules maintain lower price points compared to DDR5, making them a cost-effective choice for budget-conscious consumers and mainstream systems. DDR5, although offering enhanced performance and efficiency, faces limited market availability due to higher production costs and ongoing supply constraints. Widespread adoption of DDR5 is expected to gradually reduce prices as manufacturing scales and demand increases across high-end computing platforms.
Ideal Use Cases for DDR4 and DDR5
DDR4 memory is ideal for mainstream desktop PCs, budget gaming rigs, and office workstations where cost efficiency and compatibility with existing platforms are priorities. DDR5 excels in high-performance computing environments, such as advanced gaming systems, content creation workstations, and servers demanding higher bandwidth, improved power efficiency, and future-proofing. Choosing DDR4 suits stable, established configurations, while DDR5 targets cutting-edge applications needing greater memory speed and capacity.
Choosing the Right Memory for Your Build
Choosing the right memory for your build depends on compatibility, performance needs, and budget constraints. DDR5 offers higher bandwidth and improved power efficiency compared to DDR4, making it ideal for future-proofing high-end gaming and professional workstations. However, DDR4 remains a cost-effective choice for most mid-range systems with wide motherboard compatibility.
DDR4 vs DDR5 Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com