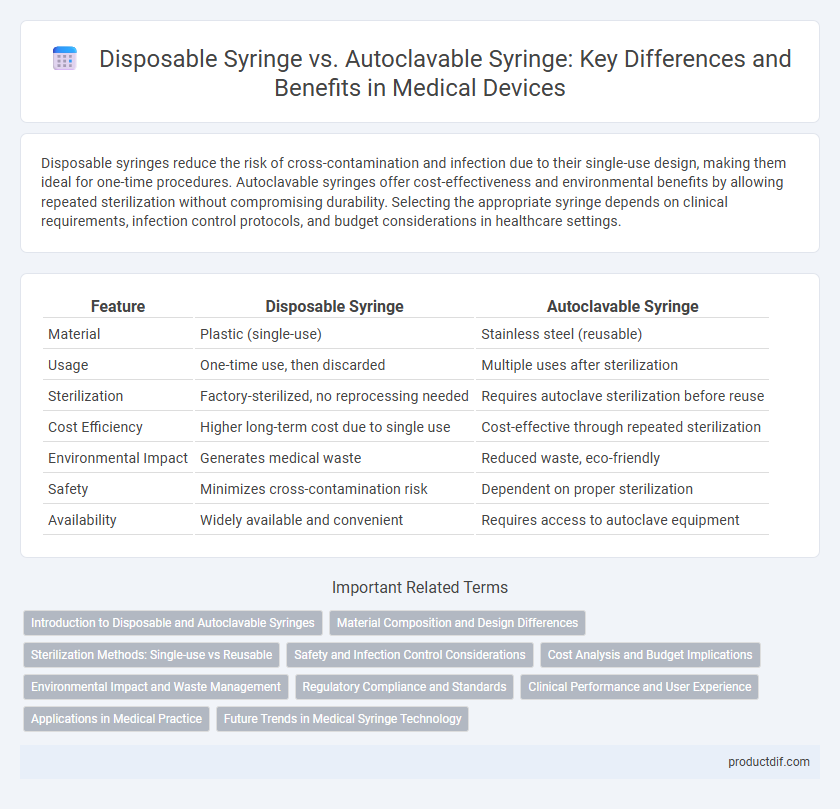
Disposable syringes reduce the risk of cross-contamination and infection due to their single-use design, making them ideal for one-time procedures. Autoclavable syringes offer cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits by allowing repeated sterilization without compromising durability. Selecting the appropriate syringe depends on clinical requirements, infection control protocols, and budget considerations in healthcare settings.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Disposable Syringe | Autoclavable Syringe |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Plastic (single-use) | Stainless steel (reusable) |
| Usage | One-time use, then discarded | Multiple uses after sterilization |
| Sterilization | Factory-sterilized, no reprocessing needed | Requires autoclave sterilization before reuse |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher long-term cost due to single use | Cost-effective through repeated sterilization |
| Environmental Impact | Generates medical waste | Reduced waste, eco-friendly |
| Safety | Minimizes cross-contamination risk | Dependent on proper sterilization |
| Availability | Widely available and convenient | Requires access to autoclave equipment |
Introduction to Disposable and Autoclavable Syringes
Disposable syringes are single-use medical devices designed to prevent cross-contamination and infection, made from lightweight plastic materials for easy and safe disposal. Autoclavable syringes consist of durable materials such as stainless steel or glass, allowing repeated sterilization through high-pressure steam autoclaving, which ensures their reusability in clinical settings. Both types serve critical roles in medical procedures, with disposable syringes emphasizing convenience and safety, while autoclavable syringes focus on cost-efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Material Composition and Design Differences
Disposable syringes are typically made from medical-grade plastic materials such as polypropylene and polyethylene, designed for single-use to ensure sterility and prevent cross-contamination. Autoclavable syringes are constructed from high-quality stainless steel or durable medical-grade plastics engineered to withstand high-temperature steam sterilization without deformation or loss of integrity. Design differences include the incorporation of sealed piston mechanisms and reinforced barrels in autoclavable syringes to maintain functionality after repeated sterilization cycles, whereas disposable syringes feature simpler, cost-effective designs optimized for single-use efficiency.
Sterilization Methods: Single-use vs Reusable
Disposable syringes utilize pre-sterilization through gamma irradiation or ethylene oxide and are discarded after a single use, eliminating cross-contamination risks. Autoclavable syringes are made of heat-resistant materials designed to withstand steam sterilization at 121degC or higher, allowing multiple uses after proper cleaning. The choice between single-use and reusable syringes impacts infection control protocols, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability in medical settings.
Safety and Infection Control Considerations
Disposable syringes offer superior safety by eliminating the risk of cross-contamination and needle-stick injuries, as they are single-use and discarded after each injection. Autoclavable syringes require thorough sterilization through autoclaving at 121degC for 15-20 minutes to ensure effective infection control, but improper sterilization can lead to pathogen transmission. Selecting disposable syringes significantly reduces nosocomial infection risks in clinical settings compared to reusable alternatives.
Cost Analysis and Budget Implications
Disposable syringes require a higher recurring expense due to single-use procurement, increasing overall supply costs in medical facilities. Autoclavable syringes, while involving greater initial investment in durable materials and sterilization equipment, reduce long-term expenditure by enabling multiple uses and minimizing waste management fees. Budget planning should weigh the upfront capital for autoclavable options against the continuous purchasing expenses and environmental costs associated with disposables.
Environmental Impact and Waste Management
Disposable syringes generate significant medical waste due to single-use plastic materials that require specialized disposal methods to prevent environmental contamination. Autoclavable syringes, made from durable materials like stainless steel, reduce waste by enabling sterilization and repeated use, thereby lowering the overall environmental footprint. Proper waste management of disposable syringes involves incineration or secure landfilling, while autoclavable syringes support sustainable practices through reuse and decreased resource consumption.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Disposable syringes comply with stringent regulatory standards such as ISO 7886-1, ensuring single-use safety and sterility to prevent cross-contamination. Autoclavable syringes must meet robust standards including ISO 7153-1 for materials and withstand multiple sterilization cycles without degradation. Compliance with FDA 21 CFR Part 820 quality system regulations is critical for both types to ensure consistent manufacturing, performance, and patient safety.
Clinical Performance and User Experience
Disposable syringes offer consistent clinical performance with reduced risk of cross-contamination, enhancing safety in single-use applications. Autoclavable syringes provide durable construction and cost-efficiency through multiple sterilization cycles but may require careful handling to maintain needle sharpness and functionality. User experience favors disposables for convenience and hygiene, while autoclavables demand adherence to sterilization protocols, potentially impacting workflow efficiency.
Applications in Medical Practice
Disposable syringes are widely used in medical practice for single-use injections, minimizing the risk of cross-contamination and infections in outpatient and emergency settings. Autoclavable syringes are preferred in surgical procedures and laboratory environments where repeated sterilization is feasible, supporting cost-efficiency and environmental sustainability. The choice between disposable and autoclavable syringes depends on factors such as infection control protocols, procedural requirements, and resource availability in healthcare facilities.
Future Trends in Medical Syringe Technology
Future trends in medical syringe technology emphasize the development of smart syringes equipped with sensors to enhance precision and patient safety. Innovations focus on bio-compatible materials that reduce environmental impact while maintaining sterility, shifting from traditional disposable designs to eco-friendly autoclavable syringes. Integration of wireless connectivity enables real-time data tracking for improved dosage accuracy and efficient inventory management in healthcare settings.
Disposable Syringe vs Autoclavable Syringe Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com