Minimally invasive surgery offers reduced trauma to the body through small incisions, leading to faster recovery times and less postoperative pain compared to open surgery. This technique utilizes advanced medical devices such as laparoscopes and robotic systems to enhance precision and visualization. Open surgery, while providing direct access to organs, typically involves larger incisions and longer hospital stays, increasing the risk of complications and extended healing periods.
Table of Comparison
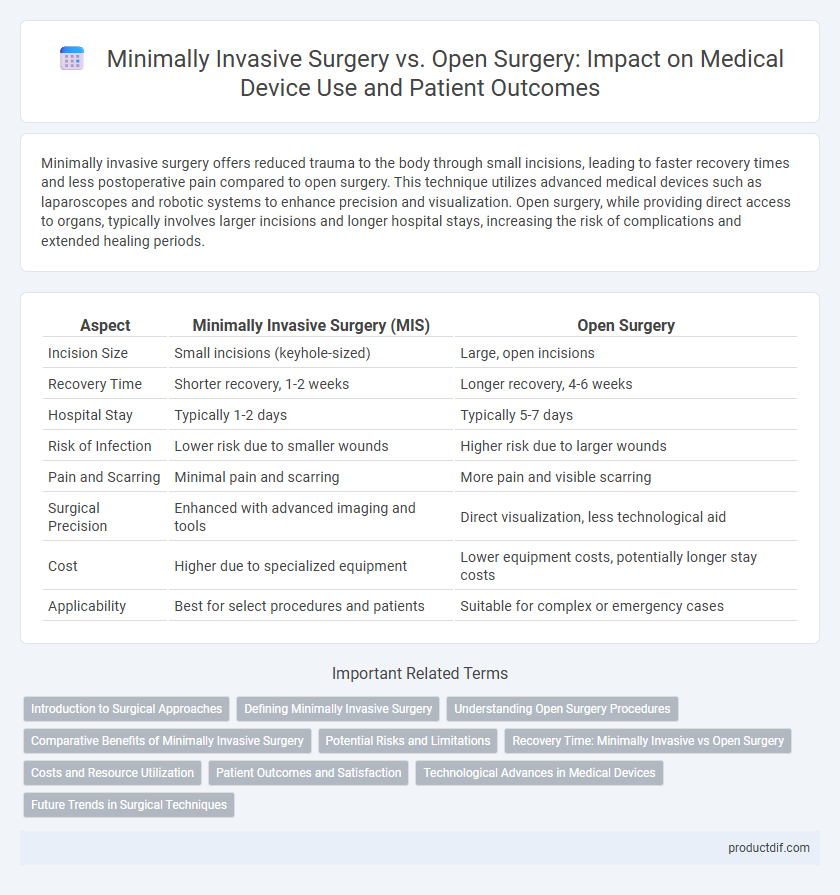
| Aspect | Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS) | Open Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Incision Size | Small incisions (keyhole-sized) | Large, open incisions |
| Recovery Time | Shorter recovery, 1-2 weeks | Longer recovery, 4-6 weeks |
| Hospital Stay | Typically 1-2 days | Typically 5-7 days |
| Risk of Infection | Lower risk due to smaller wounds | Higher risk due to larger wounds |
| Pain and Scarring | Minimal pain and scarring | More pain and visible scarring |
| Surgical Precision | Enhanced with advanced imaging and tools | Direct visualization, less technological aid |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized equipment | Lower equipment costs, potentially longer stay costs |
| Applicability | Best for select procedures and patients | Suitable for complex or emergency cases |
Introduction to Surgical Approaches
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) utilizes advanced medical devices such as laparoscopes and robotic systems to perform procedures through small incisions, reducing trauma and promoting faster recovery. Open surgery involves larger incisions to provide direct access to organs or tissues, often resulting in longer hospital stays and increased postoperative pain. The choice between minimally invasive and open approaches depends on the specific medical condition, surgeon expertise, and availability of specialized surgical instruments.
Defining Minimally Invasive Surgery
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) involves performing procedures through small incisions using specialized instruments and cameras, reducing trauma to tissues compared to traditional open surgery. This approach typically results in less postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times. Advanced medical devices such as laparoscopes and robotic systems enhance precision and visualization during MIS, improving surgical outcomes.
Understanding Open Surgery Procedures
Open surgery procedures involve making a large incision to access the surgical site directly, allowing surgeons to have a comprehensive view and manual control over the area being treated. These traditional techniques are often necessary for complex cases where extensive tissue manipulation or reconstruction is required, such as in trauma repair or tumor removal. Despite longer recovery times and increased risk of complications compared to minimally invasive surgery, open surgery remains a critical approach for ensuring precise outcomes in certain medical conditions.
Comparative Benefits of Minimally Invasive Surgery
Minimally invasive surgery offers significant advantages over open surgery, including reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times. Enhanced precision through advanced imaging and smaller incisions lowers the risk of infection and minimizes tissue damage. These benefits contribute to improved patient outcomes and decreased healthcare costs.
Potential Risks and Limitations
Minimally invasive surgery offers reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery compared to open surgery, but it carries risks such as limited visibility, potential for incomplete tumor removal, and complications related to specialized instrumentation. Open surgery provides greater access and visibility for complex cases but involves higher risks of infection, longer healing time, and increased blood loss. Both approaches require careful patient selection to mitigate risks like anesthesia complications, organ damage, and postoperative adhesions.
Recovery Time: Minimally Invasive vs Open Surgery
Minimally invasive surgery offers significantly shorter recovery times compared to open surgery due to smaller incisions and reduced tissue damage. Patients undergoing minimally invasive procedures typically experience less postoperative pain, lower risk of infection, and faster return to daily activities. In contrast, open surgery involves larger incisions that result in extended hospital stays and prolonged healing periods.
Costs and Resource Utilization
Minimally invasive surgery significantly reduces hospital stay duration and postoperative complications, leading to lower overall healthcare costs compared to open surgery. It requires specialized medical devices and advanced technology, which may increase initial procedure expenses but decreases long-term resource utilization. Open surgery often involves longer operating times, higher blood loss, and extended recovery periods, resulting in increased use of hospital resources and higher total treatment costs.
Patient Outcomes and Satisfaction
Minimally invasive surgery often results in reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and quicker return to daily activities compared to open surgery. Studies highlight higher patient satisfaction rates linked to smaller incisions, lower infection risks, and improved cosmetic outcomes. Enhanced recovery protocols following minimally invasive procedures contribute significantly to overall patient well-being and positive quality of life measures.
Technological Advances in Medical Devices
Technological advances in medical devices have revolutionized minimally invasive surgery by enabling smaller incisions, enhanced precision, and reduced patient recovery times compared to traditional open surgery. Innovations such as robotic-assisted systems, high-definition 3D imaging, and advanced laparoscopic instruments facilitate better visualization and maneuverability during procedures. These developments contribute to decreased surgical trauma, lower infection risk, and improved overall patient outcomes.
Future Trends in Surgical Techniques
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) continues to evolve with advancements in robotic-assisted systems and enhanced imaging technologies, offering greater precision and reduced patient recovery times compared to open surgery. Future trends emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence for real-time decision support and the development of nano-enhanced surgical instruments to improve targeting and reduce tissue damage. These innovations aim to expand the applications of MIS while minimizing complications associated with traditional open surgical procedures.
Minimally Invasive Surgery vs Open Surgery Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com