Wired controls offer reliable and consistent performance with minimal latency, making them ideal for precise and uninterrupted equipment operation. Wireless controls provide greater flexibility and freedom of movement, reducing clutter and enhancing convenience in various environments. Choosing between wired and wireless controls depends on the need for stability versus mobility in pet equipment usage.
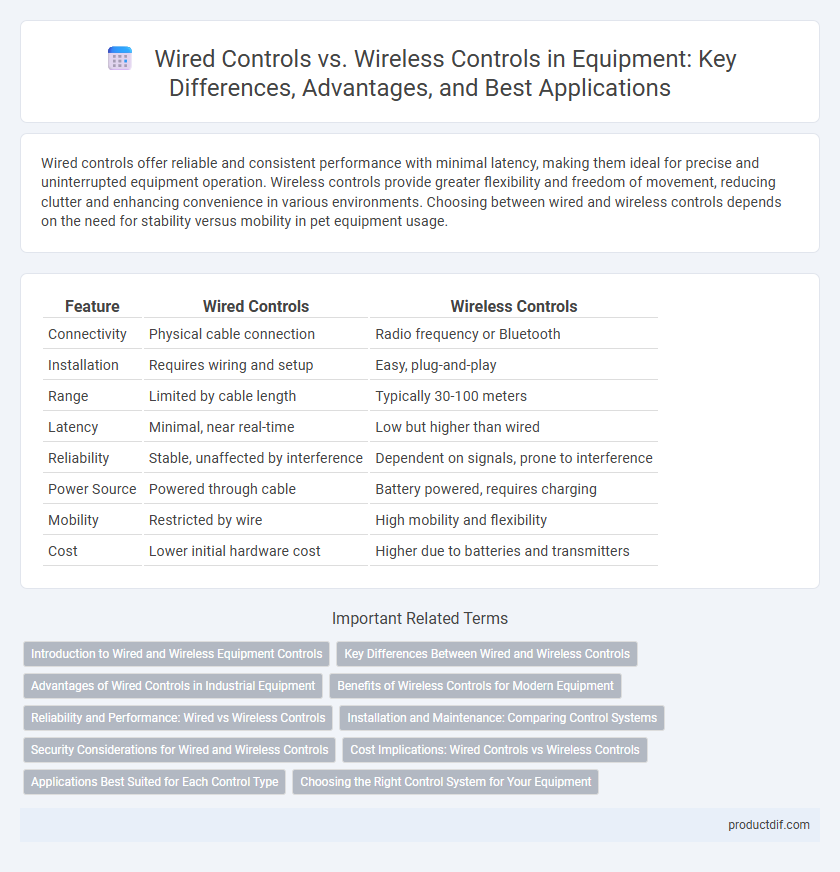
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wired Controls | Wireless Controls |
|---|---|---|
| Connectivity | Physical cable connection | Radio frequency or Bluetooth |
| Installation | Requires wiring and setup | Easy, plug-and-play |
| Range | Limited by cable length | Typically 30-100 meters |
| Latency | Minimal, near real-time | Low but higher than wired |
| Reliability | Stable, unaffected by interference | Dependent on signals, prone to interference |
| Power Source | Powered through cable | Battery powered, requires charging |
| Mobility | Restricted by wire | High mobility and flexibility |
| Cost | Lower initial hardware cost | Higher due to batteries and transmitters |
Introduction to Wired and Wireless Equipment Controls
Wired controls offer reliable, low-latency connections ideal for industrial and high-precision equipment, ensuring consistent performance through physical cables like Ethernet or USB. Wireless controls provide enhanced flexibility and ease of installation by utilizing technologies such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or radio frequency, enabling remote operation and reducing cable clutter. Choosing between wired and wireless controls depends on factors like signal reliability, installation environment, and equipment mobility requirements.
Key Differences Between Wired and Wireless Controls
Wired controls offer reliable, low-latency connections with consistent power supply, ideal for environments requiring high stability and minimal interference. Wireless controls provide greater flexibility and ease of installation, benefiting setups where mobility and remote operation are prioritized despite potential signal limitations. Key differences include installation complexity, maintenance requirements, latency, and susceptibility to signal interference or power disruptions.
Advantages of Wired Controls in Industrial Equipment
Wired controls in industrial equipment provide superior reliability and consistent signal transmission, minimizing interference and downtime in critical operations. They offer enhanced security by reducing risks of unauthorized access common in wireless systems. The stable power source and robust connection afforded by wired controls ensure precise and uninterrupted equipment management in harsh industrial environments.
Benefits of Wireless Controls for Modern Equipment
Wireless controls for modern equipment enhance operational flexibility by eliminating the need for physical connections, allowing remote management and real-time adjustments from any location. These controls reduce installation and maintenance costs by minimizing wiring infrastructure and decreasing wear and tear associated with cables. Enhanced scalability and integration with IoT systems enable advanced monitoring, predictive maintenance, and improved overall equipment efficiency.
Reliability and Performance: Wired vs Wireless Controls
Wired controls offer superior reliability due to their stable, interference-free connections, ensuring consistent performance in critical equipment applications. Wireless controls provide flexibility and ease of installation but may experience latency and signal disruptions caused by environmental factors or electromagnetic interference. Choosing between wired and wireless controls depends on weighing the priority of uninterrupted operation versus installation convenience and scalability.
Installation and Maintenance: Comparing Control Systems
Wired controls require structured installation involving physical cabling, which can increase initial labor costs and complexity but often ensures stable signal transmission and less susceptibility to interference. Wireless controls simplify installation with minimal wiring, reducing setup time and flexibility for repositioning, yet they may demand regular maintenance for battery replacement and signal troubleshooting. Maintenance for wired systems typically involves monitoring cable integrity, while wireless systems require consistent management of connectivity and potential security updates.
Security Considerations for Wired and Wireless Controls
Wired controls offer enhanced security through physical connections that reduce vulnerability to cyberattacks, making them ideal for sensitive equipment requiring reliable data integrity. Wireless controls, while providing flexibility and ease of installation, must implement robust encryption protocols and continuous network monitoring to prevent unauthorized access and signal interference. Choosing between wired and wireless controls hinges on balancing security needs with operational convenience in equipment management.
Cost Implications: Wired Controls vs Wireless Controls
Wired controls typically involve higher initial installation costs due to the need for extensive cabling and labor but offer lower long-term maintenance expenses and reduced risk of signal interference. Wireless controls generally have lower upfront costs and greater flexibility in installation, yet they may incur ongoing expenses related to battery replacement and potential signal disruptions, impacting operational reliability. Selecting between wired and wireless controls requires a detailed cost-benefit analysis considering installation scale, maintenance budgets, and application-specific reliability requirements.
Applications Best Suited for Each Control Type
Wired controls excel in applications requiring stable, interference-free connections such as industrial automation and manufacturing where reliability and real-time response are critical. Wireless controls are best suited for environments needing mobility and flexible installation, including smart home systems and remote monitoring where ease of deployment and scalability are priorities. Choosing between wired and wireless controls depends on factors like operational range, environmental conditions, and maintenance accessibility.
Choosing the Right Control System for Your Equipment
Wired controls offer reliable, low-latency connections ideal for industrial equipment where consistent performance is critical, while wireless controls provide flexibility and ease of installation, reducing cable clutter and enabling remote operation. Factors such as environmental conditions, distance, interference potential, and security requirements must guide the choice between wired and wireless systems. Prioritizing compatibility with existing equipment, maintenance needs, and cost implications ensures the optimal control system enhances operational efficiency and equipment longevity.
Wired controls vs Wireless controls Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com