RoHS compliance ensures that hardware products are free from hazardous substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium, reducing environmental and health risks during manufacturing and disposal. Non-RoHS compliant hardware often contains these harmful materials, posing challenges for recycling and increasing regulatory risks in global markets. Choosing RoHS-compliant components enhances sustainability and meets international safety standards, making them preferable for eco-conscious consumers and industries.
Table of Comparison
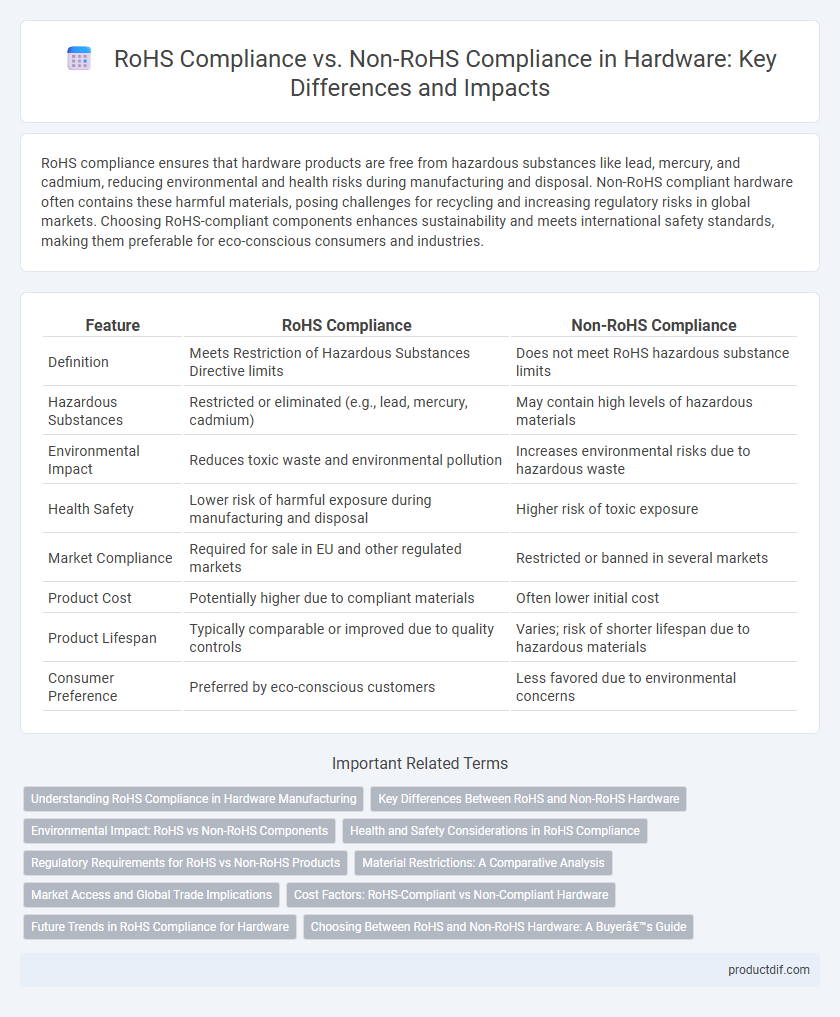
| Feature | RoHS Compliance | Non-RoHS Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Meets Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive limits | Does not meet RoHS hazardous substance limits |
| Hazardous Substances | Restricted or eliminated (e.g., lead, mercury, cadmium) | May contain high levels of hazardous materials |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces toxic waste and environmental pollution | Increases environmental risks due to hazardous waste |
| Health Safety | Lower risk of harmful exposure during manufacturing and disposal | Higher risk of toxic exposure |
| Market Compliance | Required for sale in EU and other regulated markets | Restricted or banned in several markets |
| Product Cost | Potentially higher due to compliant materials | Often lower initial cost |
| Product Lifespan | Typically comparable or improved due to quality controls | Varies; risk of shorter lifespan due to hazardous materials |
| Consumer Preference | Preferred by eco-conscious customers | Less favored due to environmental concerns |
Understanding RoHS Compliance in Hardware Manufacturing
RoHS compliance in hardware manufacturing ensures that electronic components are free from hazardous substances like lead, mercury, cadmium, and hexavalent chromium, aligning with environmental and safety regulations established by the European Union. Manufacturers adhering to RoHS standards reduce toxic waste and improve recyclability, which enhances product sustainability and market acceptance globally. Non-RoHS compliant hardware, while sometimes less costly, poses significant risks including regulatory penalties, limited market access, and increased environmental impact due to the presence of restricted hazardous materials.
