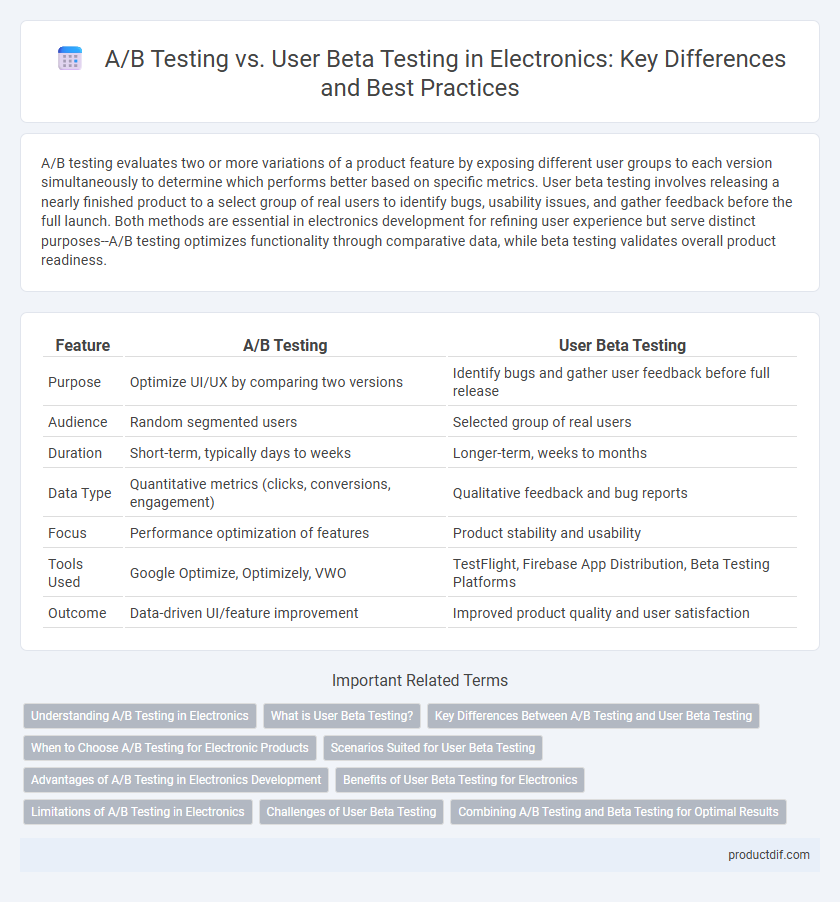
A/B testing evaluates two or more variations of a product feature by exposing different user groups to each version simultaneously to determine which performs better based on specific metrics. User beta testing involves releasing a nearly finished product to a select group of real users to identify bugs, usability issues, and gather feedback before the full launch. Both methods are essential in electronics development for refining user experience but serve distinct purposes--A/B testing optimizes functionality through comparative data, while beta testing validates overall product readiness.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | A/B Testing | User Beta Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Optimize UI/UX by comparing two versions | Identify bugs and gather user feedback before full release |
| Audience | Random segmented users | Selected group of real users |
| Duration | Short-term, typically days to weeks | Longer-term, weeks to months |
| Data Type | Quantitative metrics (clicks, conversions, engagement) | Qualitative feedback and bug reports |
| Focus | Performance optimization of features | Product stability and usability |
| Tools Used | Google Optimize, Optimizely, VWO | TestFlight, Firebase App Distribution, Beta Testing Platforms |
| Outcome | Data-driven UI/feature improvement | Improved product quality and user satisfaction |
Understanding A/B Testing in Electronics
A/B testing in electronics involves comparing two versions of a device or software feature to determine which performs better based on user interaction data and performance metrics. This method enables engineers and product designers to make data-driven decisions by analyzing variations in prototypes, interface designs, or firmware updates under controlled conditions. By isolating specific variables, A/B testing provides clear insights into user preferences and functionality improvements, accelerating product optimization and innovation cycles.
What is User Beta Testing?
User Beta Testing is a phase in electronics product development where a pre-release version of a device or software is distributed to a select group of end users outside the company for real-world evaluation. This testing collects valuable feedback on functionality, usability, and performance under actual usage conditions, helping identify bugs and user experience issues before full market launch. User Beta Testing complements A/B Testing by providing qualitative insights and uncovering problems that controlled experiments might not reveal.
Key Differences Between A/B Testing and User Beta Testing
A/B testing compares two or more variations of an electronic product's feature to identify which performs better based on user interaction data, focusing on specific metrics like click-through rates or conversion. User beta testing involves releasing a near-final version of the electronic device or software to a limited audience to gather qualitative feedback on usability, functionality, and potential bugs. The key difference lies in A/B testing's quantitative approach to optimize individual elements, while user beta testing provides holistic insights into overall user experience before full market release.
When to Choose A/B Testing for Electronic Products
A/B testing is ideal for electronic products when the goal is to compare specific design elements or feature variations to determine which version enhances user engagement or usability metrics. This method is best suited for controlled environments where quantifiable data on user preferences, performance, and behavior can be directly measured across distinct user groups. Choose A/B testing when precise, data-driven decisions are needed to optimize interface components, product features, or user flows before a full-scale product launch.
Scenarios Suited for User Beta Testing
User beta testing is ideal for scenarios where real-world performance and user interaction with electronic devices need validation before mass production. Complex hardware with multiple functionalities benefits from beta testing to uncover usability issues and hardware compatibility in diverse user environments. Products requiring feedback on ergonomics, battery life, and real-time system stability also rely on user beta testing for comprehensive evaluation.
Advantages of A/B Testing in Electronics Development
A/B testing in electronics development enables precise comparison of two design variants by directly measuring user responses, leading to data-driven optimization of product features and user interfaces. This method reduces development costs and time by identifying the most effective solutions early, minimizing reliance on subjective feedback. Automated data collection during A/B testing enhances accuracy and scalability, facilitating iterative improvements in electronic device performance and user satisfaction.
Benefits of User Beta Testing for Electronics
User beta testing in electronics provides direct feedback from real users interacting with devices in diverse environments, uncovering practical issues not identified in controlled A/B testing. It enhances product reliability by identifying hardware and software integration problems early, reducing post-launch failures and costly recalls. Engaging beta testers fosters community trust and gathers usability insights that guide user-centric improvements and feature refinement.
Limitations of A/B Testing in Electronics
A/B testing in electronics often struggles with limited variables due to the complexity of hardware components and software integration, restricting the scope of testable changes. It may not capture long-term user interactions or real-world usage scenarios, leading to incomplete data on product performance and user experience. This limitation necessitates complementary methods like user beta testing to identify nuanced issues and validate functionality in diverse operational environments.
Challenges of User Beta Testing
User Beta Testing in electronics faces significant challenges such as limited sample size, leading to less diverse feedback that may not represent the broader user base. Device variability across different hardware and software environments complicates consistent issue reproduction and troubleshooting. Coordinating feedback and managing communication between testers and developers often delays problem resolution and extends the development timeline.
Combining A/B Testing and Beta Testing for Optimal Results
Combining A/B testing with user beta testing in electronics product development leverages quantitative data from A/B tests alongside qualitative feedback from beta users, enhancing feature validation and user experience optimization. A/B testing provides statistically significant performance metrics on design variations, while beta testing uncovers real-world usability issues and user preferences in diverse environments. Integrating these methods accelerates iterative improvements, reduces launch risks, and ensures the final electronic device aligns with target audience expectations and performance benchmarks.
A/B Testing vs User Beta Testing Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com