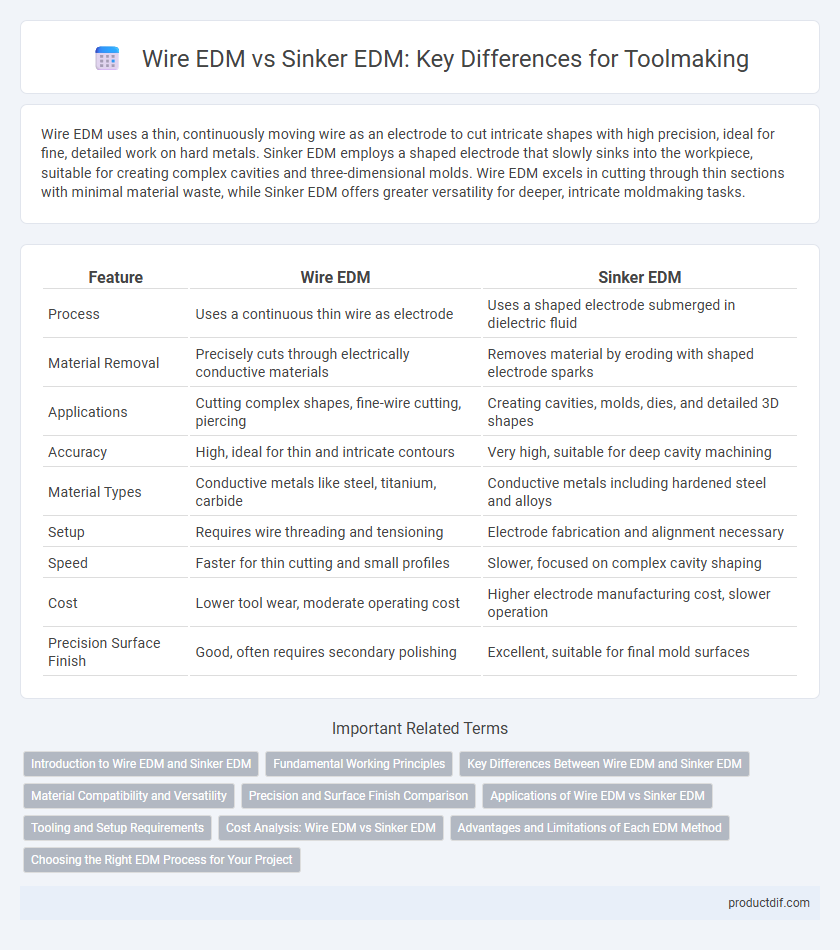
Wire EDM uses a thin, continuously moving wire as an electrode to cut intricate shapes with high precision, ideal for fine, detailed work on hard metals. Sinker EDM employs a shaped electrode that slowly sinks into the workpiece, suitable for creating complex cavities and three-dimensional molds. Wire EDM excels in cutting through thin sections with minimal material waste, while Sinker EDM offers greater versatility for deeper, intricate moldmaking tasks.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wire EDM | Sinker EDM |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Uses a continuous thin wire as electrode | Uses a shaped electrode submerged in dielectric fluid |
| Material Removal | Precisely cuts through electrically conductive materials | Removes material by eroding with shaped electrode sparks |
| Applications | Cutting complex shapes, fine-wire cutting, piercing | Creating cavities, molds, dies, and detailed 3D shapes |
| Accuracy | High, ideal for thin and intricate contours | Very high, suitable for deep cavity machining |
| Material Types | Conductive metals like steel, titanium, carbide | Conductive metals including hardened steel and alloys |
| Setup | Requires wire threading and tensioning | Electrode fabrication and alignment necessary |
| Speed | Faster for thin cutting and small profiles | Slower, focused on complex cavity shaping |
| Cost | Lower tool wear, moderate operating cost | Higher electrode manufacturing cost, slower operation |
| Precision Surface Finish | Good, often requires secondary polishing | Excellent, suitable for final mold surfaces |
Introduction to Wire EDM and Sinker EDM
Wire Electrical Discharge Machining (Wire EDM) utilizes a thin, electrically charged wire to cut intricate shapes with high precision, making it ideal for complex contours and tight tolerances in tool and die manufacturing. Sinker EDM employs a shaped electrode submerged in dielectric fluid to erode material, allowing for the creation of cavities, molds, and intricate 3D forms with excellent surface finishes. Both Wire EDM and Sinker EDM machines rely on controlled electrical discharges to remove metal, with Wire EDM excelling in linear cutting and Sinker EDM suited for three-dimensional machining tasks.
