Vertical integration enhances control over the entire production process of tools, from raw materials to final assembly, ensuring consistent quality and reducing dependency on external suppliers. Outsourcing allows manufacturers to leverage specialized expertise and lower operational costs by delegating specific production stages to third-party vendors. Choosing between vertical integration and outsourcing depends on factors such as cost efficiency, flexibility, and the strategic importance of maintaining control over proprietary processes.
Table of Comparison
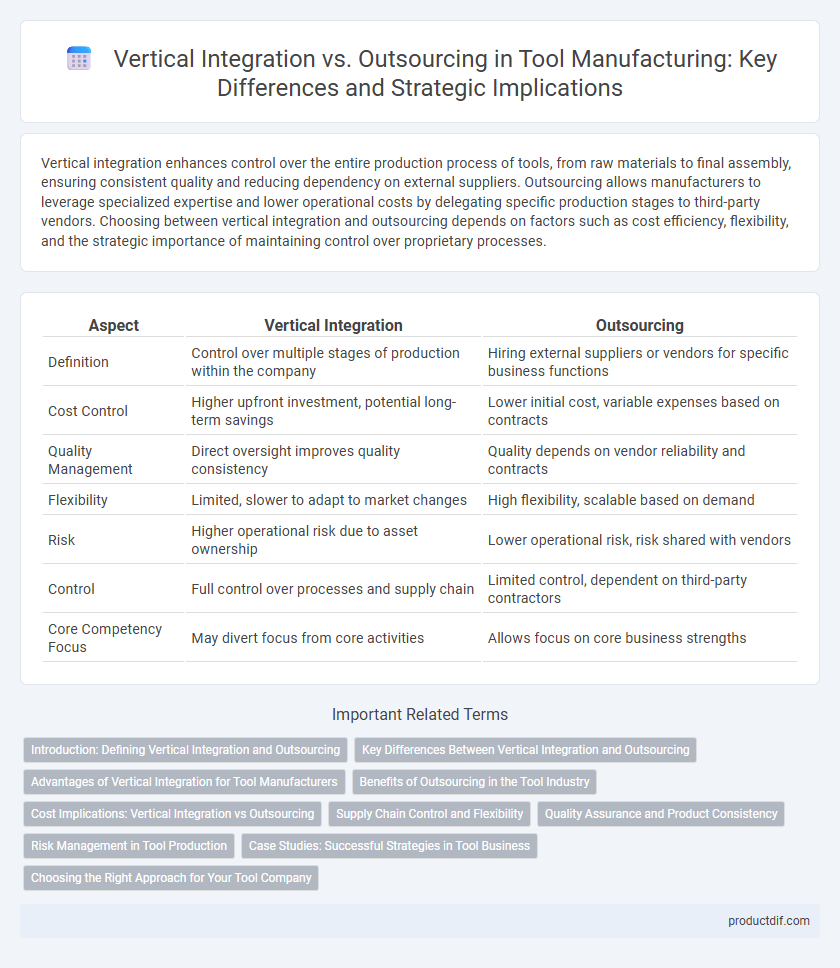
| Aspect | Vertical Integration | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Control over multiple stages of production within the company | Hiring external suppliers or vendors for specific business functions |
| Cost Control | Higher upfront investment, potential long-term savings | Lower initial cost, variable expenses based on contracts |
| Quality Management | Direct oversight improves quality consistency | Quality depends on vendor reliability and contracts |
| Flexibility | Limited, slower to adapt to market changes | High flexibility, scalable based on demand |
| Risk | Higher operational risk due to asset ownership | Lower operational risk, risk shared with vendors |
| Control | Full control over processes and supply chain | Limited control, dependent on third-party contractors |
| Core Competency Focus | May divert focus from core activities | Allows focus on core business strengths |
Introduction: Defining Vertical Integration and Outsourcing
Vertical integration involves a company controlling multiple stages of production or distribution within its supply chain, enhancing coordination and efficiency. Outsourcing refers to contracting external organizations to perform specific business functions or services, allowing companies to focus on core competencies and reduce operational costs. Both strategies impact operational control, cost management, and supply chain flexibility in distinct ways.
Key Differences Between Vertical Integration and Outsourcing
Vertical integration involves a company controlling multiple stages of production, enhancing supply chain efficiency and reducing dependency on external suppliers. Outsourcing delegates specific tasks or processes to third-party vendors, enabling cost savings and access to specialized expertise. Key differences include control over quality, cost structure, flexibility, and scalability, with vertical integration offering more control and outsourcing providing greater operational flexibility.
Advantages of Vertical Integration for Tool Manufacturers
Vertical integration enables tool manufacturers to control the entire production process, reducing dependency on external suppliers and ensuring consistent quality standards. By managing raw material sourcing, machining, and assembly in-house, manufacturers can optimize supply chain efficiency and reduce lead times. This streamlined control also facilitates innovation and customization, enhancing product differentiation and competitive advantage in the tool industry.
Benefits of Outsourcing in the Tool Industry
Outsourcing in the tool industry reduces manufacturing costs by leveraging specialized third-party expertise and economies of scale. It enhances flexibility in production capacity, enabling companies to quickly adapt to market demand without significant capital investment. Access to innovative technologies and global supplier networks improves product quality and accelerates time-to-market.
Cost Implications: Vertical Integration vs Outsourcing
Vertical integration often involves higher upfront capital investment but can reduce long-term operational costs by eliminating supplier margins and improving process control. Outsourcing typically lowers fixed costs and provides flexibility, but may incur higher per-unit expenses and less control over quality. Companies must evaluate cost trade-offs between maintaining internal capabilities and leveraging external suppliers to optimize financial performance.
Supply Chain Control and Flexibility
Vertical integration offers businesses greater supply chain control by consolidating production and distribution processes in-house, reducing dependency on external suppliers. Outsourcing enhances flexibility by allowing companies to adapt quickly to market changes through access to specialized vendors and scalable resources. Balancing these strategies depends on priorities such as maintaining quality standards versus responding swiftly to demand fluctuations.
Quality Assurance and Product Consistency
Vertical integration in tool manufacturing enhances quality assurance by maintaining direct control over every production stage, ensuring consistent materials, process standards, and strict inspection protocols. Outsourcing, while cost-effective, introduces variability in product consistency due to reliance on external suppliers with differing quality controls and standards. A strong quality management system and frequent audits are essential in outsourcing to mitigate risks and maintain product reliability.
Risk Management in Tool Production
Vertical integration in tool production enhances risk management by allowing companies to control critical manufacturing processes, ensuring consistent quality and reducing dependency on external suppliers. Outsourcing introduces risks related to supply chain disruptions, quality variability, and intellectual property security, necessitating stringent supplier vetting and contract management. Implementing robust risk assessment frameworks helps optimize the balance between in-house capabilities and external partnerships, mitigating operational and financial uncertainties.
Case Studies: Successful Strategies in Tool Business
Case studies in the tool business reveal vertical integration enables companies to control quality and reduce costs by managing manufacturing, distribution, and retail processes internally. Firms like Stanley Black & Decker demonstrate success through vertical integration by enhancing innovation speed and supply chain resilience. Conversely, outsourcing allows businesses such as Bosch to leverage specialized expertise and scale production flexibly, optimizing efficiency and market responsiveness.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Tool Company
Vertical integration in a tool company enhances control over the supply chain, ensuring consistent quality and reducing production costs. Outsourcing offers flexibility and access to specialized skills, allowing companies to scale operations and focus on core competencies. Evaluating factors like cost efficiency, market demand, and internal capabilities helps determine the optimal approach for maximizing profitability and innovation.
Vertical integration vs Outsourcing Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com