An ECG monitor provides real-time heart rhythm analysis during a short examination, typically in clinical settings, offering immediate diagnostic information. In contrast, a Holter monitor records continuous heart activity over 24 to 48 hours or longer, capturing intermittent arrhythmias that may not appear during brief ECG tests. Both devices are essential for cardiac assessment but differ in duration and application, with Holter monitors being ideal for extended monitoring outside the hospital.
Table of Comparison
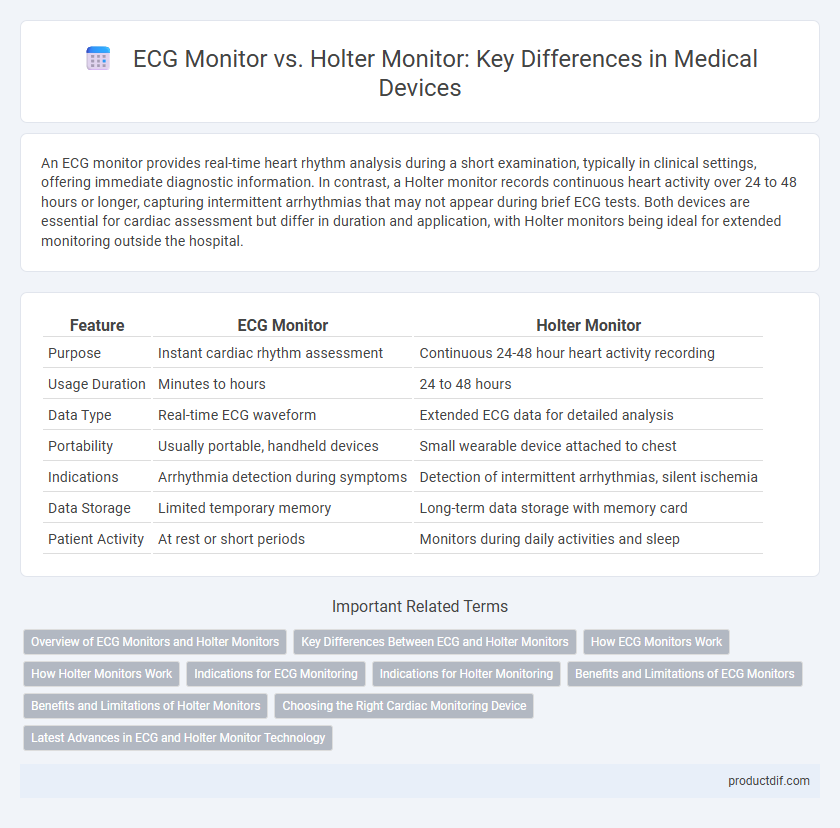
| Feature | ECG Monitor | Holter Monitor |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Instant cardiac rhythm assessment | Continuous 24-48 hour heart activity recording |
| Usage Duration | Minutes to hours | 24 to 48 hours |
| Data Type | Real-time ECG waveform | Extended ECG data for detailed analysis |
| Portability | Usually portable, handheld devices | Small wearable device attached to chest |
| Indications | Arrhythmia detection during symptoms | Detection of intermittent arrhythmias, silent ischemia |
| Data Storage | Limited temporary memory | Long-term data storage with memory card |
| Patient Activity | At rest or short periods | Monitors during daily activities and sleep |
Overview of ECG Monitors and Holter Monitors
ECG monitors provide real-time heart activity tracking through electrodes attached to the chest, offering immediate data on cardiac rhythm and electrical signals during short-term examinations. Holter monitors function as portable, continuous ECG recording devices worn for 24 to 48 hours, capturing extended heart activity data to detect intermittent arrhythmias or other cardiac abnormalities. Both devices utilize electrocardiography technology but serve different diagnostic purposes based on monitoring duration and data comprehensiveness.
