Modular design allows for flexible hardware configurations by enabling individual components to be easily added, replaced, or upgraded without affecting the entire system. Integrated design, on the other hand, combines multiple functions into a single unit, optimizing space and reducing latency but limiting customization and repair options. Choosing between modular and integrated designs depends on the need for scalability, maintenance, and specific performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
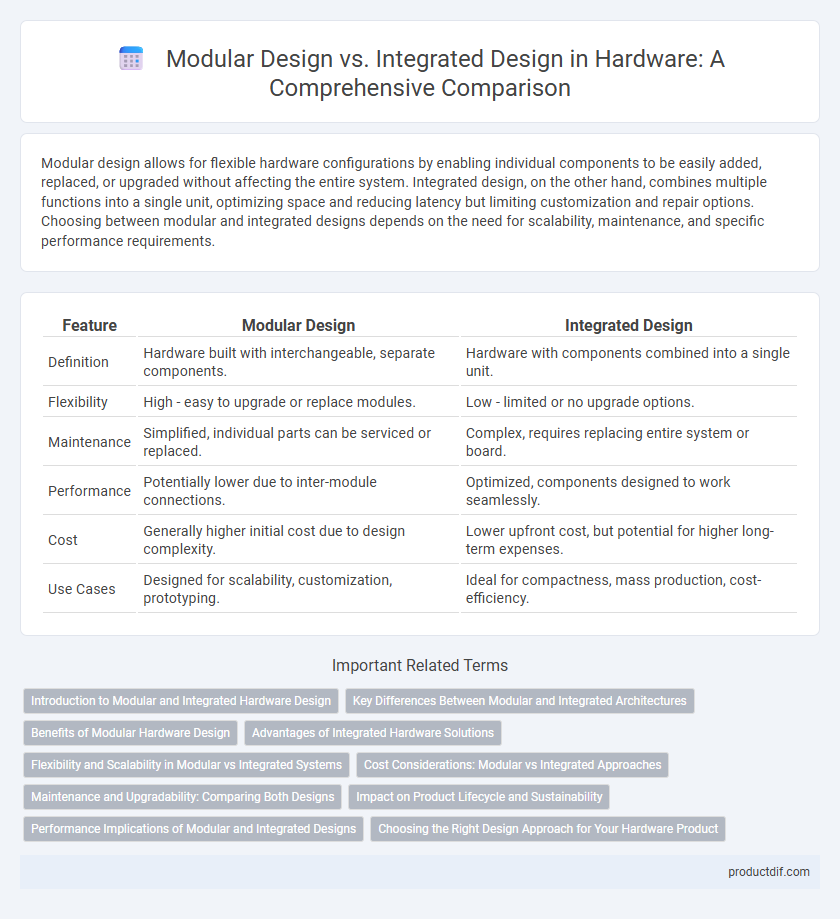
| Feature | Modular Design | Integrated Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hardware built with interchangeable, separate components. | Hardware with components combined into a single unit. |
| Flexibility | High - easy to upgrade or replace modules. | Low - limited or no upgrade options. |
| Maintenance | Simplified, individual parts can be serviced or replaced. | Complex, requires replacing entire system or board. |
| Performance | Potentially lower due to inter-module connections. | Optimized, components designed to work seamlessly. |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost due to design complexity. | Lower upfront cost, but potential for higher long-term expenses. |
| Use Cases | Designed for scalability, customization, prototyping. | Ideal for compactness, mass production, cost-efficiency. |
Introduction to Modular and Integrated Hardware Design
Modular hardware design divides a system into independent, interchangeable components that enable easy upgrades and maintenance, enhancing flexibility and scalability. Integrated hardware design combines components into a single unit, optimizing performance, reducing size, and minimizing power consumption. Both approaches impact manufacturing complexity, repairability, and system customization depending on application requirements.
Key Differences Between Modular and Integrated Architectures
Modular design in hardware enables independent development, testing, and replacement of components, enhancing flexibility and simplifying maintenance. Integrated design combines multiple functions into a single unit to optimize space, improve performance, and reduce manufacturing costs. Key differences include scalability, with modular systems offering easier upgrades, while integrated systems provide higher efficiency and reduced latency.
Benefits of Modular Hardware Design
Modular hardware design enhances system flexibility by allowing easy upgrades and replacements of individual components without affecting the entire system. It supports cost efficiency through simplified maintenance and reduced downtime, enabling quick troubleshooting and parts swapping. Scalability is improved as users can customize configurations to meet evolving performance needs or expand functionality seamlessly.
Advantages of Integrated Hardware Solutions
Integrated hardware solutions offer enhanced performance by minimizing latency and improving data throughput through tightly coupled components. They provide a more compact footprint, reducing space requirements and simplifying system assembly. Cost efficiency is achieved by lowering manufacturing complexity and enabling streamlined maintenance processes.
Flexibility and Scalability in Modular vs Integrated Systems
Modular hardware design offers superior flexibility by allowing individual components to be upgraded or replaced without affecting the entire system, making it ideal for evolving technological needs. Scalability is enhanced in modular systems through the seamless addition or removal of modules to adapt to changing workload demands. In contrast, integrated design typically delivers compactness and optimized performance but limits scalability and flexibility due to tightly coupled components.
Cost Considerations: Modular vs Integrated Approaches
Modular design often incurs higher initial costs due to the complexity of multiple interchangeable components, but it offers significant savings in maintenance and upgrade expenses by enabling targeted replacements and upgrades. Integrated design typically benefits from economies of scale and lower manufacturing costs, resulting in reduced upfront investment and improved production efficiency. Cost considerations must balance the advantages of modular flexibility against the streamlined manufacturing and assembly processes of integrated systems.
Maintenance and Upgradability: Comparing Both Designs
Modular design in hardware offers superior maintenance and upgradability by allowing individual components to be easily replaced or upgraded without affecting the entire system. Integrated design, while often more compact and efficient, restricts maintenance options and limits the potential for future upgrades due to tightly coupled components. Choosing modular hardware significantly reduces downtime and extends the system's lifecycle, especially in environments requiring frequent updates or repairs.
Impact on Product Lifecycle and Sustainability
Modular design enhances product lifecycle by enabling easier upgrades, repairs, and component replacements, significantly reducing electronic waste and supporting sustainability goals. Integrated design often leads to limited repair options and shorter product lifespans, increasing disposal rates and environmental impact. Emphasizing modularity aligns with circular economy principles, promoting resource efficiency and long-term sustainability in hardware development.
Performance Implications of Modular and Integrated Designs
Modular designs enable easier upgrades and customization but may introduce latency or signal degradation due to interconnections, potentially impacting performance compared to integrated designs. Integrated designs typically offer higher efficiency and faster data processing by minimizing communication delays between components on a single chip. However, integrated systems lack the flexibility of modular setups, which can affect scalability and long-term adaptability in hardware performance.
Choosing the Right Design Approach for Your Hardware Product
Modular design offers flexibility and ease of customization by allowing individual components to be replaced or upgraded independently, making it ideal for products requiring frequent updates or tailored configurations. Integrated design provides compactness and enhanced performance through tightly coupled components, reducing latency and improving efficiency for hardware products prioritizing speed and reliability. Selecting the right design approach depends on factors such as product lifecycle, scalability requirements, maintenance complexity, and target user needs.
Modular design vs Integrated design Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com