USB-C Power Delivery offers a universal fast-charging protocol capable of delivering up to 100W, supporting a wide range of devices from smartphones to laptops with intelligent power negotiation. Quick Charge, developed by Qualcomm, provides rapid charging primarily for compatible smartphones, optimizing voltage and current to accelerate battery replenishment. While USB-C Power Delivery emphasizes broad device compatibility and higher power output, Quick Charge focuses on maximizing charging speed for specific mobile technologies.
Table of Comparison
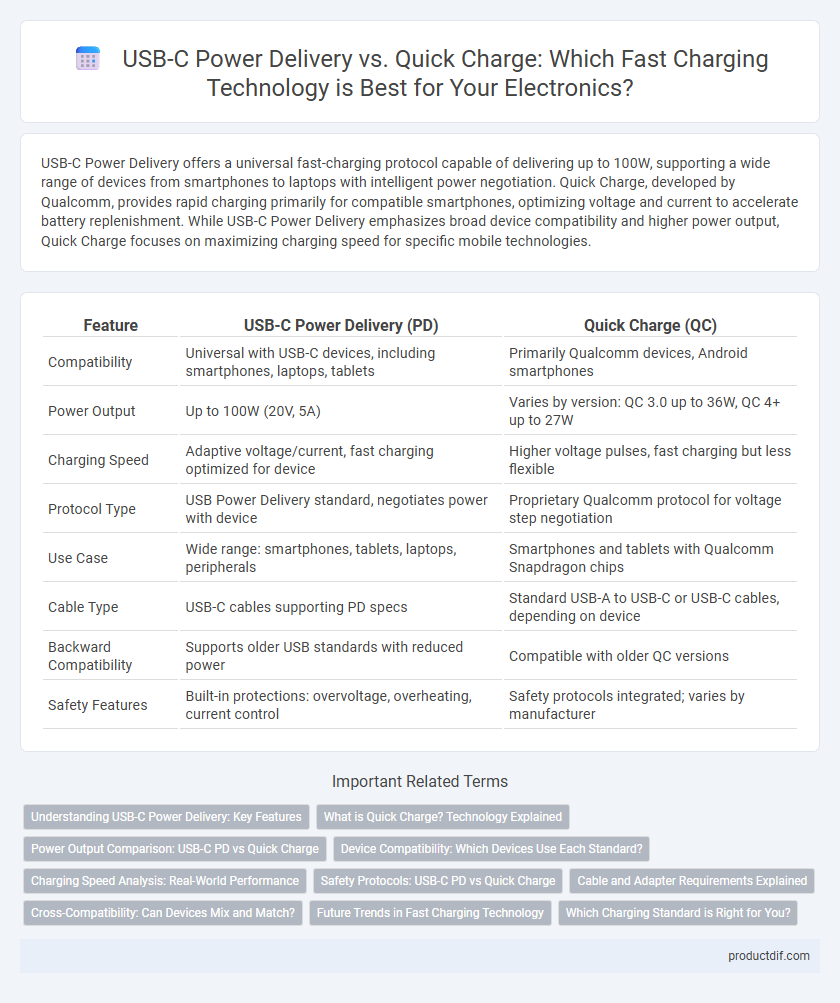
| Feature | USB-C Power Delivery (PD) | Quick Charge (QC) |
|---|---|---|
| Compatibility | Universal with USB-C devices, including smartphones, laptops, tablets | Primarily Qualcomm devices, Android smartphones |
| Power Output | Up to 100W (20V, 5A) | Varies by version: QC 3.0 up to 36W, QC 4+ up to 27W |
| Charging Speed | Adaptive voltage/current, fast charging optimized for device | Higher voltage pulses, fast charging but less flexible |
| Protocol Type | USB Power Delivery standard, negotiates power with device | Proprietary Qualcomm protocol for voltage step negotiation |
| Use Case | Wide range: smartphones, tablets, laptops, peripherals | Smartphones and tablets with Qualcomm Snapdragon chips |
| Cable Type | USB-C cables supporting PD specs | Standard USB-A to USB-C or USB-C cables, depending on device |
| Backward Compatibility | Supports older USB standards with reduced power | Compatible with older QC versions |
| Safety Features | Built-in protections: overvoltage, overheating, current control | Safety protocols integrated; varies by manufacturer |
Understanding USB-C Power Delivery: Key Features
USB-C Power Delivery (USB PD) supports power levels up to 100W with flexible voltage and current adjustments, enabling faster and safer charging for a wide range of devices. It uses a sophisticated communication protocol between the charger and device to intelligently manage power delivery, optimizing efficiency and thermal conditions. USB PD also facilitates bidirectional power flow, allowing devices like laptops to act as both power sources and sinks.
