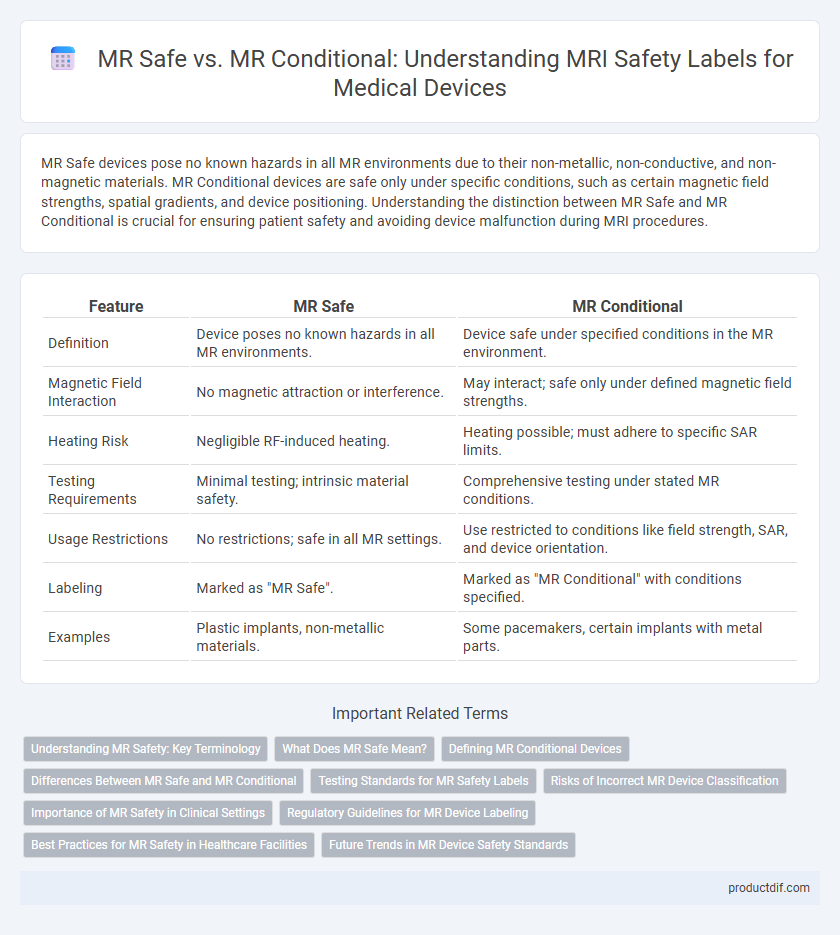
MR Safe devices pose no known hazards in all MR environments due to their non-metallic, non-conductive, and non-magnetic materials. MR Conditional devices are safe only under specific conditions, such as certain magnetic field strengths, spatial gradients, and device positioning. Understanding the distinction between MR Safe and MR Conditional is crucial for ensuring patient safety and avoiding device malfunction during MRI procedures.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | MR Safe | MR Conditional |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Device poses no known hazards in all MR environments. | Device safe under specified conditions in the MR environment. |
| Magnetic Field Interaction | No magnetic attraction or interference. | May interact; safe only under defined magnetic field strengths. |
| Heating Risk | Negligible RF-induced heating. | Heating possible; must adhere to specific SAR limits. |
| Testing Requirements | Minimal testing; intrinsic material safety. | Comprehensive testing under stated MR conditions. |
| Usage Restrictions | No restrictions; safe in all MR settings. | Use restricted to conditions like field strength, SAR, and device orientation. |
| Labeling | Marked as "MR Safe". | Marked as "MR Conditional" with conditions specified. |
| Examples | Plastic implants, non-metallic materials. | Some pacemakers, certain implants with metal parts. |
Understanding MR Safety: Key Terminology
MR Safe devices pose no known hazards in all MRI environments due to their construction from non-conductive, non-metallic materials. MR Conditional products are safe under specific MRI conditions defined by the manufacturer, such as field strength, spatial gradient, and scan duration. Understanding these definitions ensures proper device selection and patient safety during MRI procedures.
What Does MR Safe Mean?