Fundamental Working Principles
Wire EDM uses a thin, electrically charged wire to cut through metal by generating sparks that erode the workpiece, allowing for precise and intricate shapes. Sinker EDM operates by immersing a shaped electrode into the workpiece and discharging electrical sparks between the electrode and the material to create cavities or complex contours. Both methods rely on controlled electrical discharges to erode metal without physical contact, ensuring high precision in manufacturing hard materials.
Key Differences Between Wire EDM and Sinker EDM
Wire EDM uses a continuously moving thin wire as an electrode to cut intricate shapes in electrically conductive materials, offering high precision and minimal material waste. Sinker EDM employs a shaped electrode that is submerged in dielectric fluid to erode cavities or complex three-dimensional contours, ideal for deep hole drilling and mold making. Wire EDM excels in cutting thin, flat parts with tight tolerances, while Sinker EDM is preferable for creating detailed cavities and complex geometries in hard materials.
Material Compatibility and Versatility
Wire EDM excels in cutting hard, conductive materials such as hardened steel, titanium, and Inconel with high precision, making it ideal for intricate and thin parts. Sinker EDM handles complex geometries and cavities in a wider range of materials, including non-conductive metals like tungsten carbide and certain composites, offering greater versatility for mold making and aerospace components. The choice between Wire EDM and Sinker EDM depends on the specific material properties and part design requirements, optimizing efficiency and finish quality.
Precision and Surface Finish Comparison
Wire EDM offers higher precision with a typical tolerance of +-0.002 mm, ideal for intricate components requiring tight dimensional control. Sinker EDM provides a superior surface finish, achieving smoothness levels up to Ra 0.1 mm, suitable for complex cavity molds and dies. Both methods excel in different applications, with Wire EDM favored for fine cuts and Sinker EDM for enhanced surface quality.
Applications of Wire EDM vs Sinker EDM
Wire EDM excels in producing intricate and precise external geometries for aerospace components and medical instruments, where tight tolerances and fine finishes are critical. Sinker EDM is preferred for creating complex cavity shapes and internal features in molds, dies, and automotive parts due to its ability to machine deep cavities and undercuts. Both technologies complement each other in manufacturing environments that require a combination of high precision and complex internal or external geometries.
Tooling and Setup Requirements
Wire EDM requires precise wire guides, tension control, and dielectric fluid management for accurate machining, making tooling setup more complex and specialized. Sinker EDM tooling involves custom-shaped electrodes and careful insulation preparation, demanding significant electrode fabrication and setup time. Both processes require meticulous calibration, but Wire EDM generally offers faster setup with standardized tooling compared to the custom electrode dependency of Sinker EDM.
Cost Analysis: Wire EDM vs Sinker EDM
Wire EDM typically offers lower operational costs due to reduced electrode wear and faster machining speeds, making it more cost-effective for high-precision, thin materials. Sinker EDM incurs higher expenses from custom electrode fabrication and longer machining times, which increase labor and material costs, though it excels in complex cavity shapes. Selecting between Wire EDM and Sinker EDM hinges on balancing upfront tooling cost against production volume and geometric complexity requirements.
Advantages and Limitations of Each EDM Method
Wire EDM offers precise cutting with minimal material waste, ideal for complex, thin parts and conductive metals, but is limited by slower process speeds and thickness constraints. Sinker EDM excels in intricate cavity shapes and harder materials with faster material removal rates, though it requires dielectric fluid immersion and can cause more electrode wear. Selecting between Wire and Sinker EDM depends on part geometry, material properties, and production volume requirements.
Choosing the Right EDM Process for Your Project
Wire EDM offers high precision and is ideal for cutting complex shapes in hard metals with minimal material waste, making it perfect for intricate designs and aerospace components. Sinker EDM excels at creating deep cavities and complex 3D shapes in molds and dies, providing superior surface finish and accuracy for tooling applications. Selecting the right EDM process depends on factors like workpiece geometry, material thickness, and desired surface quality to optimize efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Wire EDM vs Sinker EDM Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com