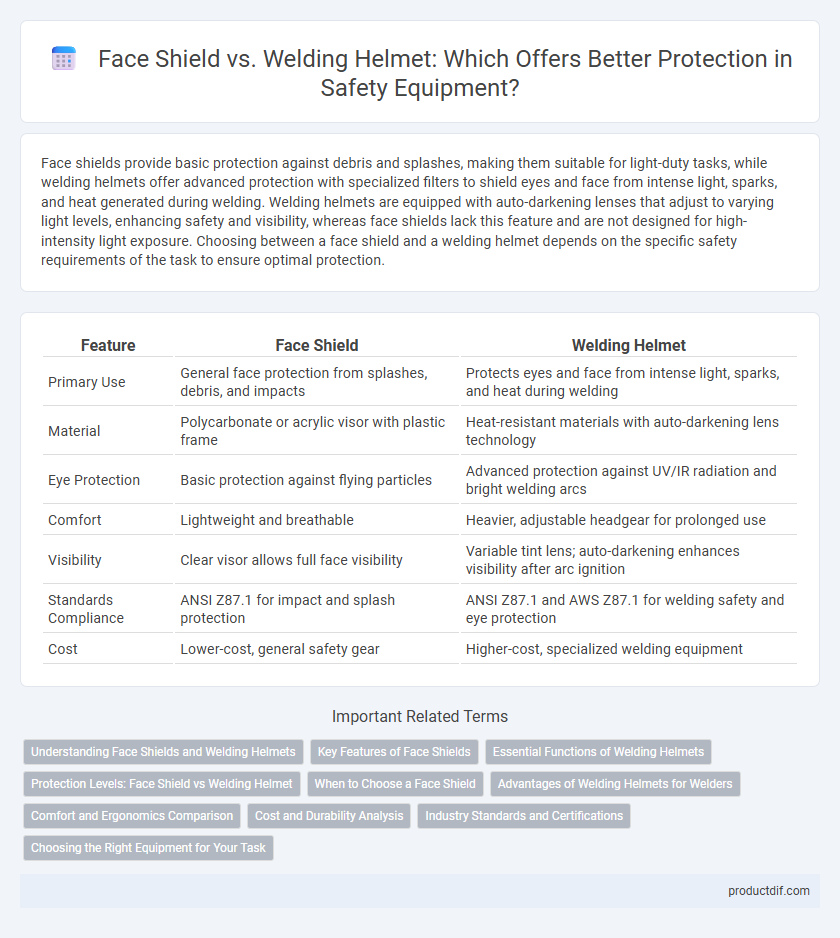
Face shields provide basic protection against debris and splashes, making them suitable for light-duty tasks, while welding helmets offer advanced protection with specialized filters to shield eyes and face from intense light, sparks, and heat generated during welding. Welding helmets are equipped with auto-darkening lenses that adjust to varying light levels, enhancing safety and visibility, whereas face shields lack this feature and are not designed for high-intensity light exposure. Choosing between a face shield and a welding helmet depends on the specific safety requirements of the task to ensure optimal protection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Face Shield | Welding Helmet |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | General face protection from splashes, debris, and impacts | Protects eyes and face from intense light, sparks, and heat during welding |
| Material | Polycarbonate or acrylic visor with plastic frame | Heat-resistant materials with auto-darkening lens technology |
| Eye Protection | Basic protection against flying particles | Advanced protection against UV/IR radiation and bright welding arcs |
| Comfort | Lightweight and breathable | Heavier, adjustable headgear for prolonged use |
| Visibility | Clear visor allows full face visibility | Variable tint lens; auto-darkening enhances visibility after arc ignition |
| Standards Compliance | ANSI Z87.1 for impact and splash protection | ANSI Z87.1 and AWS Z87.1 for welding safety and eye protection |
| Cost | Lower-cost, general safety gear | Higher-cost, specialized welding equipment |
Understanding Face Shields and Welding Helmets
Face shields provide basic protection against flying debris, chemical splashes, and sparks, making them suitable for light industrial tasks and laboratory use. Welding helmets feature auto-darkening filters and impact-resistant lenses designed specifically to shield the eyes and face from intense ultraviolet and infrared radiation generated during welding processes. Choosing between a face shield and a welding helmet depends on the nature of the task, with welding helmets offering advanced protection critical for arc welding safety.