Key Differences Between ECG and Holter Monitors
ECG monitors provide a snapshot of the heart's electrical activity during a short, controlled test typically lasting a few minutes, useful for diagnosing immediate cardiac issues. Holter monitors offer continuous cardiac monitoring over 24 to 48 hours, capturing irregular heart rhythms and transient arrhythmias that might be missed during a standard ECG. The primary difference lies in duration and diagnostic scope: ECG monitors are ideal for quick assessments, while Holter monitors deliver extended, real-time data critical for detecting intermittent cardiac abnormalities.
How ECG Monitors Work
ECG monitors work by detecting the electrical activity of the heart through electrodes placed on the skin, providing real-time data on heart rhythm and electrical impulses. These devices capture voltage fluctuations generated by cardiac muscle depolarization and repolarization, enabling immediate analysis of arrhythmias and other cardiac abnormalities. Continuous signal acquisition and digital processing ensure precise waveform recording for diagnostic interpretation.
How Holter Monitors Work
Holter monitors continuously record a patient's heart activity typically over 24 to 48 hours using portable devices with electrodes attached to the chest. They capture detailed ECG data during daily activities, enabling detection of arrhythmias or cardiac events that standard ECG monitors might miss in short-term readings. This extended monitoring provides comprehensive insights into heart rhythm variability and episodic abnormalities for accurate diagnosis.
Indications for ECG Monitoring
ECG monitors are primarily indicated for detecting arrhythmias, ischemic changes, and monitoring cardiac function during acute events such as myocardial infarction or chest pain evaluation. Holter monitors are prescribed for continuous ambulatory ECG recording over 24-48 hours to capture intermittent arrhythmias, syncope, or unexplained palpitations. Both devices complement diagnostic accuracy by providing different durations and environments of cardiac rhythm analysis.
Indications for Holter Monitoring
Holter monitoring is indicated for continuous recording of cardiac electrical activity over 24 to 48 hours, particularly useful in detecting intermittent arrhythmias, unexplained syncope, and palpitations not captured during a standard ECG. It provides detailed insight into heart rate variability, ventricular ectopy, and asymptomatic ischemic episodes during daily activities. Holter monitors are essential for assessing arrhythmia burden and guiding treatment in patients with suspected or known cardiac rhythm disorders.
Benefits and Limitations of ECG Monitors
ECG monitors provide real-time cardiac rhythm analysis, enabling immediate detection of arrhythmias and ischemic changes, which is crucial in emergency and clinical settings. Their non-invasive, easy-to-use design allows for rapid deployment and continuous monitoring in controlled environments but typically lacks the extended recording duration offered by Holter monitors. Limitations include susceptibility to motion artifacts and the inability to capture intermittent arrhythmias outside the monitoring period, reducing diagnostic sensitivity for transient cardiac events.
Benefits and Limitations of Holter Monitors
Holter monitors provide continuous ECG recording over 24 to 48 hours, enabling detection of intermittent arrhythmias that may be missed during a standard ECG. Their portability allows patients to maintain normal activities, offering a comprehensive heart rhythm analysis in real-life settings. Limitations include limited monitoring duration and potential user discomfort, which can affect data quality and patient compliance.
Choosing the Right Cardiac Monitoring Device
Selecting the right cardiac monitoring device depends on the patient's diagnostic needs and monitoring duration. An ECG monitor provides real-time, short-term cardiac activity analysis, ideal for detecting immediate arrhythmias during clinical visits. In contrast, a Holter monitor offers continuous 24- to 48-hour heart rhythm tracking, capturing intermittent abnormalities not always present during brief ECG recordings.
Latest Advances in ECG and Holter Monitor Technology
Recent advances in ECG and Holter monitor technology include the integration of AI algorithms for enhanced arrhythmia detection and real-time data analysis, improving diagnostic accuracy. Wearable devices now offer extended monitoring durations beyond traditional 24-48 hours, enabling continuous cardiac event tracking with increased patient comfort. Innovations in wireless connectivity and cloud-based platforms facilitate remote monitoring and seamless data sharing with healthcare providers.
ECG Monitor vs Holter Monitor Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com