Key Differences Between RoHS and Non-RoHS Hardware
RoHS compliance mandates restriction of hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, and specific flame retardants in hardware, ensuring environmental safety and human health protection. Non-RoHS hardware typically contains these restricted materials, resulting in higher toxicity and environmental risks during disposal and recycling. RoHS-certified hardware often meets stricter international standards, enhances market acceptance, and reduces regulatory liabilities compared to non-RoHS counterparts.
Environmental Impact: RoHS vs Non-RoHS Components
RoHS-compliant hardware significantly reduces hazardous substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium in electronic components, minimizing environmental pollution and health risks during disposal and recycling. Non-RoHS components often contain higher levels of toxic materials, contributing to soil and water contamination and posing challenges to e-waste management. Compliance with RoHS standards supports global environmental regulations aimed at sustainable electronics manufacturing and waste reduction.
Health and Safety Considerations in RoHS Compliance
RoHS compliance restricts the use of hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and hexavalent chromium, significantly reducing health risks to workers and consumers by minimizing exposure to toxic materials. Non-RoHS compliant hardware often contains these harmful chemicals, increasing the potential for heavy metal poisoning, environmental contamination, and respiratory issues during manufacturing and disposal. Ensuring RoHS compliance enhances workplace safety standards and supports sustainable electronics production by promoting the use of safer, environmentally friendly materials.
Regulatory Requirements for RoHS vs Non-RoHS Products
RoHS compliance mandates strict adherence to the European Union's directive limiting hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, and cadmium in electronic hardware to protect environmental and human health. Non-RoHS compliant products lack these regulatory restrictions, resulting in potential exposure to harmful materials and being prohibited in markets with enforced RoHS standards. Regulatory requirements for RoHS products include certification, documentation, and consistent testing to verify conformity, whereas non-RoHS products often face import restrictions and limited market access in RoHS-regulated regions.
Material Restrictions: A Comparative Analysis
RoHS compliance mandates strict limits on hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, PBB, and PBDE in electronic hardware, ensuring reduced environmental and health risks. Non-RoHS compliant hardware may contain unrestricted levels of these toxic materials, increasing the potential for harmful environmental contamination and human exposure. The material restrictions under RoHS significantly impact the selection of components and manufacturing processes, driving innovation towards safer, eco-friendly electronic products.
Market Access and Global Trade Implications
RoHS compliance ensures hardware products meet strict European Union regulations on hazardous substances, facilitating seamless market access within the EU and other regions adopting similar standards. Non-RoHS compliant hardware risks restricted entry into key markets, increased tariffs, and potential legal penalties, impacting global trade competitiveness. Manufacturers prioritizing RoHS adherence benefit from broader export opportunities and alignment with international environmental directives, enhancing supply chain sustainability.
Cost Factors: RoHS-Compliant vs Non-Compliant Hardware
RoHS-compliant hardware often incurs higher initial costs due to the use of restricted hazardous substances and specialized materials, which require stringent testing and certification processes. Non-RoHS-compliant hardware generally offers lower upfront expenses but poses potential long-term liabilities, including regulatory fines and environmental disposal costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that RoHS compliance mitigates risks related to product recalls and supply chain restrictions, enhancing sustainability and market access.
Future Trends in RoHS Compliance for Hardware
Future trends in RoHS compliance for hardware emphasize stricter regulations and expanded substance restrictions to address emerging environmental and health concerns. The hardware industry is increasingly adopting lead-free and halogen-free materials, enhancing recyclability and sustainability in electronic components. Advancements in testing technologies and global harmonization of RoHS standards are driving broader compliance and innovation in eco-friendly hardware design.
Choosing Between RoHS and Non-RoHS Hardware: A Buyer’s Guide
Choosing between RoHS-compliant and non-RoHS hardware requires evaluating environmental regulations and product application needs. RoHS-compliant hardware restricts hazardous substances, ensuring safer disposal and regulatory adherence, while non-RoHS hardware may offer legacy compatibility but risks regulatory non-compliance. Prioritizing RoHS-compliant components aligns with sustainable practices and global market acceptance, critical for long-term product viability.
RoHS Compliance vs Non-RoHS Compliance Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com