Telehealth devices enable real-time virtual consultations between patients and healthcare providers, facilitating immediate diagnosis and treatment without in-person visits. Remote patient monitoring devices continuously collect and transmit patient health data, such as vital signs, to healthcare professionals for ongoing assessment and early detection of potential issues. Both technologies enhance patient care, but telehealth emphasizes interactive communication while remote monitoring focuses on data-driven health management.
Table of Comparison
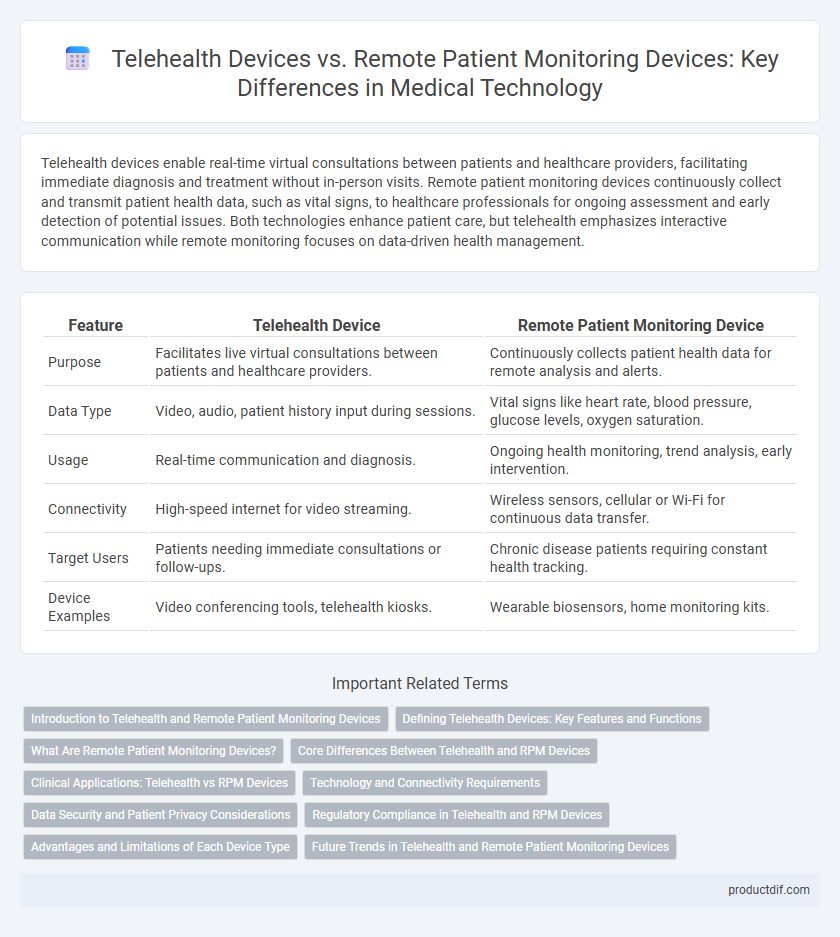
| Feature | Telehealth Device | Remote Patient Monitoring Device |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Facilitates live virtual consultations between patients and healthcare providers. | Continuously collects patient health data for remote analysis and alerts. |
| Data Type | Video, audio, patient history input during sessions. | Vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, glucose levels, oxygen saturation. |
| Usage | Real-time communication and diagnosis. | Ongoing health monitoring, trend analysis, early intervention. |
| Connectivity | High-speed internet for video streaming. | Wireless sensors, cellular or Wi-Fi for continuous data transfer. |
| Target Users | Patients needing immediate consultations or follow-ups. | Chronic disease patients requiring constant health tracking. |
| Device Examples | Video conferencing tools, telehealth kiosks. | Wearable biosensors, home monitoring kits. |
Introduction to Telehealth and Remote Patient Monitoring Devices
Telehealth devices facilitate real-time virtual consultations between patients and healthcare providers, enabling remote diagnosis and treatment through video, audio, and digital communication tools. Remote patient monitoring devices continuously collect and transmit vital health data, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels, allowing clinicians to monitor chronic conditions and detect potential health issues early. Both technologies enhance patient access to care, reduce hospitalization rates, and improve chronic disease management through seamless data integration and remote intervention.
