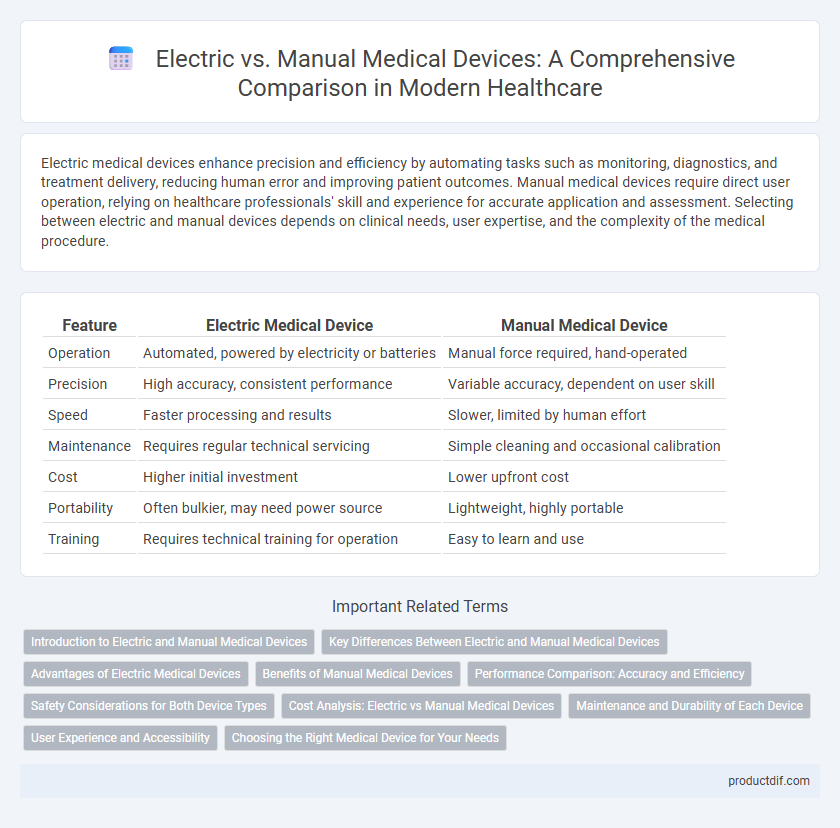
Electric medical devices enhance precision and efficiency by automating tasks such as monitoring, diagnostics, and treatment delivery, reducing human error and improving patient outcomes. Manual medical devices require direct user operation, relying on healthcare professionals' skill and experience for accurate application and assessment. Selecting between electric and manual devices depends on clinical needs, user expertise, and the complexity of the medical procedure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electric Medical Device | Manual Medical Device |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Automated, powered by electricity or batteries | Manual force required, hand-operated |
| Precision | High accuracy, consistent performance | Variable accuracy, dependent on user skill |
| Speed | Faster processing and results | Slower, limited by human effort |
| Maintenance | Requires regular technical servicing | Simple cleaning and occasional calibration |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Portability | Often bulkier, may need power source | Lightweight, highly portable |
| Training | Requires technical training for operation | Easy to learn and use |
Introduction to Electric and Manual Medical Devices
Electric medical devices utilize powered components and electronic circuits to perform diagnostic, therapeutic, or monitoring functions, enhancing precision and efficiency in medical procedures. Manual medical devices, relying on physical human operation without electrical power, emphasize simplicity, portability, and cost-effectiveness in clinical settings. Understanding the core differences between electric and manual medical devices aids healthcare professionals in selecting appropriate tools based on procedural requirements and resource availability.
Key Differences Between Electric and Manual Medical Devices
Electric medical devices offer enhanced precision, automation, and real-time data monitoring, which significantly improve diagnostic accuracy and treatment efficiency compared to manual medical devices. Manual medical devices rely on human operation, providing tactile feedback and simple mechanical functions but generally lack the advanced functionalities and integration capabilities of electric devices. The choice between electric and manual medical devices depends on factors such as the complexity of medical procedures, required accuracy, and resource availability in healthcare settings.
Advantages of Electric Medical Devices
Electric medical devices provide enhanced precision and consistency in diagnostics and treatments, reducing human error. They often offer faster operation and improved efficiency, leading to better patient outcomes and streamlined clinical workflows. Advanced features such as real-time monitoring and automated data recording further support accurate decision-making in medical care.
Benefits of Manual Medical Devices
Manual medical devices offer enhanced control and precision during procedures, reducing the risk of mechanical failure common in electric devices. They provide greater portability and ease of sterilization, making them ideal for diverse clinical settings with limited access to power sources. Their simplicity ensures lower maintenance costs and increased reliability, especially in resource-constrained environments.
Performance Comparison: Accuracy and Efficiency
Electric medical devices demonstrate superior accuracy and efficiency compared to manual medical devices due to advanced sensor technology and automated controls that reduce human error. Precision in measurements and faster processing times enhance diagnostic reliability and patient outcomes in clinical settings. Manual devices, while simpler and cost-effective, often require extensive user skill and are prone to variability, impacting overall performance consistency.
Safety Considerations for Both Device Types
Electric medical devices require rigorous safety standards to prevent electrical hazards, including insulation integrity, grounding, and protection against short circuits. Manual medical devices demand strict attention to ergonomic design and material safety to minimize user fatigue and contamination risks. Both device types must comply with regulatory guidelines such as ISO 13485 and ensure routine maintenance and sterilization protocols to guarantee patient and operator safety.
Cost Analysis: Electric vs Manual Medical Devices
Electric medical devices typically have higher upfront costs due to advanced technology and installation requirements, while manual medical devices are generally more affordable initially with minimal maintenance expenses. Over time, electric devices may reduce labor costs and improve efficiency, potentially offsetting their initial investment through enhanced patient outcomes and faster procedures. Cost analysis must also factor in durability, calibration needs, and long-term operational expenses between electric and manual medical devices.
Maintenance and Durability of Each Device
Electric medical devices require regular calibration, software updates, and electrical component inspections to maintain optimal functionality and prevent malfunctions. Manual medical devices generally have fewer maintenance requirements but must be routinely cleaned, lubricated, and inspected for mechanical wear to ensure durability. Electric devices often have higher durability due to advanced materials and precise engineering, yet they are more susceptible to damage from power surges and component failure compared to the simpler, more robust manual devices.
User Experience and Accessibility
Electric medical devices enhance user experience by offering automated functions that reduce physical effort and increase accuracy, making procedures more efficient and less prone to error. They improve accessibility for patients with limited mobility or dexterity, enabling easier operation through intuitive interfaces or remote controls. Manual medical devices, while often simpler and more affordable, may require more skill and effort, potentially limiting usability for some patients and healthcare providers.
Choosing the Right Medical Device for Your Needs
Choosing the right medical device requires evaluating the precision, ease of use, and specific healthcare requirements. Electric medical devices offer enhanced accuracy, faster operation, and integration with digital health records, making them ideal for complex diagnostics and continuous monitoring. Manual medical devices provide simplicity, reliability, and affordability, suitable for basic procedures and environments with limited access to power sources.
Electric medical device vs Manual medical device Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com