MR Safe refers to medical devices that pose no known hazards in all MRI environments, including static magnetic fields, gradient magnetic fields, and radiofrequency fields. These devices are made entirely of non-ferromagnetic materials, ensuring they do not interfere with MRI scans or cause harm to patients. Regulatory standards such as ASTM F2503 classify MR Safe devices to guarantee safety during MRI procedures.
Defining MR Conditional Devices
MR Conditional devices are medical implants or equipment tested and documented to pose no hazard under specific magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) conditions, such as defined static magnetic field strength, spatial gradient, and RF energy limits. These devices require strict adherence to manufacturer guidelines to ensure patient safety during MRI scans, differentiating them from MR Safe devices, which have no known risks in any MRI environment. Understanding the precise operational parameters of MR Conditional devices is critical for clinicians to avoid adverse events and ensure effective imaging outcomes.
Differences Between MR Safe and MR Conditional
MR Safe devices are composed of non-metallic, non-conductive materials that pose no risk during MRI scans, allowing safe use in any MRI environment. MR Conditional devices contain materials or components that may interact with the magnetic field but are safe under specific conditions such as defined MRI field strengths or scan durations. Understanding these differences ensures proper device selection and patient safety during magnetic resonance imaging procedures.
Testing Standards for MR Safety Labels
MR Safe and MR Conditional labels for medical devices are determined based on rigorous testing standards outlined by ASTM International, specifically ASTM F2503. MR Safe devices are non-metallic and pose no risk in the MRI environment, requiring minimal testing, while MR Conditional devices undergo extensive testing to assess potential heating, displacement, and image artifact risks under specified MRI conditions. The testing standards evaluate factors such as static magnetic field strength, spatial gradient, and RF fields to ensure accurate and reliable safety labeling for clinical use.
Risks of Incorrect MR Device Classification
Incorrect classification of medical devices as MR Safe or MR Conditional can lead to severe safety risks, including device malfunction, patient injury, or interference with MRI imaging. MR Safe devices pose no known hazards in all MRI environments, while MR Conditional devices are safe only under specific conditions, such as certain magnetic field strengths or imaging protocols. Misclassification increases the likelihood of unexpected device heating, displacement, or electromagnetic interference, compromising patient safety and diagnostic accuracy.
Importance of MR Safety in Clinical Settings
MR Safe devices pose no risk in magnetic resonance environments, ensuring patient and staff safety during MRI scans. MR Conditional devices require specific conditions to prevent hazards, making adherence to guidelines critical to avoid device malfunction or injury. Prioritizing MR safety minimizes scanning complications, reduces liability, and improves diagnostic accuracy in clinical settings.
Regulatory Guidelines for MR Device Labeling
MR Safe devices are non-metallic, non-electrically conductive, and pose no known hazards in the MRI environment, meeting specific ASTM International standards for regulatory labeling. MR Conditional devices must operate safely under defined MRI conditions, including specific magnetic field strengths, spatial gradient limits, and radiofrequency exposure levels, as outlined in FDA and IEC guidelines. Proper labeling following these regulatory requirements ensures clear communication of safety parameters to healthcare providers, minimizing risk during MRI procedures.
Best Practices for MR Safety in Healthcare Facilities
MR Safe devices pose no known hazards in all MR environments, ensuring unrestricted use during MRI exams, while MR Conditional devices require specific conditions such as magnetic field strength and device orientation for safe operation. Healthcare facilities should implement rigorous screening protocols, maintain detailed device labeling, and train staff on the latest Manufacturer guidelines to minimize risks associated with MR Conditional equipment. Adhering to these best practices enhances patient safety, prevents device malfunction, and ensures compliance with regulatory standards in magnetic resonance environments.
Future Trends in MR Device Safety Standards
Future trends in MR device safety standards emphasize enhanced MR Safe classifications with broader compatibility across higher magnetic field strengths and more complex imaging sequences. Advances in material science and real-time monitoring technologies aim to reduce risks associated with MR Conditional devices, promoting seamless integration into dynamic MRI environments. Regulatory agencies are increasingly adopting stringent, evidence-based frameworks to ensure patient safety while facilitating innovation in MR-compatible medical devices.
MR Safe vs MR Conditional Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com