A straight blade offers precise, clean cuts ideal for slicing and push cuts, while a serrated blade excels at gripping and tearing through tough or fibrous materials like rope and bread. Straight blades are easier to sharpen and maintain a smooth edge, whereas serrated blades stay effective longer without frequent sharpening due to their saw-like teeth. Choosing between a straight and serrated blade depends on the specific cutting tasks and material types encountered.
Table of Comparison
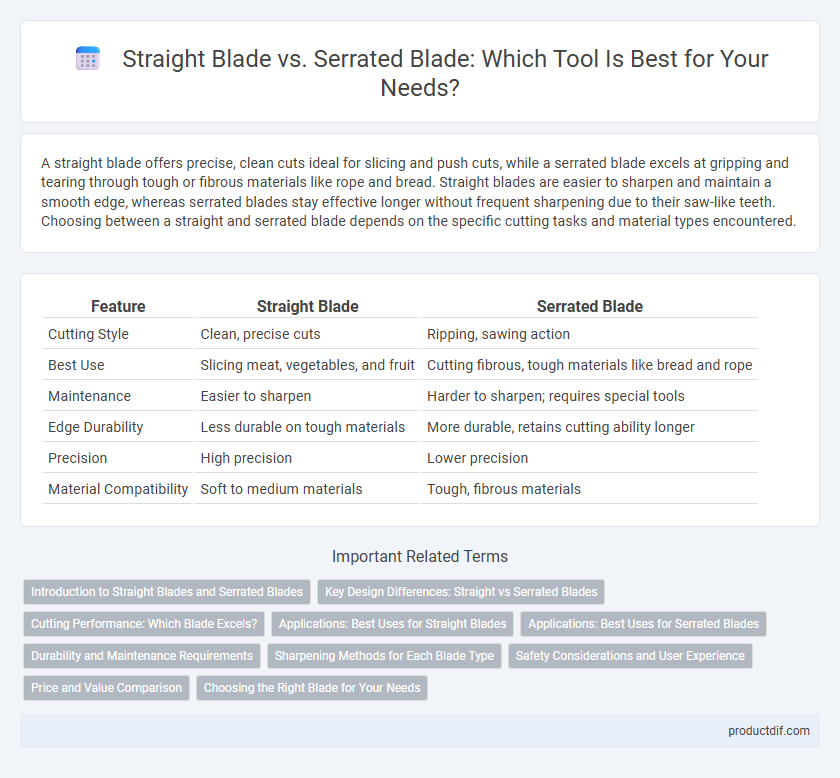
| Feature | Straight Blade | Serrated Blade |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Style | Clean, precise cuts | Ripping, sawing action |
| Best Use | Slicing meat, vegetables, and fruit | Cutting fibrous, tough materials like bread and rope |
| Maintenance | Easier to sharpen | Harder to sharpen; requires special tools |
| Edge Durability | Less durable on tough materials | More durable, retains cutting ability longer |
| Precision | High precision | Lower precision |
| Material Compatibility | Soft to medium materials | Tough, fibrous materials |
Introduction to Straight Blades and Serrated Blades
Straight blades feature a smooth, sharp edge ideal for precise cutting tasks such as slicing or carving, offering clean cuts with minimal resistance. Serrated blades possess a saw-like edge designed to grip and tear through tougher materials like rope, bread, or fibrous foods, maintaining effectiveness even when dull. Choosing between these blades depends on the specific cutting needs, with straight blades excelling in detail and serrated blades providing durability on coarse surfaces.
Key Design Differences: Straight vs Serrated Blades
Straight blades feature a smooth, sharp edge designed for clean, precise cuts and are ideal for slicing through soft materials with minimal resistance. Serrated blades have a toothed edge that grips and tears tougher or fibrous materials more efficiently, making them suitable for cutting bread, rope, or meats. The key design difference lies in the edge geometry: smooth for straight blades to facilitate smooth slicing and jagged for serrated blades to improve grip and cutting power on challenging surfaces.
Cutting Performance: Which Blade Excels?
Straight blades deliver precise, clean cuts ideal for slicing through soft materials with minimal resistance, making them perfect for tasks requiring accuracy. Serrated blades excel when cutting tougher, fibrous materials, as their saw-like teeth grip and tear effectively, reducing cutting effort. Selecting between straight and serrated blades depends on the material texture and cutting precision needed for optimal performance.
Applications: Best Uses for Straight Blades
Straight blades excel in precision cutting tasks requiring clean, controlled slices such as carving, slicing fruits, and making intricate cuts in woodworking. Their smooth edge allows for effortless push and pull motions that minimize tearing, making them ideal for filleting fish or cutting vegetables. These blades are preferred in situations demanding accuracy and fine detail over aggressive cutting or sawing motions.
Applications: Best Uses for Serrated Blades
Serrated blades excel in cutting through tough, fibrous materials such as rope, fabric, and bread crusts due to their saw-like teeth that grip and slice efficiently. They are ideal for outdoor activities including camping and fishing, where cutting through thick vegetation or slippery surfaces is common. Their design ensures clean cuts on soft or hard surfaces without crushing, making them indispensable in kitchen and utility tools.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Straight blades typically offer superior durability due to their solid edge design, which resists chipping and dulling over extended use. Serrated blades have a more complex edge requiring frequent sharpening with specialized tools to maintain performance, making their maintenance more demanding. The simpler upkeep and longer lifespan of straight blades make them a preferred choice for heavy-duty and precision cutting tasks.
Sharpening Methods for Each Blade Type
Straight blades require sharpening with a whetstone or honing rod, maintaining a consistent angle of 20 degrees for a fine, smooth edge ideal for precise cuts. Serrated blades demand sharpening tools like a tapered diamond rod that fits between the serrations, preserving the scalloped edge essential for slicing through tough or fibrous materials. Proper sharpening techniques extend blade life and enhance cutting efficiency for both straight and serrated blades.
Safety Considerations and User Experience
Straight blades offer precise control and cleaner cuts, reducing the risk of slippage and enhancing user safety during detailed tasks. Serrated blades grip tougher materials like rope or fabric more effectively, but their jagged edges can increase the chance of accidental nicks or cuts if not handled carefully. Choosing the appropriate blade type depends on the task's demands and the user's experience level to maintain optimal safety and efficiency.
Price and Value Comparison
Straight blades typically offer a lower price point compared to serrated blades due to simpler manufacturing processes and less material complexity. Serrated blades, while often more expensive, provide enhanced cutting efficiency and durability, delivering greater long-term value for tasks involving tough or fibrous materials. Evaluating the balance between initial cost and functional lifespan helps determine the best investment for specific cutting needs.
Choosing the Right Blade for Your Needs
Straight blades offer precise, clean cuts ideal for tasks requiring control, such as slicing fruits or shaving wood. Serrated blades excel at cutting through tough or fibrous materials like bread and rope, providing a sawing motion that reduces effort. Selecting the right blade depends on your specific use case, balancing precision with cutting power.
straight blade vs serrated blade Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com