Defining Telehealth Devices: Key Features and Functions
Telehealth devices enable real-time audio and video communication between patients and healthcare providers, facilitating virtual consultations and immediate clinical assessments. These devices integrate interactive tools such as digital stethoscopes, otoscopes, and high-resolution cameras to enhance diagnostic accuracy remotely. Their core functions focus on enabling synchronous interactions and delivering patient care without in-person visits, distinguishing them from remote patient monitoring devices that primarily collect and transmit health data asynchronously.
What Are Remote Patient Monitoring Devices?
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) devices are advanced medical tools designed to collect health data from patients in real-time, often outside traditional clinical settings. These devices track vital signs such as blood pressure, glucose levels, and heart rate, transmitting data directly to healthcare providers for ongoing analysis and timely intervention. RPM devices improve chronic disease management by enabling continuous monitoring and personalized care adjustments.
Core Differences Between Telehealth and RPM Devices
Telehealth devices enable real-time, interactive communication between patients and healthcare providers through video calls, audio, and messaging, facilitating virtual consultations and clinical decision-making remotely. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) devices focus on collecting and transmitting patient health data such as vital signs, glucose levels, or cardiac rhythms continuously or at regular intervals to healthcare professionals for ongoing assessment and early intervention. The core difference lies in telehealth's emphasis on synchronous communication for direct care delivery versus RPM's continuous data collection for chronic disease management and preventive care.
Clinical Applications: Telehealth vs RPM Devices
Telehealth devices enable real-time interaction between patients and healthcare providers, supporting virtual consultations, diagnostics, and treatment adjustments across various clinical settings. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) devices continuously collect and transmit biomedical data such as heart rate, blood glucose, and oxygen saturation, allowing clinicians to track chronic conditions and intervene promptly. Clinical applications of telehealth specialize in episodic care coordination and virtual visits, whereas RPM devices focus on long-term health management and early detection of clinical deterioration.
Technology and Connectivity Requirements
Telehealth devices require robust, high-speed internet connectivity to support real-time audio and video communication between patients and healthcare providers, often utilizing platforms compatible with smartphones, tablets, and computers. Remote patient monitoring (RPM) devices depend on continuous data transmission through wireless technologies such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or cellular networks to collect and send vital health metrics like heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels to centralized healthcare systems. Both technologies demand secure encryption protocols and interoperability standards to ensure data privacy, reliability, and seamless integration with electronic health records (EHR) systems.
Data Security and Patient Privacy Considerations
Telehealth devices transmit real-time audio and video data, requiring robust encryption protocols such as TLS and end-to-end encryption to safeguard patient confidentiality during virtual consultations. Remote patient monitoring devices continuously collect sensitive health data like heart rate and glucose levels, necessitating secure data storage solutions compliant with HIPAA and GDPR standards to prevent unauthorized access. Both device types must implement multi-factor authentication and regular security audits to maintain data integrity and protect patient privacy effectively.
Regulatory Compliance in Telehealth and RPM Devices
Telehealth devices and remote patient monitoring (RPM) devices both require strict adherence to regulatory standards set by agencies like the FDA and HIPAA to ensure patient safety and data security. Compliance involves meeting specific requirements for device classification, risk assessment, and real-time data transmission protocols, with RPM devices often facing more rigorous scrutiny due to continuous monitoring capabilities. Effective regulatory compliance in these devices reduces the risk of data breaches, ensures interoperability, and facilitates smoother market entry across different healthcare systems.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Device Type
Telehealth devices offer real-time audio and video communication between patients and healthcare providers, enhancing accessibility and immediate consultation but may face limitations like reliance on internet connectivity and reduced ability to capture continuous physiological data. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) devices provide continuous, real-time data collection such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels, enabling proactive disease management and early intervention; however, they may require patient training and can generate large volumes of data needing efficient analysis. Both device types improve patient care but differ in functionality, with telehealth excelling in interactive communication and RPM excelling in continuous health data tracking.
Future Trends in Telehealth and Remote Patient Monitoring Devices
Telehealth devices are evolving with integrated AI analytics to support real-time diagnostics and personalized care, enhancing accessibility beyond traditional healthcare settings. Remote patient monitoring devices are advancing with wearable sensors capable of continuous vital sign tracking, enabling proactive intervention and reducing hospital readmissions. Future trends emphasize interoperability, data security, and patient-centered designs to optimize chronic disease management and improve healthcare outcomes globally.
Telehealth Device vs Remote Patient Monitoring Device Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com