Key Features of Face Shields
Face shields provide full-face protection with a clear visor that resists impact, chemical splashes, and debris, making them ideal for general safety applications. They offer lightweight comfort and excellent visibility, allowing users to maintain situational awareness while being shielded from hazards. Unlike welding helmets, face shields do not feature specialized filters for intense light or sparks but excel in protecting against non-welding risks.
Essential Functions of Welding Helmets
Welding helmets provide comprehensive protection against intense ultraviolet and infrared radiation, shielding the eyes and face from sparks, spatter, and harmful fumes during welding operations. Equipped with auto-darkening filters, these helmets enable welders to see clearly before striking an arc and adjust lens tint instantly for optimal visibility and safety. Face shields offer basic impact protection but lack the specialized filtration and adaptive features critical for high-risk welding environments.
Protection Levels: Face Shield vs Welding Helmet
Face shields provide basic protection against flying debris, chemical splashes, and light impact, suitable for general industrial tasks, while welding helmets offer advanced protection against intense light, ultraviolet (UV), and infrared (IR) radiation generated during welding processes. Welding helmets typically feature auto-darkening filters that adjust opacity to safeguard the welder's eyes and face from radiant heat, sparks, and spatter, ensuring compliance with ANSI Z87.1 and CSA Z94.3 safety standards. In terms of protection levels, welding helmets deliver comprehensive safety tailored specifically for welding hazards, whereas face shields serve as supplementary gear for lower-risk environments.
When to Choose a Face Shield
Choose a face shield when protection against splashes, flying debris, and chemical exposure is required, especially in environments involving grinding, cutting, or handling hazardous liquids. Unlike welding helmets, face shields provide full-face coverage without integrated eye filters, making them unsuitable for welding but ideal for general impact and splash protection. Opt for a face shield to ensure comfort and versatility during tasks that do not involve intense light radiation or sparks typical of welding operations.
Advantages of Welding Helmets for Welders
Welding helmets offer superior protection against intense heat, sparks, and harmful UV and infrared radiation, which face shields cannot fully block. Equipped with auto-darkening filters, they enhance visibility and allow welders to work efficiently without lifting the helmet. The robust design of welding helmets provides comprehensive coverage, reducing the risk of eye injuries and burns in high-risk welding environments.
Comfort and Ergonomics Comparison
Face shields offer lightweight protection and greater visibility, enhancing comfort for short-duration tasks but provide less ergonomic support during extended use. Welding helmets feature adjustable headgear, balanced weight distribution, and cushioned interiors designed to reduce strain, making them more suitable for prolonged welding activities. The ergonomic design of welding helmets prioritizes user posture and reduces fatigue, while face shields excel in breathability and ease of movement.
Cost and Durability Analysis
Face shields generally have a lower upfront cost compared to welding helmets, making them more accessible for basic protection tasks. Welding helmets, constructed with high-impact materials and equipped with auto-darkening filters, offer superior durability and long-term investment value, especially in professional welding environments. The enhanced durability of welding helmets reduces replacement frequency, offsetting their higher initial price over time.
Industry Standards and Certifications
Face shields and welding helmets must comply with specific industry standards to ensure maximum protection in industrial settings. Welding helmets typically adhere to ANSI Z87.1 and EN 175 standards, offering impact resistance and filtering harmful UV and IR radiation during welding processes, while face shields generally follow ANSI Z87.1 standards for impact protection and chemical splash resistance. Certifications such as CE marking in Europe and CSA standards in Canada further validate the compliance and reliability of these protective devices.
Choosing the Right Equipment for Your Task
Selecting the appropriate safety equipment depends on the specific hazards and requirements of your welding task. Face shields provide basic protection against sparks and debris but lack the specialized filtering and impact resistance needed for welding arcs. Welding helmets feature auto-darkening filters and robust construction, offering superior protection against intense light and heat while enhancing visibility and comfort during prolonged use.
Face shield vs Welding helmet Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com