What is Quick Charge? Technology Explained
Quick Charge is a proprietary fast-charging technology developed by Qualcomm that increases charging speed by delivering higher voltage and current through USB connections. It uses intelligent communication between the charger and device to optimize power transfer while managing heat and safety. Compatible with a wide range of devices, Quick Charge significantly reduces charging time compared to conventional USB charging standards.
Power Output Comparison: USB-C PD vs Quick Charge
USB-C Power Delivery (PD) supports power output up to 100W, enabling fast charging for laptops, tablets, and smartphones, while Quick Charge primarily delivers up to 36W optimized for rapid charging of smartphones. USB-C PD offers dynamic voltage scaling from 5V to 20V and currents up to 5A, facilitating versatile power delivery across a broader range of devices compared to Quick Charge's fixed voltage options like 9V or 12V. The higher power output capability and universal compatibility of USB-C PD make it more suitable for power-intensive electronics than Quick Charge's device-specific charging profiles.
Device Compatibility: Which Devices Use Each Standard?
USB-C Power Delivery (PD) is widely compatible with modern devices including smartphones, laptops, tablets, and gaming consoles, supporting various power levels up to 100W for efficient charging. Quick Charge technology, primarily developed by Qualcomm, targets a broad range of Android smartphones and accessories, optimizing fast charging speeds but with limited support in non-Qualcomm devices. Device compatibility depends largely on the chipset and manufacturer implementation, making USB-C PD the more universal standard across diverse electronics.
Charging Speed Analysis: Real-World Performance
USB-C Power Delivery supports higher power levels up to 100W, enabling faster charging for laptops and smartphones with compatible devices. Quick Charge, primarily designed for Qualcomm processors, delivers rapid current bursts to reduce charging time, usually peaking at 27W or 30W in common versions. Real-world performance varies based on device compatibility, cable quality, and charger output, with USB-C PD often providing more consistent and efficient charging speeds across a broader range of electronics.
Safety Protocols: USB-C PD vs Quick Charge
USB-C Power Delivery (USB PD) incorporates dynamic voltage and current adjustments alongside built-in overvoltage, overcurrent, and thermal protection to prevent device damage and ensure user safety. Quick Charge technology from Qualcomm employs intelligent negotiation for voltage levels but offers less granular control and fewer comprehensive safety features compared to USB PD. The standardized safety protocols in USB-C PD make it a more reliable choice for protecting a wide range of devices during fast charging.
Cable and Adapter Requirements Explained
USB-C Power Delivery (PD) requires a USB-C cable and compatible PD adapter to deliver variable power levels up to 100W, ensuring efficient charging across devices like laptops and smartphones. Quick Charge technology, primarily used with USB-A or USB-C cables, depends on Qualcomm-compatible adapters and supports faster voltage and current shifts but generally offers lower power output than USB-C PD. For optimal charging, using certified cables and adapters that match the specific protocol standards is crucial to avoid power negotiation failures or device damage.
Cross-Compatibility: Can Devices Mix and Match?
USB-C Power Delivery (PD) and Quick Charge (QC) are different fast charging protocols with varying voltage and current specifications, influencing cross-compatibility. Many modern devices support USB-C PD due to its standardized nature, promoting broader interoperability across brands, while Quick Charge is typically limited to Qualcomm-enabled devices. Using a USB-C PD charger with a Quick Charge device or vice versa may result in slower charging speeds or fallback to standard charging, but both protocols generally prioritize device safety through communication handshakes to prevent damage.
Future Trends in Fast Charging Technology
USB-C Power Delivery (PD) is evolving to support higher wattages and smarter power negotiation, with future trends aiming at 240W delivery for laptops and gaming devices, enhancing universal compatibility and charging speed. Quick Charge continues innovating with adaptive algorithms to optimize battery health and charge efficiency, targeting faster times for smartphones and wearables while maintaining safety standards. The convergence of USB-C PD and Quick Charge technologies is expected to drive a unified fast-charging ecosystem, promoting interoperability and seamless user experiences across electronic devices.
Which Charging Standard is Right for You?
USB-C Power Delivery offers universal compatibility across a wide range of devices with adjustable wattage up to 100W, making it ideal for smartphones, tablets, and laptops requiring fast, efficient charging. Quick Charge is optimized primarily for Qualcomm-powered devices, providing rapid charging speeds but with more limited device support. Choosing the right standard depends on your device ecosystem and power needs: USB-C PD suits multi-device users needing high wattage flexibility, while Quick Charge benefits those with specific Qualcomm hardware seeking maximum speed.
USB-C Power Delivery vs Quick Charge Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com