Hydraulic lifts provide powerful lifting capabilities through fluid pressure, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications and rough terrain. Electric lifts operate quietly and offer precise control with lower maintenance requirements, suitable for indoor environments and lighter loads. Choosing between hydraulic and electric lifts depends on the specific operational needs, load capacity, and work environment.
Table of Comparison
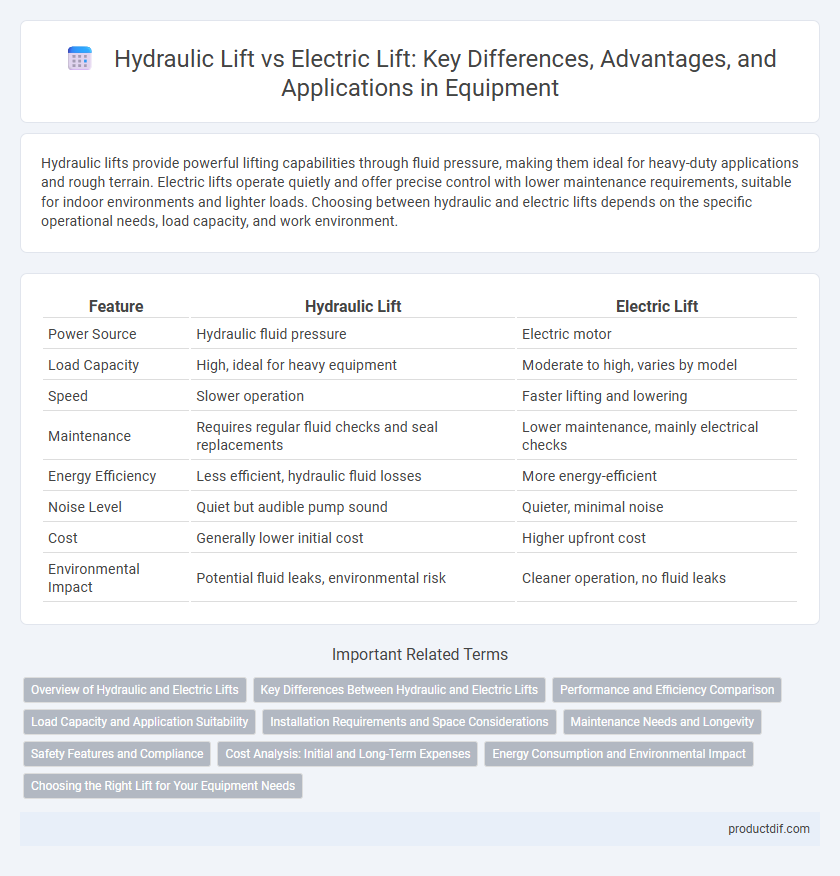
| Feature | Hydraulic Lift | Electric Lift |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Hydraulic fluid pressure | Electric motor |
| Load Capacity | High, ideal for heavy equipment | Moderate to high, varies by model |
| Speed | Slower operation | Faster lifting and lowering |
| Maintenance | Requires regular fluid checks and seal replacements | Lower maintenance, mainly electrical checks |
| Energy Efficiency | Less efficient, hydraulic fluid losses | More energy-efficient |
| Noise Level | Quiet but audible pump sound | Quieter, minimal noise |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher upfront cost |
| Environmental Impact | Potential fluid leaks, environmental risk | Cleaner operation, no fluid leaks |
Overview of Hydraulic and Electric Lifts
Hydraulic lifts use fluid pressure to raise and lower platforms, providing smooth and powerful lifting ideal for heavy loads and lower-height applications. Electric lifts operate with electric motors and cables or screw drives, offering energy efficiency and precise control, suitable for high-rise buildings and frequent use. Both systems vary in maintenance needs, cost, and installation complexity, influencing their selection for commercial or industrial equipment lifting.
Key Differences Between Hydraulic and Electric Lifts
Hydraulic lifts utilize fluid pressure to generate lifting force, making them ideal for heavy loads and offering smooth, stable movement with excellent load distribution. Electric lifts rely on motor-driven mechanisms, providing faster operation, energy efficiency, and cleaner installation without the need for underground pits. Understanding these distinctions--load capacity, speed, maintenance, and installation requirements--helps select the appropriate lift for specific commercial or industrial applications.
Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Hydraulic lifts excel in heavy-load capacity and smooth, precise movements, making them ideal for industrial settings with demanding lifting requirements. Electric lifts offer superior energy efficiency and faster operation speeds, reducing operational costs and downtime in environments prioritizing productivity. Choosing between hydraulic and electric lifts depends on balancing load requirements, energy consumption, and maintenance considerations for optimal performance.
Load Capacity and Application Suitability
Hydraulic lifts typically offer higher load capacity, handling weights from 2,000 to 20,000 pounds, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications such as automotive repair and construction. Electric lifts, with load capacities generally ranging from 500 to 5,000 pounds, excel in precision tasks and environments requiring quieter operation, like warehouses and retail settings. Selecting between hydraulic and electric lifts depends on the specific load requirements and the operational context, where hydraulic systems suit heavy lifting and electric models are preferred for lighter, more controlled movements.
Installation Requirements and Space Considerations
Hydraulic lifts require a machine room or pit for the hydraulic pump and cylinder installation, demanding more space and structural support compared to electric lifts. Electric lifts often utilize a machine-room-less (MRL) design, reducing the need for additional floor space and allowing for easier integration into existing buildings. Choosing between hydraulic and electric lifts depends on available space, building structure, and installation complexity.
Maintenance Needs and Longevity
Hydraulic lifts require regular inspection of fluid levels and seals to prevent leaks and ensure smooth operation, while electric lifts focus on battery health and motor function. Hydraulic systems often experience longer service life due to robust build but may demand more frequent maintenance to address wear on pumps and cylinders. Electric lifts benefit from fewer moving parts, reducing maintenance frequency and potential downtime, ultimately extending operational longevity in environments with moderate usage.
Safety Features and Compliance
Hydraulic lifts incorporate robust pressure relief valves and emergency lowering systems to ensure safety during power failures, meeting stringent OSHA and ANSI standards. Electric lifts offer advanced overload protection, anti-drop mechanisms, and automatic braking systems compliant with EN 81 and ASME A17.1 regulations. Both systems are designed to minimize operational hazards, prioritizing worker protection and regulatory compliance.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term Expenses
Hydraulic lifts generally have lower initial purchase costs compared to electric lifts, making them more budget-friendly for short-term use. However, hydraulic lifts often incur higher long-term expenses due to regular hydraulic fluid replacement, maintenance of seals, and potential leaks. Electric lifts, despite higher upfront investment, typically offer better energy efficiency and reduced maintenance costs, resulting in lower total ownership costs over time.
Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact
Hydraulic lifts typically consume more energy due to their reliance on fluid power systems, leading to higher operational costs and increased carbon emissions. Electric lifts use energy more efficiently through electric motors, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced environmental impact. Advances in electric lift technology further enhance energy savings and support sustainable building management.
Choosing the Right Lift for Your Equipment Needs
Hydraulic lifts provide powerful lifting capacity and smooth operation, making them ideal for heavy-duty equipment requiring precise control and stability. Electric lifts offer energy efficiency and lower maintenance costs, suited for indoor environments and lighter loads with frequent usage. Selecting the right lift depends on load weight, operational frequency, and workspace conditions to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Hydraulic lift vs Electric lift Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com